British Columbia Ferry Services Inc., operating as BC Ferries (BCF), is a former provincial Crown corporation, now operating as an independently managed, publicly owned Canadian company. BC Ferries provides all major passenger and vehicle ferry services for coastal and island communities in the Canadian province of British Columbia. Set up in 1960 to provide a similar service to that provided by the Black Ball Line and the Canadian Pacific Railway, which were affected by job action at the time, BC Ferries has become the largest passenger ferry line in North America, operating a fleet of 41 vessels with a total passenger and crew capacity of over 27,000, serving 47 locations on the B.C. coast.
British Columbia Highway 101, also known as the Sunshine Coast Highway, is a 156 kilometres (97 mi) long highway that is the main north–south thoroughfare on the Sunshine Coast in British Columbia, Canada.

The Alaska Marine Highway (AMH) or the Alaska Marine Highway System (AMHS) is a ferry service operated by the U.S. state of Alaska. It has its headquarters in Ketchikan, Alaska.

MV Skeena Queen is a ferry built in 1997 and named after the Skeena River. She was intended to be part of a class of spartan, utilitarian ferries, in the "Century ferry class", designed by the naval architects McLaren and Sons In 1994 the 10-year plan of BC Ferries called for construction of three Century-class ferries, to service the busier Gulf Island routes in British Columbia operated by BC Ferries. The name for the class was derived from the capacity, which is approximately 100 cars. However, the only ferry of the class actually built was Skeena Queen. She runs solely on the Swartz Bay-Saltspring Island route.

Coastal-class ferries, also known as the "Super-C class" are three ferries owned and operated by BC Ferries of British Columbia, Canada and were built at the Flensburger Schiffbau-Gesellschaft shipyard in Flensburg, Germany. They are the second-largest ships in the BC Ferries fleet, surpassed only by the two larger, single-ended Spirit-class ferries. At the time of their building, the three ships were the largest double-ended ferries in the world, however the record has since been surpassed.

MV Queen of Nanaimo is a Burnaby-class passenger vessel that was operated by BC Ferries from the time it entered service in 1964 until 2017. Queen of Nanaimo was used to ferry passengers and vehicles from mainland British Columbia, Canada to the islands off its coast. In 2017, the vessel was sold to Goundar Shipping Ltd. and renamed MV Lomaiviti Princess V for service in Fiji.

The V-class ferries, also known as the Victoria class, originally included seven ferries operated by BC Ferries built between 1962 and 1965. The V class were a continuation of the previous Sidney-class design with some cosmetic changes and different engines. These vessels were the backbone of service on the Tsawwassen – Swartz Bay route prior to the arrival of MV Spirit of British Columbia in 1993. Four of these vessels underwent vehicle capacity increases three times. The lead ship of the class, Queen of Victoria suffered significant damage in a collision in 1970.

The Powell River-class ferry is a class of ships formerly operated by BC Ferries. The open deck vessels were mostly used on low-to-moderate volume routes, with Mayne Queen having operated permanently on Route 5, connecting the Outer Gulf Islands with Swartz Bay, Powell River Queen having served on Route 23, Campbell River to Quadra Island, and Bowen Queen having been on relief duty, typically filling in on Routes 4, 5, and 9.

The K-class ferries are a group of similarly designed ferries operated by both BC Ferries and TransLink in British Columbia, Canada.

Earls Cove is a small settlement located on Jervis Inlet in the Sunshine Coast region of British Columbia. It is a terminal for the BC Ferries route across the inlet to Saltery Bay, linking the Lower Sunshine Coast with the Upper Sunshine Coast. Earls Cove is at the north end of the Sechelt Peninsula and on the east side of the mouth of Jervis Inlet, adjacent to Agamemnon Channel, across which is Nelson Island.

BC Ferries operates two T-class ferries for use on small inter-island routes. They have raised bows, which make it easier for the ships to travel in the rough seas often found on British Columbia's central coast. The ferries carry 30 cars and 150 passengers. Both were built in 1969. They were originally owned and operated by the British Columbia Ministry of Transportation until 1985, when the Ministry's saltwater ferries and routes were transferred to BC Ferries, including the T class. The two T-class ferries are Tachek and Quadra Queen II.

Howe Sound is a roughly triangular sound, that joins a network of fjords situated immediately northwest of Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. It was designated as a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve in 2021.

MV Queen of Surrey is a double-ended C-class roll-on/roll-off ferry in the BC Ferries fleet. The ship was launched in 1980 and entered service in 1981. The ferry normally operates on BC Ferries' Horseshoe Bay to Langdale route. She is named for the city of Surrey. On May 12, 2003, Queen of Surrey suffered an engine fire that disabled the ferry in Howe Sound. No one was injured and the ship was returned to service. In 2004, the ferry was involved in a collision with a tugboat, and in 2019 she struck a fixed structure at the Langdale terminal. The 2019 crash lead to passengers being stranded on the vessel for over ten hours.

MV Malaspina Sky is an Intermediate-class ferry in the BC Ferries fleet built in 2008.

MV Queen of Chilliwack was a ferry owned by BC Ferries, built in Norway in 1978, then known as Bastø I. The ferry route she was assigned to was the Moss–Horten Ferry in the Oslofjord.

The MV Quinitsa is an automobile ferry operated by BC Ferries. It was built in 1977 by Vancouver Shipyards in Vancouver, British Columbia. The ferry was originally part of the Ministry of Transportation and Highways' (MoT) saltwater ferry fleet until 1985, when the MoT's saltwater ferries—including Quinitsa—were transferred to BC Ferries.

N-class ferries are a class of RORO ferries, of which one remaining example is owned by BC Ferries and has the distinction of being the smallest vessel in their fleet.
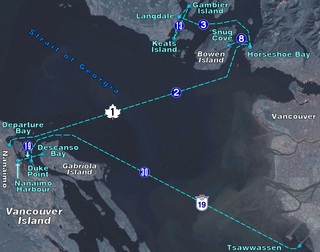
The Bowen Island ferry travels between Snug Cove on Bowen Island, and Horseshoe Bay in the District of West Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, a trip of three nautical miles across Queen Charlotte Channel. A scheduled ferry has been in operation since 1921, when Bowen Island was a popular holiday destination. Prior to that year, transportation to the island was by steamship from Vancouver, with only one trip daily. The Bowen Island ferry used a fleet of small passenger vessels until 1956, when a single car ferry began passenger service, and that ferry began carrying vehicles in 1958. In 2022 the route carried in excess of 1.2 million passengers plus 570,000 vehicles.

Saltery Bay is an unincorporated community on the Sunshine Coast of southern British Columbia, Canada. It is located about 30 kilometres (19 mi) southeast of the city of Powell River. It is adjacent to Saltery Bay Provincial Park.


















