Bears are carnivoran mammals of the family Ursidae. They are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans. Although only eight species of bears are extant, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats throughout most of the Northern Hemisphere and partially in the Southern Hemisphere. Bears are found on the continents of North America, South America, and Eurasia. Common characteristics of modern bears include large bodies with stocky legs, long snouts, small rounded ears, shaggy hair, plantigrade paws with five nonretractile claws, and short tails.

Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfamilies, they are a form taxon; they do not represent a monophyletic group, since swans and geese are not considered ducks. Ducks are mostly aquatic birds, and may be found in both fresh water and sea water.

The class Heterotardigrada includes tardigrades that have cephalic appendages and legs with four separate but similar digits or claws on each. 444 species have been described.

Panarthropoda is a proposed animal clade containing the extant phyla Arthropoda, Tardigrada and Onychophora. Panarthropods also include extinct marine legged worms known as lobopodians ("Lobopodia"), a paraphyletic group where the last common ancestor and basal members (stem-group) of each extant panarthropod phylum are thought to have risen. However the term "Lobopodia" is sometimes expanded to include tardigrades and onychophorans as well.

Meiobenthos, also called meiofauna, are small benthic invertebrates that live in marine or freshwater environments, or both. The term meiofauna loosely defines a group of organisms by their size—larger than microfauna but smaller than macrofauna—rather than by their taxonomy. This fauna includes both animals that turns into macrofauna later in life, and those small enough to belong to the meiobenthos their entire life. In marine environments there can be thousands individuals in 10 cm3 of sediment, and counts animals like nematodes, copepods, rotifers, tardigrades and ostracods, but protists like ciliates and foraminifers within the size range of the meiobethos are also often included. In practice, the term usually includes organisms that can pass through a 1 mm mesh but are retained by a 45 μm mesh, though exact dimensions may vary. Whether an organism will pass through a 1 mm mesh also depends upon whether it is alive or dead at the time of sorting.

Animals in space originally served to test the survivability of spaceflight, before human spaceflights were attempted. Later, many species were flown to investigate various biological processes and the effects microgravity and space flight might have on them. Bioastronautics is an area of bioengineering research that spans the study and support of life in space. To date, seven national space programs have flown animals into space: the United States, Soviet Union, France, Argentina, China, Japan and Iran.

Cryptobiosis or anabiosis is a metabolic state in extremophilic organisms in response to adverse environmental conditions such as desiccation, freezing, and oxygen deficiency. In the cryptobiotic state, all measurable metabolic processes stop, preventing reproduction, development, and repair. When environmental conditions return to being hospitable, the organism will return to its metabolic state of life as it was prior to cryptobiosis.

Nepidae is a family of exclusively aquatic Heteropteran insects in the order Hemiptera. They are commonly called water scorpions for their superficial resemblance to scorpions, due to their raptorial forelegs and the presence of a long slender process at the posterior end of the abdomen, resembling a tail. There are 14 genera in the family, in two subfamilies, Nepinae and Ranatrinae. Members of the genus Ranatra, the most widespread and species-rich genus, are sometimes called needle bugs or water stick insects as they are slenderer than Nepa.

Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All of the proteins of the albumin family are water-soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Albumins are commonly found in blood plasma and differ from other blood proteins in that they are not glycosylated. Substances containing albumins are called albuminoids.

Terrestrial animals are animals that live predominantly or entirely on land, as compared with aquatic animals, which live predominantly or entirely in the water, and amphibians, which rely on aquatic and terrestrial habitats. Some groups of insects are terrestrial, such as ants, butterflies, earwigs, cockroaches, grasshoppers and many others, while other groups are partially aquatic, such as mosquitoes and dragonflies, which pass their larval stages in water.

Microfauna refers to microscopic animals and organisms that exhibit animal-like qualities. Microfauna are represented in the animal kingdom and the protist kingdom.

Opsin-5, also known as G-protein coupled receptor 136 or neuropsin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OPN5 gene. Opsin-5 is a member of the opsin subfamily of the G protein-coupled receptors. It is a photoreceptor protein sensitive to ultraviolet (UV) light. The OPN5 gene was discovered in mouse and human genomes and its mRNA expression was also found in neural tissues. Neuropsin is bistable at 0 °C and activates a UV-sensitive, heterotrimeric G protein Gi-mediated pathway in mammalian and avian tissues.

A eurytherm is an organism, often an endotherm, that can function at a wide range of ambient temperatures. To be considered a eurytherm, all stages of an organism's life cycle must be considered, including juvenile and larval stages. These wide ranges of tolerable temperatures are directly derived from the tolerance of a given eurythermal organism's proteins. Extreme examples of eurytherms include Tardigrades (Tardigrada), the desert pupfish, and green crabs, however, nearly all mammals, including humans, are considered eurytherms. Eurythermy can be an evolutionary advantage: adaptations to cold temperatures, called cold-eurythemy, are seen as essential for the survival of species during ice ages. In addition, the ability to survive in a wide range of temperatures increases a species' ability to inhabit other areas, an advantage for natural selection.

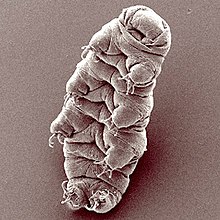
Tardigrades, known colloquially as water bears or moss piglets, are a phylum of eight-legged segmented micro-animals. They were first described by the German zoologist Johann August Ephraim Goeze in 1773, who called them Kleiner Wasserbär. In 1777, the Italian biologist Lazzaro Spallanzani named them Tardigrada, which means "slow steppers".
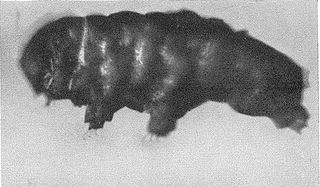
Beorn leggi is an extinct species of tardigrade and the first known fossil tardigrade, discovered c. 1940 and described in 1964 from Late Cretaceous amber from Manitoba, Canada. It is the only species in the genus Beorn, and family Beornidae. It is one of two fossil tardigrades known from the Cretaceous, the other being Milnesium swolenskyi from the Turonian New Jersey amber.
Styraconyx is a genus of tardigrades in the family Styraconyxidae. The genus was named and first described by Gustav Thulin in 1942.
Batillipes mirus is a species of marine tardigrade that lives on sandy surfaces, including near beaches. It has cosmopolitan distribution. The species is known from both marine and brackish waters.
Milnesium swolenskyi is a species of tardigrade from the Cretaceous period. It, Beorn and Paradoryphoribius are the only known tardigrade genera in the fossil record. The type specimen AMNH NJ-796 was found in Turonian New Jersey amber, from about 93.9 to 89.8 million years ago (mya).
Bertolanius is a genus of tardigrades belonging to the family Eohypsibiidae.