
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the second-most populous country, the seventh-largest country by land area, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar and Indonesia.

India is the second most populated country in the world with nearly a fifth of the world's population. According to the 2019 revision of the World Population Prospects the population stood at 1,352,642,280.

The Prime Minister of India, officially the Prime Minister of the Republic of India, is the leader of the executive branch of the Government of India. The prime minister is the chief adviser to the President of India and the head of the Union Council of Ministers. They can be a member of any of the two houses of the Parliament of India—the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha ; but has to be a member of the political party or coalition, having a majority in the Lok Sabha.

Tamil Nadu is a state in southern India. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu lies in the southernmost part of the Indian subcontinent and is bordered by the union territory of Puducherry and the South Indian states of Kerala, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh. It is bounded by the Eastern Ghats on the north, by the Nilgiri Mountains, the Meghamalai Hills, and Kerala on the west, by the Bay of Bengal in the east, by the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait on the southeast, and by the Indian Ocean on the south. The state shares a maritime border with the nation of Sri Lanka.

West Bengal is a state in the eastern region of India along the Bay of Bengal. With over 91 million inhabitants, it is the fourth-most populous state and the fourteenth-largest state by area in India. Covering an area of 88,752 km2 (34,267 sq mi), it is also the seventh-most populous country subdivision of the world. Part of the Bengal region of the Indian subcontinent, it borders Bangladesh in the east, and Nepal and Bhutan in the north. It also borders the Indian states of Odisha, Jharkhand, Bihar, Sikkim and Assam. The state capital is Kolkata, the third-largest metropolis, and seventh largest city by population in India. West Bengal includes the Darjeeling Himalayan hill region, the Ganges delta, the Rarh region and the coastal Sundarbans. The state's main ethnic group are the Bengalis, with the Bengali Hindus forming the demographic majority.

Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. It is bordered by the state of Haryana on three sides and by Uttar Pradesh to the east. The NCT covers an area of 1,484 square kilometres (573 sq mi). According to the 2011 census, Delhi's city proper population was over 11 million, the second-highest in India after Mumbai, while the whole NCT's population was about 16.8 million. Delhi's urban area is now considered to extend beyond the NCT boundaries, and include the neighbouring satellite cities of Ghaziabad, Faridabad, Gurgaon and Noida in an area called the National Capital Region (NCR) and had an estimated 2016 population of over 26 million people, making it the world's second-largest urban area according to the United Nations. Recent estimates of the metro economy of its urban area have ranked Delhi either the most or second-most productive metro area of India. Delhi is the second-wealthiest city in India after Mumbai and is home to 18 billionaires and 23,000 millionaires. Delhi ranks fifth among the Indian states and union territories in human development index. Delhi has the second-highest GDP per capita in India. Delhi is of great historical significance as an important commercial, transport, and cultural hub, as well as the political centre of India.

The East India Company (EIC), also known as the Honourable East India Company (HEIC), East India Trading Company (EITC), the English East India Company or the British East India Company, and informally known as John Company, Company Bahadur, or simply The Company was an English and later British joint-stock company founded in 1600. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies, and later with Qing China. The company seized control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent, colonised parts of Southeast Asia and Hong Kong after the First Opium War, and maintained trading posts and colonies in the Persian Gulf Residencies.

The Bharatiya Janata Party is one of two major political parties in India, along with the Indian National Congress. It is the current ruling political party of the Republic of India, having been so since 2014. The BJP is a right-wing party, and its policy has historically reflected Hindu nationalist positions. It has close ideological and organisational links to the much older Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS). As of 2019, it is the country's largest political party in terms of representation in the national parliament and state assemblies and is by far the world's largest party in terms of primary membership, with the second largest party, the Chinese Communist Party, having about half the registered members of the BJP.

The Indian National Congress, is a political party in India with widespread roots. Founded in 1885, it was the first modern nationalist movement to emerge in the British Empire in Asia and Africa. From the late 19th century, and especially after 1920, under the leadership of Mahatma Gandhi, Congress became the principal leader of the Indian independence movement. Congress led India to independence from the United Kingdom, and powerfully influenced other anti-colonial nationalist movements in the British Empire, making it one of the world's oldest active political parties.

Uttar Pradesh is a state in northern India. With roughly 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populous state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was created on 1 April 1937 as the United Provinces of Agra and Oudh during British rule, and was renamed Uttar Pradesh in 1950, giving it the acronym UP. The state is divided into 18 divisions and 75 districts, with the capital being Lucknow and financial & industrial capital being Kanpur. On 9 November 2000, a new state, Uttaranchal, was carved from the state's Himalayan hill region. The two major rivers of the state, the Ganges and Yamuna, join at Triveni Sangam in Allahabad and flow further east as Ganges. Other prominent rivers are Gomti and Saryu. The forest cover in the state is 6.09% of the state's geographical area.
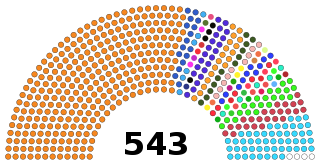
The Lok Sabha, or House of the People, is the lower house of India's bicameral Parliament, with the upper house being the Rajya Sabha. Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by an adult universal suffrage and a first-past-the-post system to represent their respective constituencies, and they hold their seats for five years or until the body is dissolved by the President on the advice of the council of ministers. The house meets in the Lok Sabha Chambers of the Sansad Bhavan, New Delhi.

India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, for a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions.

The Communist Party of India (Marxist) is a communist political party in India. It is one of the national parties of India. The party emerged from a split from the Communist Party of India in 1964. The CPI(M) was formed in Calcutta from 31 October to 7 November 1964.

Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam is a political party in India, particularly in the state of Tamil Nadu and the union territory of Puducherry. It is currently the ruling party in Tamil Nadu and is part of the Indian political front the United Progressive Alliance (UPA). DMK is a Dravidian party, adhering to the social-democratic and social justice principles of C. N. Annadurai and Periyar E. V. Ramasamy. It was founded in 1949 by Annadurai as a breakaway faction from the Dravidar Kazhagam headed by Periyar E. V. Ramasamy.

Narendra Damodardas Modi is an Indian politician serving as the 14th and current prime minister of India since 2014. He was the chief minister of Gujarat from 2001 to 2014 and is the member of Parliament for Varanasi. Modi is a member of the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) and its National Democratic Alliance (NDA). He is also a member of the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS), a Hindu nationalist volunteer organisation. He is the first prime minister born after India's independence, the second non-Congress one to win two consecutive terms after Atal Bihari Vajpayee and the first from outside the Congress to win both terms with a majority in the Lok Sabha.

The All India Trinamool Congress is an Indian political party which is predominantly active in West Bengal. The party is led by current chief minister of West Bengal Mamata Banerjee. Following the 2019 general election, it is currently the fourth-largest party in the Lok Sabha with 20 seats. Since its inception the party has been at the forefront of the anti-communist movement in West Bengal.

Mamata Banerjee is an Indian politician who is serving as the 8th and current Chief Minister of West Bengal since 2011, the first woman to hold the office. She founded the All India Trinamool Congress party in 1998 after separating from the Indian National Congress, and became its first chairperson. She is often referred to as Didi

The British Raj was the rule by the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent from 1858 to 1947. The rule is also called Crown rule in India, or direct rule in India. The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage, and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom, which were collectively called British India, and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British tutelage or paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially.

Kerala is a state on the southwestern Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South Canara, and Travancore. Spread over 38,863 km2 (15,005 sq mi), Kerala is the twenty-first largest Indian state by area. It is bordered by Karnataka to the north and northeast, Tamil Nadu to the east and south, and the Lakshadweep Sea to the west. With 33,406,061 inhabitants as per the 2011 Census, Kerala is the thirteenth-largest Indian state by population. It is divided into 14 districts with the capital being Thiruvananthapuram. Malayalam is the most widely spoken language and is also the official language of the state.

The COVID-19 pandemic in India is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The first case of COVID-19 in India, which originated from China, was reported on 30 January 2020. India currently has the largest number of confirmed cases in Asia. As of May 2021, India has the second-highest number of confirmed cases in the world with nearly 20 million reported cases of COVID-19 infection and 249,992 deaths as of 11 May 2021.


















