The Central Provinces and Berar was a province of British India and later the Dominion of India which existed from 1903 to 1950. It was formed by the merger of the Central Provinces with the province of Berar, which was territory leased by the British from the Hyderabad State. Through an agreement signed on 5 November 1902, 6th Nizam Mahbub Ali Khan, Asaf Jah VI leased Berar permanently to the British for an annual payment of 25 lakhs rupees. Lord Curzon decided to merge Berar with the Central Provinces, and this was proclaimed on 17 September 1903.

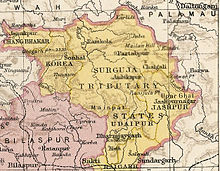
Korea State, currently spelt as Koriya, was a small princely state in the British Empire of India. After Indian independence in 1947, the ruler of Korea acceded to the Union of India on 1 January 1948, and Koriya was made part of Surguja District of Central Provinces and Berar province. In January 1950, "Central Provinces and Berar" province was renamed Madhya Pradesh state. After November 2000, Korea and the former princely state of Changbhakar became Koriya district of Chhattisgarh state.

Bamra State or Bamanda State, covering an area of 5,149 km2, was one of the princely states of India during the British Raj. Its capital was in Debagarh (Deogarh). Bamra State acceded to India in 1948.

The Eastern States Agency was an agency or grouping of princely states in eastern India, during the latter years of the British Raj. It was created in 1933, by the unification of the former Chhattisgarh States Agency and the Orissa States Agency; the agencies remained intact within the grouping. In 1936, the Bengal States Agency was added.
Sarangarh is a New District in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh.

The history of human settlement in the western Indian state of Rajasthan dates back to about 100,000 years ago. Around 5000 to 2000 BCE many regions of Rajasthan belonged as the site of the Indus Valley Civilization. Kalibangan is the main Indus site of Rajasthan, here fire altars have been discovered, similar to those found at Lothal.

Changbhakar State, also known as Chang Bhakar, was one of the small princely states of British Empire in India in the Chhattisgarh States Agency. It included 117 villages and had an area of 2,330 square kilometres (899 sq mi) with a 1941 population of 21,266 people. Bharatpur was the capital of the princely state.

Bundi State, founded by Hada Rao Devda, was a princely state in India. The former state was located in modern-day Rajasthan. It was ruled by Hada Chauhan Rajputs.

Saraikela State also spelt Seraikela, Saraikella or Seraikella, was a small princely state in India during the British Raj, in the region that is now the Jharkhand state. Its capital was at Saraikela.

Raigarh was a princely state in India during the British Raj. The state was ruled by the Gond dynasty of Gond clan.

Khaniadhana or Khaniyadhana was a princely state of British India ruled by the Judev dynasty of Bundela Rajputs. The capital of the State was Khaniadhana. It was part of the Bundelkhand Agency and later the Central India Agency.

Udaipur State was one of the princely states of India during the British Raj. The town of Dharamjaigarh was the former state's capital.

Kharsawan State, also spelt Kharsua or kharaswan, (Odia:ଖରସୁଆଁ) was a princely state in India during the British Raj. The state had a privy purse of 33,000 rupees. It was one of the Odia Princely states of India during the period of the British Raj and the major language spoken in the area is Odia.

Surguja State was one of the main princely states of Central India during the period of the British Raj, even though it was not entitled to any gun salute. Formerly, it was placed under the Central India Agency, but in 1905 it was transferred to the Eastern States Agency.

Sarangarh was a princely state in India during the British Raj ruled by a Raj Gond dynasty. The emblem of the state was a turtle.

Sambalpur State, also known as Hirakhand Kingdom, was a kingdom founded in 1570. It ruled over Western Odisha and Eastern Chhattisgarh in central-eastern India prior to the Maratha occupation in 1800 AD. From 1849 AD, it was integrated with British Raj as a British District. Its capital was present-day Sambalpur city in Western Odisha.

Kanker State was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj. Its last ruler, Maharajadhiraj Bhanu Pratap Deo, signed the accession to the Indian Union in 1947.

Rairakhol State was a minor princely state during the British Raj in India. It was one of the Chota Nagpur States and had its capital at Rairakhol (Redhakhol), located in the present-day Sambalpur district of Odisha. It had an area of 2,157 square kilometres (833 sq mi) and a population of 26,888 in 1901. The average revenue was Rs. 55,000 in 1904.

Raghogarh State, also known as Raghugarh and as Khichiwara, was a princely state of the Gwalior Residency, under the Central India Agency of the British Raj. It was a Thikana state of about 109 km2 with 19,446 inhabitants in 1901. The Parbati River marked the western border of the state. The capital was at Raghogarh in the present-day Guna district of Madhya Pradesh.