Gondwana is a region of India, named after the Gondi people who live there. The name of the ancient continent of Gondwanaland was derived from Gondwana, because some of the earliest rock formations of this continent were first investigated in part of the region, in modern Odisha.

Major-general Sir William Henry Sleeman KCB was a British soldier and administrator in British India. He is best known for his work from the 1830s in suppressing the organized criminal gangs known as Thuggee. He also discovered the holotype specimen of the sauropod dinosaur Titanosaurus indicus in Jabalpur in 1828.

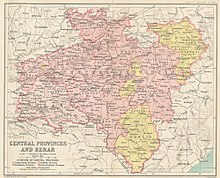
The Central Provinces and Berar was a province of British India and later the Dominion of India which existed from 1903 to 1950. It was formed by the merger of the Central Provinces with the province of Berar, which was territory leased by the British from the Hyderabad State. Through an agreement signed on 5 November 1902, 6th Nizam Mahbub Ali Khan, Asaf Jah VI leased Berar permanently to the British for an annual payment of 25 lakhs Rupees. Lord Curzon decided to merge Berar with the Central Provinces, and this was proclaimed on 17 September 1903.

Sagar is a city in the state of Madhya Pradesh in central India. Situated on a spur of the Vindhya Range, 1,758 feet (536 m) above sea-level. The city is around 172 kilometres (107 mi) northeast of state capital, Bhopal.

Mahakoshal is a region of central India. Mahakoshal lies in the upper or eastern reaches of the Narmada River valley in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. Jabalpur is the largest city in the region. Nimar region lies to the west, in the lower reaches of the Narmada valley.
Mandla is a town with municipality in Mandla district in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is the administrative headquarters of Mandla District. The town is situated in a loop of the Narmada River, which surrounds it on three sides, and for 15 miles between Mandla and Ramnagar, Madhya Pradesh the river flows in a deep bed unbroken by rocks. The Narmada is worshiped here, and many ghats have been constructed on the banks of the river. It was a capital of the Gondwana Kingdom who built a palace and a fort, which in the absence of proper care have gone to ruins.

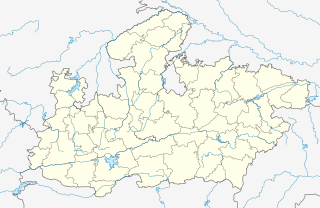
Jabalpur Division is an administrative geographical unit of Madhya Pradesh state of India. Jabalpur is the administrative headquarters of the division. As of 2005, the division consists of districts of Balaghat, Chhindwara, Jabalpur, Katni, Mandla, Narsinghpur, Dindori and Seoni.

Narsinghpur district is a district of Madhya Pradesh state in central India. The city of Narsinghpur is administrative headquarters of the district. As of 2001 Narsinghpur is the most literate district of MP. Village Singhpur bada in Narsinghpur is also considered as bahubali's and goon's village

Sagar district is a district of Madhya Pradesh state in central India. The town of Sagar serves as its administrative center.
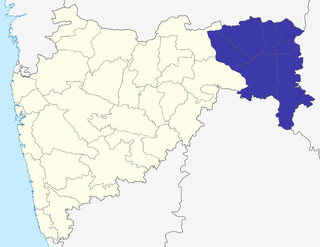
The Nagpur division is one of six administrative divisions of the state of Maharashtra in India. Nagpur is the easternmost division in the state, with an administrative headquarters in the city of Nagpur. It covers 51,336 km² (19,821 mi²). The Amravati and Nagpur divisions make up the Vidarbha region.

Nagpur Province was a province of British India that covered parts of the present-day states of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Chhattisgarh. The city of Nagpur was the capital of the province.

The Saugor and Nerbudda Territories, was a region of British India, located in the central part of present-day Madhya Pradesh state in central India. It included the present-day districts of Sagar (Saugor), Damoh, Jabalpur, and Narsinghpur.

The Central Provinces was a province of British India. It comprised British conquests from the Mughals and Marathas in central India, and covered parts of present-day Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra states. Its capital was Nagpur. It became the Central Provinces and Berar in 1903.

Kareli is a city and a Municipality in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. Kareli is financial capital of the district Narsinghpur. It is well connected by transportation. Near Kareli, an ancient fair called Barman Mela is organised every year in the month of January on the bank of the river Narmada. There are many historic and religious places in Kareli like Deepeshwar Temple Barman, Chougan Fort. India's longest Road NH-44 passes through Kareli and also connected to almost every part of the country by rail network. Before the construction of the Bina-Katni branch of the Indian Midland Railway, the metaled road from Saugor crossing the Nerbudda at Barmhan brought the bulk of the produce of the Sagar District to Kareli station. A mail cart ran from Kareli to Sagar, a distance of 122 km (76 mi). The trade of Kareli has now considerably declined, but it is still the exporting station for the southern parts of the Rehli tahsil of Sagar and the north of Narsinghpur. A cotton-ginning factory, the property of Raja Gokul Das, was opened in 1904. This is the nearest rail station and market for towns of Sagar district.
Seth Govind Das was an Indian independence activist and a distinguished parliamentarian. He belonged to the Maheshwari merchant family of Raja Gokuldas of Jabalpur. The family began as the banking firm of Sevaram Khushalchand, one of the "great firms" as termed by T.A. Timberg.

Chhattisgarh Division was a former administrative division of the Central Provinces of British India. It was located in the east of the Central Provinces and encompassed the upper Mahanadi River basin, in the central part of present-day Chhattisgarh state of India.

The Haihaiyavansi Kingdom was a kingdom in the upper Mahanadi River basin in eastern India, comprising the central portion of present-day Chhattisgarh state and west-central Orissa. The kingdom was ruled by the Haihaiyavansi from the 12th to the 18th centuries AD.

Rai Bahadur Sir Bipin Krishna Bose was an Indian advocate.

Robertson College, Jabalpur, is considered to be the oldest such institution in Madhya Pradesh.

The Nerbudda Division, named after the Narmada River (Nerbudda), was a former administrative division of the Central Provinces of British India. It encompassed a good part of the Narmada River basin in the eastern part of present-day Madhya Pradesh state of India. The Nerbudda Division had an area of 47,609.2 km2 with a population of 1,785,008 in 1901.