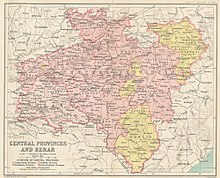
The Central Provinces and Berar was a province of British India and later the Dominion of India which existed from 1903 to 1950. It was formed by the merger of the Central Provinces with the province of Berar, which was territory leased by the British from the Hyderabad State. Through an agreement signed on 5 November 1902, 6th Nizam Mahbub Ali Khan, Asaf Jah VI leased Berar permanently to the British for an annual payment of 25 lakhs rupees. Lord Curzon decided to merge Berar with the Central Provinces, and this was proclaimed on 17 September 1903.

Sambalpur District is a district in the western part of state of Odisha, India. The historic city of Sambalpur is the district headquarters.

Bilaspur district is a district of the Chhattisgarh state of India. Bilaspur city is the headquarters of the district. As of 2011, it is the second most populous district of Chhattisgarh, after Raipur.
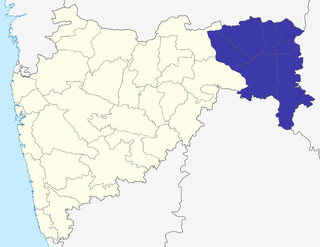
The Nagpur Division is one of six administrative divisions of the state of Maharashtra in India. Nagpur is the easternmost division in the state, with an administrative headquarters in the city of Nagpur. It covers 51,336 km² (19,821 mi²). The Amravati and Nagpur divisions make up the Vidarbha region.

Nagpur Province was a province of British India that covered parts of the present-day states of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Chhattisgarh. The city of Nagpur was the capital of the province.

The Eastern States Agency was an agency or grouping of princely states in eastern India, during the latter years of the Indian Empire. It was created in 1933, by the unification of the former Chhattisgarh States Agency and the Orissa States Agency; the agencies remained intact within the grouping. In 1936, the Bengal States Agency was added.

The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another, they existed between 1612 and 1947, conventionally divided into three historical periods:

The Central Provinces was a province of British India. It comprised British conquests from the Mughals and Marathas in central India, and covered parts of present-day Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra states. Nagpur was the primary winter capital while Pachmarhi served as the regular summer retreat. It became the Central Provinces and Berar in 1903.

Chota Nagpur Division, also known as the South-West Frontier, was an administrative division of British India. It included most of the present-day state of Jharkhand as well as adjacent portions of West Bengal, Orissa, and Chhattisgarh.
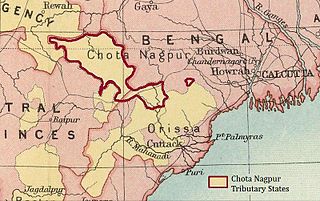
The Chota Nagpur Tributary States or Chota Nagpur States were a group of non-salute states at the time of British Raj, located on the Chhota Nagpur Plateau. British suzerainty over the states was exercised through the government of the Bengal Presidency.
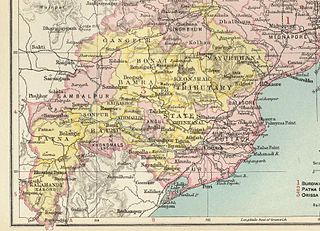
The Orissa Tributary States, also known as the Garhjats and as the Orissa Feudatory States, were a group of princely states of British India now part of the present-day Indian state of Odisha.
The Kingdom of Nagpur was an Indian kingdom in the 18th and 19th centuries. It came under the rule of the Marathas of the Bhonsle dynasty in the mid-18th century and became part of the Maratha Empire. The city of Nagpur was the capital of the state.

The Berar Division, formerly Berar Province, was one of the former administrative divisions of the Central Provinces and Berar of British India. Ellichpur (Achalpur) was the capital and the administrative headquarters of the division.
The History of Sambalpur in the Indian state of Orissa can be traced back to 100 AD. It was mentioned in the book of Ptolemy as Sambalaka on the left bank of river "Manada", now known as Mahanadi. Other evidence is available from the records of Xuanzang, and in the writings of the celebrated King Indrabhuti of Sambalaka of Odra Desha or Oddiyan, the founder of Vajrayana Buddhism and the Lama cult. He has written the book Jñānasiddhi.

The States Reorganisation Act, 1956 was a major reform of the boundaries of India's states and territories, organising them along linguistic lines.

The Nerbudda Division, named after the Narmada River (Nerbudda), was a former administrative division of the Central Provinces of British India. It encompassed a good part of the Narmada River basin in the eastern part of present-day Madhya Pradesh state of India. The Nerbudda Division had an area of 47,609.2 km2 with a population of 1,785,008 in 1901.

Sambalpur State, also known as Hirakhand Kingdom was a sovereign state founded in the 1570 CE. It ruled over a vast kingdom spread across Western Odisha and Eastern Chhattisgarh in central-eastern India prior to the Maratha occupation in 1800 AD. From 1849 AD it was integrated with British Raj as a British District. Its capital was present-day Sambalpur city in Western Odisha.

The Divisions of British India were administrative units of the Government of the British Raj or Indian Empire.

The Jubbulpore Division, named after its capital Jabalpur (Jubbulpore), was one of the four former administrative divisions of the Central Provinces of British India. It was located in the Mahakoshal region of present-day Madhya Pradesh state of India. The Jubbulpore Division had an area of 48,401 km² with a population of 2,201,633 in 1881.

Rairakhol State was a princely state during the British Raj in what is today India. It was one of the Chota Nagpur States and had its capital at Rairakhol (Redhakhol), located in the present-day Sambalpur district of Odisha. It had an area of 2,157 square kilometres (833 sq mi) and a population of 26,888 in 1901, the average revenue was Rs.55,000 in 1904.