
The Good Conduct Medal is one of the oldest military awards of the United States Armed Forces. The U.S. Navy's variant of the Good Conduct Medal was established in 1869, the Marine Corps version in 1896, the Coast Guard version in 1923, the Army version in 1941, and the Air Force version in 1963; the Air Force Good Conduct Medal was temporarily discontinued from February 2006 to February 2009, followed by its subsequent reinstatement.

The Army of India Medal (AIM) was a campaign medal approved in 1851 for issue to officers and men of the British Army and the Army of the Honourable East India Company. A retrospective award following the precedent set by the Naval General Service Medal and the Military General Service Medal, it served to reward service in various actions from 1803 to 1826.

The Decoration for Officers of the Royal Naval Volunteer Reserve, post-nominal letters VD until c. 1947 and VRD thereafter, was instituted in 1908. It could be awarded to part-time commissioned officers in the United Kingdom's Royal Naval Volunteer Reserve after twenty years of service as efficient and thoroughly capable officers. The decoration was a Naval version of the Volunteer Officers' Decoration and its successor, the Territorial Decoration.

The Efficiency Medal was instituted in 1930 for award to part-time warrant officers, non-commissioned officers and men after twelve years of efficient service on the active list of the Militia or the Territorial Army of the United Kingdom, or of the other Auxiliary Military Forces throughout the British Empire. At the same time a clasp was instituted for award to holders of the medal upon completion of further periods of six years of efficient service.

The Efficiency Decoration, post-nominal letters TD for recipients serving in the Territorial Army of the United Kingdom or ED for those serving in the Auxiliary Military Forces, was instituted in 1930 for award to part-time officers after twenty years of service as an efficient and thoroughly capable officer. The decoration superseded the Volunteer Officers' Decoration, the Colonial Auxiliary Forces Officers' Decoration and the Territorial Decoration.
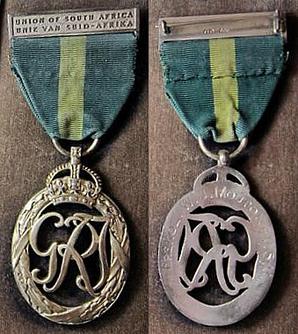
The Efficiency Decoration (South Africa), post-nominal letters ED, was instituted in 1930 for award to efficient and thoroughly capable part-time officers in the Citizen Force of the Union of South Africa after twenty years of service. The decoration superseded the Colonial Auxiliary Forces Officers' Decoration.

The Efficiency Medal (South Africa) was instituted in 1930 for award to part-time warrant officers, non-commissioned officers and men after twelve years of efficient service on the active list of the Citizen Force of the Union of South Africa. At the same time, a clasp was instituted for award to holders of the medal upon completion of further periods of six years of efficient service. The medal superseded the Colonial Auxiliary Forces Long Service Medal.

The Seringapatam Medal, or Sri Ranga Pattanam Medal, is a campaign medal that was awarded by the Governor-General of India to all British and Indian soldiers who participated in the British victory in the Battle of Seringapatam in 1799.

The Colonial Auxiliary Forces Officers' Decoration, post-nominal letters VD, was established in 1899 as recognition for long and meritorious service as a part-time commissioned officer in any of the organized military forces of the British Colonies, Dependencies and Protectorates. It superseded the Volunteer Officers' Decoration for India and the Colonies in all these territories, but not in the Indian Empire.

The Royal Naval Volunteer Reserve Long Service and Good Conduct Medal, initially designated the Royal Naval Volunteer Reserve Long Service Medal, was instituted in 1908. It could be awarded to part-time ratings in the United Kingdom's Royal Naval Volunteer Reserve after twelve years of service and good conduct. The medal was a Naval version of the Volunteer Long Service Medal and its successor, the Territorial Force Efficiency Medal.

The Indian Meritorious Service Medal (for Europeans of Indian Army) was a medal to recognize long and meritorious service by European non-commissioned officers in service of the East India Company's Army.

The Indian Long Service and Good Conduct Medal was a long service medal awarded to Indian other ranks in the British Indian Army.

The Volunteer Long Service Medal was instituted in 1894 as an award for long service by other ranks and some officers of the United Kingdom's Volunteer Force. Award of the medal was discontinued when it was superseded by the Territorial Force Efficiency Medal in 1908.

The Army Long Service and Good Conduct Medal was instituted by King William IV in 1830. The medal remained in use for 100 years, until it was replaced by the Medal for Long Service and Good Conduct (Military) in 1930. During that time the reverse of the medal remained virtually unchanged, while the design of the obverse was altered during the reigns of Queen Victoria, King Edward VII and King George V.

In May 1895, Queen Victoria authorised Colonial governments to adopt various British military medals and to award them to their local military forces. The Cape of Good Hope introduced this system in September 1895 and, in 1896, instituted the Army Long Service and Good Conduct Medal (Cape of Good Hope).

In May 1895, Queen Victoria authorised Colonial governments to adopt various British military medals and to award them to their local military forces. The Colony of Natal introduced this system in August 1895 and, in 1897, instituted the Army Long Service and Good Conduct Medal (Natal).

The Volunteer Officers' Decoration was instituted in 1892 as an award for long and meritorious service by officers of the United Kingdom's Volunteer Force. In 1894, the grant of the decoration was extended to commissioned officers of Volunteer Forces throughout the British Empire. A separate new decoration was instituted, the Volunteer Officers' Decoration for India and the Colonies, post-nominal letters VD.

The Volunteer Long Service Medal was instituted in 1894 as an award for long service by other ranks and some officers of the United Kingdom's Volunteer Force. In 1896, the grant of the medal was extended to other ranks and officers who had served in the ranks of the Volunteer Forces throughout the British Empire. A separate new medal was instituted, the Volunteer Long Service Medal for India and the Colonies. Awarding of this medal was discontinued in stages when it was superseded in most territories by the Colonial Auxiliary Forces Long Service Medal in 1899 and in the remainder by the Efficiency Medal in 1930.

The Nepal Medal was awarded by the Honourable East India Company (HEIC) to native Indian officers, and Indian soldiers for particularly distinguished conduct, during the Anglo-Nepalese War of 1814–16.

The Burma Medal is a campaign medal awarded by the Governor-General of India to native Indian soldiers of the armies of the Honourable East India Company (HEIC) who participated in the First Burma War from April 1824 to February 1826.




















