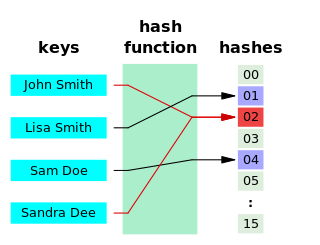
A hash function is any function that can be used to map data of arbitrary size to fixed-size values, though there are some hash functions that support variable length output. The values returned by a hash function are called hash values, hash codes, hash digests, digests, or simply hashes. The values are usually used to index a fixed-size table called a hash table. Use of a hash function to index a hash table is called hashing or scatter storage addressing.
A commitment scheme is a cryptographic primitive that allows one to commit to a chosen value while keeping it hidden to others, with the ability to reveal the committed value later. Commitment schemes are designed so that a party cannot change the value or statement after they have committed to it: that is, commitment schemes are binding. Commitment schemes have important applications in a number of cryptographic protocols including secure coin flipping, zero-knowledge proofs, and secure computation.

A cryptographic hash function (CHF) is a hash algorithm that has special properties desirable for a cryptographic application:

In computer science, a hash list is typically a list of hashes of the data blocks in a file or set of files. Lists of hashes are used for many different purposes, such as fast table lookup and distributed databases.

In cryptography and computer science, a hash tree or Merkle tree is a tree in which every "leaf" node is labelled with the cryptographic hash of a data block, and every node that is not a leaf is labelled with the cryptographic hash of the labels of its child nodes. A hash tree allows efficient and secure verification of the contents of a large data structure. A hash tree is a generalization of a hash list and a hash chain.
In cryptography, a Lamport signature or Lamport one-time signature scheme is a method for constructing a digital signature. Lamport signatures can be built from any cryptographically secure one-way function; usually a cryptographic hash function is used.

In cryptography, the Merkle–Damgård construction or Merkle–Damgård hash function is a method of building collision-resistant cryptographic hash functions from collision-resistant one-way compression functions. This construction was used in the design of many popular hash algorithms such as MD5, SHA-1 and SHA-2.

In cryptography, a nonce is an arbitrary number that can be used just once in a cryptographic communication. It is often a random or pseudo-random number issued in an authentication protocol to ensure that old communications cannot be reused in replay attacks. They can also be useful as initialization vectors and in cryptographic hash functions.
A hash chain is the successive application of a cryptographic hash function to a piece of data. In computer security, a hash chain is a method used to produce many one-time keys from a single key or password. For non-repudiation, a hash function can be applied successively to additional pieces of data in order to record the chronology of data's existence.
Transient-key cryptography is a form of public-key cryptography wherein keypairs are generated and assigned to brief intervals of time instead of to individuals or organizations, and the blocks of cryptographic data are chained through time. In a transient-key system, private keys are used briefly and then destroyed, which is why it is sometimes nicknamed “disposable crypto.” Data encrypted with a private key associated with a specific time interval can be irrefutably linked to that interval, making transient-key cryptography particularly useful for digital trusted timestamping. Transient-key cryptography was invented in 1997 by Dr. Michael Doyle of Eolas, and has been adopted in the ANSI ASC X9.95 Standard for trusted timestamps.
Trusted timestamping is the process of securely keeping track of the creation and modification time of a document. Security here means that no one—not even the owner of the document—should be able to change it once it has been recorded provided that the timestamper's integrity is never compromised.
In hash-based cryptography, the Merkle signature scheme is a digital signature scheme based on Merkle trees and one-time signatures such as the Lamport signature scheme. It was developed by Ralph Merkle in the late 1970s and is an alternative to traditional digital signatures such as the Digital Signature Algorithm or RSA. NIST has approved specific variants of the Merkle signature scheme in 2020.
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of cryptographic hash functions. See the individual functions' articles for further information. This article is not all-inclusive or necessarily up-to-date. An overview of hash function security/cryptanalysis can be found at hash function security summary.
In the BitTorrent file distribution system, a torrent file or meta-info file is a computer file that contains metadata about files and folders to be distributed, and usually also a list of the network locations of trackers, which are computers that help participants in the system find each other and form efficient distribution groups called swarms. Torrent files are normally named with the extension .torrent.
Linked timestamping is a type of trusted timestamping where issued time-stamps are related to each other.
Double-spending is a monetary design problem, a good money is verifiably scarce and where a unit of value can be spent more than once, the monetary property of scarcity is challenged. As with counterfeit money, such double-spending leads to inflation by creating a new amount of copied currency that did not previously exist. Like all increasingly abundant resources, this devalues the currency relative to other monetary units or goods and diminishes user trust as well as the circulation and retention of the currency.
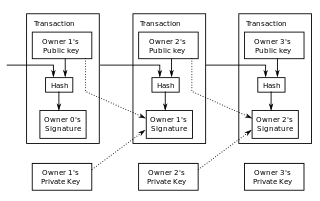
The Bitcoin protocol is the set of rules that govern the functioning of Bitcoin. Its key components and principles are: a peer-to-peer decentralized network with no central oversight; the blockchain technology, a public ledger that records all Bitcoin transactions; mining and proof of work, the process to create new bitcoins and verify transactions; and cryptographic security.

Rendezvous or highest random weight (HRW) hashing is an algorithm that allows clients to achieve distributed agreement on a set of options out of a possible set of options. A typical application is when clients need to agree on which sites objects are assigned to.
Hash-based cryptography is the generic term for constructions of cryptographic primitives based on the security of hash functions. It is of interest as a type of post-quantum cryptography.

OpenTimestamps (OTS) is an open-source project that aims to provide a standard format for blockchain timestamping. With the advent of systems like Bitcoin, it is possible to create and verify proofs of existence of documents (timestamps) without relying on a trusted third party; this represents an enhancement in term of security, since it excludes the possibility of a malicious trusted third party to compromise the timestamp.












