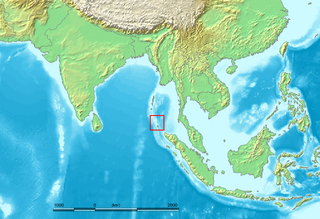
The Nicobar Islands are an archipelagic island chain in the eastern Indian Ocean. They are located in Southeast Asia, 150 kilometres (93 mi) northwest of Aceh on Sumatra, and separated from Thailand to the east by the Andaman Sea. Located 1,300 kilometres (810 mi) southeast of the Indian subcontinent, across the Bay of Bengal, they are part of India, as the Nicobar district within the union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
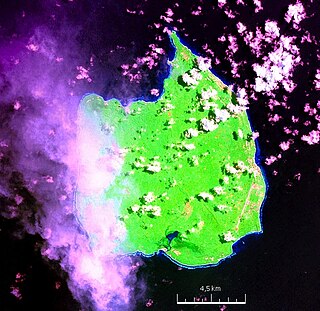
Car Nicobar is the northernmost of the Nicobar Islands. It is also one of three local administrative divisions of the Indian district of Nicobar, part of the Indian union territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Annual rainfall is 2800 millimetres.
Nancowry is an island in the central part of the Nicobar Islands chain, located in the northeast Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea.
Trinket Island is one of the 24 islands that make up the Nicobar Islands chain, located in the northeast Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea. It is located east of Kamorta Island.

The Nicobar Islands rain forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in the Nicobar Islands. The Nicobar Islands are in the Indian Ocean, lying north of Sumatra and south of the Andaman Islands. The islands are politically part of India, although physically closer to Southeast Asia. Millions of years of isolation from the mainland has given rise to a distinct flora and fauna, including many endemic species.
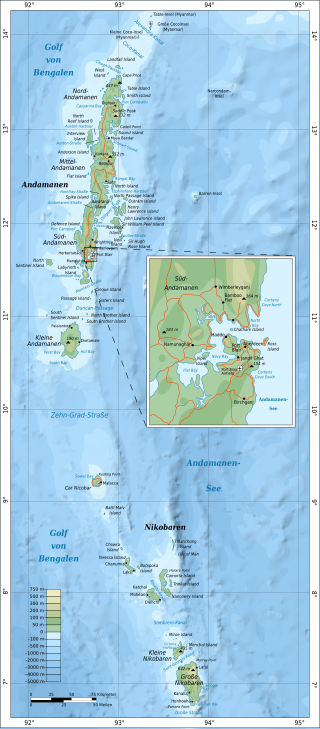
Nicobar district is one of three districts in the Indian union territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The district's administrative territory encompasses all of the Nicobar Islands, which are located in the Indian Ocean, between the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea. The headquarters of the district is the village of Malacca, located on the island of Car Nicobar.
The Austrian colonization of the Nicobar Islands involved a series of three separate attempts by the Habsburg monarchy, and later the Austrian Empire, to colonize and settle the Nicobar Islands. Only the first of these, launched in 1778, was successful. The second attempt was canceled, and the third, in 1886, was abandoned due to prior colonization by the British in 1868. The Nicobar Islands had been previously colonized by the Danish in 1756; the Danes abandoned the islands after multiple outbreaks of malaria, but continued to lay formal claim to the islands until 1848.
Kamorta or Kalatapu is a village on the Kamorta Island, in the Nicobar district of Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It is located in the Nancowry tehsil. This is also the home of Indian Naval Base named INS Kardip, which was commissioned in 1973.
Kakana is a village in the Nicobar district of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. It is located in the Car Nicobar tehsil.
Kakana is a village in the Nicobar district of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. It is located in the Nancowry tehsil.
Jhoola is a village in the Nicobar district of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. It is located in the Nancowry tehsil.
Munak is a village in the Nicobar district of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. It is located in the Nancowry tehsil.
Pilpilow is a village in the Nicobar district of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. It is located in the Nancowry tehsil.
Payuha is a village in the Nicobar district of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. It is located in the Nancowry tehsil.
Ramzoo is a village in the Nicobar district of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. It is located in the Nancowry tehsil.
Tapong is a village in the Nicobar district of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. It is located on the Nancowry Island, around 10 km from the Champin village, and comes under the administration of the Nancowry tehsil.
Alukian or Alhukheck is a village in the Nicobar district of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. It is located in the Nancowry tehsil, on the Kamorta Island.
Nancowry Subdivision is one of three local administrative divisions of the Indian district of Nicobar, part of the Indian union territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands.

ISO 7010 is an International Organization for Standardization technical standard for graphical hazard symbols on hazard and safety signs, including those indicating emergency exits. It uses colours and principles set out in ISO 3864 for these symbols, and is intended to provide "safety information that relies as little as possible on the use of words to achieve understanding."






