ISO/IEC 8859 is a joint ISO and IEC series of standards for 8-bit character encodings. The series of standards consists of numbered parts, such as ISO/IEC 8859-1, ISO/IEC 8859-2, etc. There are 15 parts, excluding the abandoned ISO/IEC 8859-12. The ISO working group maintaining this series of standards has been disbanded.
ISO/IEC 8859-3:1999, Information technology — 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets — Part 3: Latin alphabet No. 3, is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1988. It is informally referred to as Latin-3 or South European. It was designed to cover Turkish, Maltese and Esperanto, though the introduction of ISO/IEC 8859-9 superseded it for Turkish. The encoding remains popular with users of Esperanto, though use is waning as application support for Unicode becomes more common.
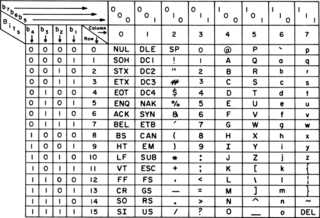
ISO/IEC 646 is the name of a set of ISO standards, described as Information technology — ISO 7-bit coded character set for information interchange and developed in cooperation with ASCII at least since 1964. Since its first edition in 1967 it has specified a 7-bit character code from which several national standards are derived.
The Joint Photographic Experts Group is the joint committee between ISO/IEC JTC 1 and ITU-T that created and maintains the JPEG, JPEG 2000, and JPEG XR standards. It is one of two sub-groups of ISO/IEC Joint Technical Committee 1, Subcommittee 29, Working Group 1 – titled as Coding of still pictures. In the ITU-T, its work falls in the domain of the ITU-T Visual Coding Experts Group (VCEG). ISO/IEC JTC1 SC29 Working Group 1 is responsible for the JPEG and JBIG standards. The scope of the organization includes the work of both the Joint Photographic Experts Group and Joint Bi-level Image Experts Group.
Articles related to standards include:
ISO/IEC 8859-4:1998, Information technology — 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets — Part 4: Latin alphabet No. 4, is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1988. It is informally referred to as Latin-4 or North European. It was designed to cover Estonian, Latvian, Lithuanian, Greenlandic, and Sami. It has been largely superseded by ISO/IEC 8859-10 and Unicode. Microsoft has assigned code page 28594 a.k.a. Windows-28594 to ISO-8859-4 in Windows. IBM has assigned code page 914 to ISO 8859-4.
ISO/IEC 8859-7:2003, Information technology — 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets — Part 7: Latin/Greek alphabet, is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1987. It is informally referred to as Latin/Greek. It was designed to cover the modern Greek language. The original 1987 version of the standard had the same character assignments as the Greek national standard ELOT 928, published in 1986. The table in this article shows the updated 2003 version which adds three characters. Microsoft has assigned code page 28597 a.k.a. Windows-28597 to ISO-8859-7 in Windows. IBM has assigned code page 813 to ISO 8859-7.
ISO/IEC 8859-16:2001, Information technology — 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets — Part 16: Latin alphabet No. 10, is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 2001. It is informally referred to as Latin-10 or South-Eastern European. It was designed to cover Albanian, Croatian, Hungarian, Polish, Romanian, Serbian and Slovenian, but also French, German, Italian and Irish Gaelic.
A telegraph code is one of the character encodings used to transmit information through telegraphy machines. The most famous such code is Morse code.

ArmSCII or ARMSCII is a set of obsolete single-byte character encodings for the Armenian alphabet defined by Armenian national standard 166-9. ArmSCII is an acronym for Armenian Standard Code for Information Interchange, similar to ASCII for the American standard. It has been superseded by the Unicode standard.
ISO/IEC 6937:2001, Information technology — Coded graphic character set for text communication — Latin alphabet, is a multibyte extension of ASCII, or rather of ISO/IEC 646-IRV. It was developed in common with ITU-T for telematic services under the name of T.51, and first became an ISO standard in 1983. Certain byte codes are used as lead bytes for letters with diacritics (accents). The value of the lead byte often indicates which diacritic that the letter has, and the follow byte then has the ASCII-value for the letter that the diacritic is on. Only certain combinations of lead byte and follow byte are allowed, and there are some exceptions to the lead byte interpretation for some follow bytes. However, there are no combining characters at all are encoded in ISO/IEC 6937. But one can represent some free-standing diacritics, often by letting the follow byte have the code for ASCII space.
YUSCII is an informal name for several JUS standards for 7-bit character encoding. These include:
The Video Coding Experts Group or Visual Coding Experts Group is a working group of the ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) concerned with video coding standards. It is responsible for standardization of the "H.26x" line of video coding standards, the "T.8xx" line of image coding standards, and related technologies.
A IA5String is a restricted character string type in the ASN.1 notation. It is used to represent ISO 646 (IA5) characters.
The National Replacement Character Set, or NRCS for short, was a feature supported by later models of Digital's (DEC) computer terminal systems, starting with the VT200 series in 1983. NRCS allowed individual characters from one character set to be replaced by one from another set, allowing the construction of different character sets on the fly. It was used to customize the character set to different local languages, without having to change the terminal's ROM for different counties, or alternately, include many different sets in a larger ROM. Many 3rd party terminals and terminal emulators supporting VT200 codes also supported NRCS.
The ISO basic Latin alphabet is a Latin-script alphabet and consists of two sets of 26 letters, codified in various national and international standards and used widely in international communication. They are the same letters that comprise the English alphabet.
The Israeli Standards Institute's Standard SI 960 defines a 7-bit Hebrew code page. It is derived from, but does not conform to, ISO/IEC 646; more specifically, it follows ASCII except for the lowercase letters and backtick (`), which are replaced by the naturally ordered Hebrew alphabet. It is also known as DEC Hebrew (7-bit), because DEC standardized this character set before it became an international standard. Kermit named it hebrew-7 and HEBREW-7.