| Chota Nagpur Tributary States | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group of princely states of British India | |||||||||
| 1821–1947 | |||||||||
 | |||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
• 1881 | 41,580 km2 (16,050 sq mi) | ||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
• 1881 | 678,002 | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Sanads issued to Chota Nagpur rulers | 1821 | ||||||||
| 1947 | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand and Odisha | ||||||||


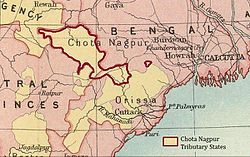
The Chota Nagpur Tributary States [1] or Chota Nagpur States were a group of small, non-salute states (minor princely states) during the British Raj in India, located on the Chota Nagpur Plateau. British suzerainty over the states was exercised through the government of the Bengal Presidency.
Contents
These states were nine in number and became part of the Indian states of Madhya Pradesh, Bihar and Odisha following Indian Independence. [2]