
Stearns County is a county in the U.S. state of Minnesota. As of the 2020 census, the population was 158,292. Its county seat and largest city is St. Cloud.

St. Joseph or Saint Joseph is a city in Stearns County, Minnesota, United States. The population was 7,029 at the 2020 census. It is home to the College of Saint Benedict.

Cold Spring is a city in Stearns County, Minnesota, United States, at the gateway of the Sauk River Chain of Lakes, an interconnected system of 14 bay-like lakes fed and connected by the Sauk River. Cold Spring is part of the St. Cloud Metropolitan Statistical Area. Its population was 4,025 at the 2010 census.

Holdingford is a city in Stearns County, Minnesota, United States. The population was 708 at the 2010 census. It claims to be "The Gateway to Lake Wobegon", the fictional central Minnesota town created by author Garrison Keillor.

St. Cloud or Saint Cloud is a city in the U.S. state of Minnesota and the largest population center in the state's central region. The population was 68,881 at the 2020 census, making it Minnesota's 12th-largest city. St. Cloud is the county seat of Stearns County and was named after the city of Saint-Cloud, France, which was named after the 6th-century French monk Clodoald.

The Rocky Mountain locust is an extinct species of grasshopper that ranged through the western half of the United States and some western portions of Canada with large numbers seen until the end of the 19th century. Sightings often placed their swarms in numbers far larger than any other locust species, with one famous sighting in 1875 estimated at 198,000 square miles (510,000 km2) in size, weighing 27.5 million tons and consisting of some 12.5 trillion insects, the greatest concentration of animals ever speculatively guessed, according to Guinness World Records.
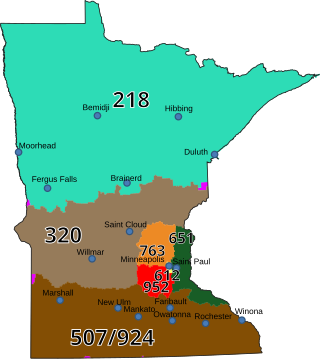
Area code 320 is a telephone area code in the North American Numbering Plan for most of the central part of the U.S. state of Minnesota. The numbering plan area (NPA) excludes the Twin Cities metro region. The area code was created in 1996, by a split of NPA 612, which stretched border-to-border from Wisconsin through the Twin Cities to South Dakota. 320 was the fourth Minnesota area code, and the first new one in the state in 42 years.

Saint Augusta or St. Augusta, formerly named Ventura, is a city in Stearns County, Minnesota, United States, directly south of the city of St. Cloud. The population was 3,497 at the 2020 census.

The Sauk River is a 122-mile-long (196 km) tributary of the Mississippi River in central Minnesota in the United States. It drains small lakes in Stearns County. In the Ojibwe language it is called Ozaagi-ziibi, meaning "River of the Sauks".

The Diocese of Saint Cloud is a Latin Church diocese of the Catholic Church in central Minnesota in the United States. It is a suffragan diocese of the metropolitan Archdiocese of Saint Paul and Minneapolis.

Magnus of Füssen, otherwise Magnoald or Mang, was a missionary saint in southern Germany, also known as the Apostle of the Allgäu. He is believed to have been a contemporary either of Gall or of Boniface and is venerated as the founder of St. Mang's Abbey, Füssen.

Francis Xavier Pierz was a Slovenian-American Roman Catholic priest and missionary to the Ottawa and Ojibwe Indians in present-day Michigan, Wisconsin, Ontario, and Minnesota. Because his letters convinced numerous Catholic German Americans to settle in Central Minnesota after the Treaty of Traverse des Sioux in 1851, Fr. Pierz is referred to as the "Father of the Diocese of Saint Cloud."
CentraCare is an integrated health care system in Central Minnesota. The nonprofit includes six hospitals, seven senior care facilities, 18 clinics, four pharmacies and numerous inpatient and outpatient specialty care services.

Northern Lines Railway is a shortline railroad operating 17 miles (27 km) of track in and near St. Cloud in central Minnesota. The railroad was formed in 2004 to operate Burlington Northern Santa Fe trackage in and near the St. Cloud area and started operations in 2005. Interchange is made with BNSF in east St. Cloud or at the rail yard in central St. Cloud.

The St. Cloud Metropolitan Statistical Area, as defined by the United States Census Bureau, consists of two counties in central Minnesota, anchored by the city of St. Cloud. In the 2010 census, the MSA had a population of 201,093; a July 1, 2012, Census Bureau estimate placed the population at 190,014. As of the 2020 census, the population was 199,671.

Great River Regional Library is a library system serving Benton, Morrison, Sherburne, Stearns, Todd and Wright Counties in central Minnesota. It is a consolidated library system consisting of 32 branch libraries, with a headquarters at the St. Cloud Public Library.
Joseph Francis Busch was an American prelate of the Catholic Church. He served as bishop of the Diocese of Lead in South Dakota from 1910 to 1915 and bishop of the Diocese of Saint Cloud in Minnesota from 1915 until his death in 1953.

Assumption Chapel, also known as the Grasshopper Chapel, is a Roman Catholic Marian shrine, "Calvary Hill", and pilgrimage chapel. The shrine stands upon one of the tallest hills in Stearns County, and which is known locally as, meaning "Mary's Mountain", on the outskirts of Cold Spring, Minnesota. The chapel stands in a region of Minnesota largely settled in the 1850s by German-American Catholics who were invited to the area by Slovenian-American missionary Fr. Francis Xavier Pierz and which remained, until shortly before the Second World War, a major center for the speaking of the German language in the United States.

The Church of St. Joseph is a historic Roman Catholic church building in St. Joseph, Minnesota, United States. It is part of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Saint Cloud. It was constructed in a German immigrant community in 1869, though the tower wasn't completed until 1884. A rectory stands east of the church. Both buildings were listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1982 for their state-level significance in the themes of architecture, exploration/settlement, and religion. The property was nominated for reflecting the settlement of rural Stearns County by Catholic immigrant groups clustered in small, ethnic hamlets dominated by a central church.





















