
Mimosa is a genus of about 590 species of herbs and shrubs, in the mimosoid clade of the legume family Fabaceae. The generic name is derived from the Greek word μῖμος (mimos), an "actor" or "mime", and the feminine suffix -osa, "resembling", suggesting its 'sensitive leaves' which seem to 'mimic conscious life'.

Cota tinctoria, the golden marguerite, yellow chamomile, or oxeye chamomile, is a species of perennial flowering plant in the sunflower family. Other common names include dyer's chamomile, Boston daisy, and Paris daisy. In horticulture this plant is still widely referred to by its synonym Anthemis tinctoria.

Sesbania is a genus of flowering plants in the pea family, Fabaceae, and the only genus found in tribe Sesbanieae. Riverhemp is a common name for plants in this genus. Notable species include the rattlebox, spiny sesbania, and Sesbania sesban, which is used in cooking. Plants of this genus, some of which are aquatic, can be used in alley cropping to increase the soil's nitrogen content. The species of rhizobia responsible for nitrogen fixation in Sesbania rostrata is Azorhizobium caulinodans.

Leucanthemum is a genus of flowering plants in the aster family, Asteraceae. It is mainly distributed in southern and central Europe. Some species are known on other continents as introduced species, and some are cultivated as ornamental plants. The name Leucanthemum derives from the Greek words λευκός – leukos ("white") and ἄνθεμον – anthemon ("flower"). Common names for Leucanthemum species usually include the name daisy, but "daisy" can also refer to numerous other genera in the Asteraceae family.

Anthemis is a genus of aromatic flowering plants in the family Asteraceae, closely related to Chamaemelum, and like that genus, known by the common name chamomile; some species are also called dog-fennel or mayweed. Anthemis are native to the Mediterranean region and southwest Asia east to Iran. A number of species have also become naturalized in the United Kingdom and other parts of the world.

Cladanthus is a genus of plants in the sunflower family, native to the Mediterranean region.

Forestiera is a genus of flowering plants in the olive family, Oleaceae. Members of the genus are often called swampprivets. Most are shrubs.

Aeschynomene is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae, and was recently assigned to the informal monophyletic Dalbergia clade of the Dalbergieae. They are known commonly as jointvetches. These legumes are most common in warm regions and many species are aquatic. The genus as currently circumscribed is paraphyletic and it has been suggested that the subgenus Ochopodium be elevated to a new genus within the Dalbergieae, though other changes will also be required to render the genus monophyletic.

Symphionema is a genus of two species of small shrubs in the family Proteaceae. Both species are endemic to New South Wales in Australia.

Anthemideae is a tribe of flowering plants in the family, Asteraceae, and the subfamily Asteroideae. They are distributed worldwide with concentrations in central Asia, the Mediterranean Basin, and southern Africa. Most species of plant known as chamomile belong to genera of this tribe.

Mauranthemum is a genus of flowering plants in the daisy family.

Leucanthemum paludosum, commonly known as creeping daisy or mini marguerite, is a perennial plant of the family Asteraceae.
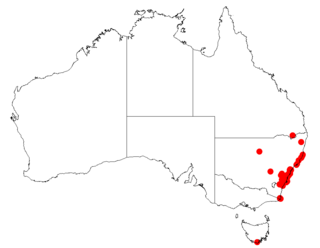
Symphionema paludosum is a plant in the family Proteaceae. It is endemic to New South Wales in eastern Australia. It is one of the many species authored by Robert Brown.

Cota is a genus belonging to the chamomile tribe within the sunflower family. It is native to Europe, North Africa, and southwestern Asia, with a few species naturalized elsewhere. It is an herbaceous plant with flower heads including white or yellow ray florets and yellow disc florets.

Dipodium paludosum is a terrestrial orchid species that is native to south-east Asia. It occurs in Cambodia, Thailand, Vietnam, the Philippines, Sumatra, Peninsular Malaysia and Borneo. The leaves up to 30 cm long and 2.5 cm wide. The axillary racemes comprise 6 to 12 fleshy flowers which are each up to 4 cm wide and are cream with purple-magenta spots.

Júlio Augusto Henriques was a Portuguese botanist and professor at the University of Coimbra. He developed the Herbarium of the University and Coimbra Botanical Garden. He also founded the Broterian Society, which brought together various scientists botanists, geologists and naturalists. He was a large admirer of the work of Charles Darwin. He also wrote many articles about the flora of Portugal.

Glebionidinae is a small subtribe of flowering plants in the tribe Anthemideae of the family Asteraceae. Its members include species used in the production of garden marguerites.

Hypericum nanum is a species of flowering plant in the family Hypericaceae which is native to Lebanon, Syria, and Israel.
Archanthemis is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Asteraceae.
Castrilanthemum is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Asteraceae. It contains a single species, Castrilanthemum debeauxii.


















