RAF Mount Pleasant is a Royal Air Force station in the British Overseas Territory of the Falkland Islands. The airfield goes by the motto of "Defend the right" and is part of the British Forces South Atlantic Islands (BFSAI). Home to between 1,000 and 2,000 British military personnel, it is about 33 miles (53 km) southwest of Stanley, the capital of the Falklands—on the island of East Falkland. The world's longest corridor, 2,600 feet (800 m) long, links the barracks, messes, and recreational and welfare areas of the station, and was nicknamed the "Death Star Corridor" by personnel.

The Indian Air Force (IAF) is the air arm of the Indian Armed Forces. Its primary mission is to secure Indian airspace and to conduct aerial warfare during armed conflicts. It was officially established on 8 October 1932 as an auxiliary air force of the British Empire which honoured India's aviation service during World War II with the prefix Royal. After India gained independence from United Kingdom in 1947, the name Royal Indian Air Force was kept and served in the name of the Dominion of India. With the transition to a republic in 1950, the prefix Royal was removed.
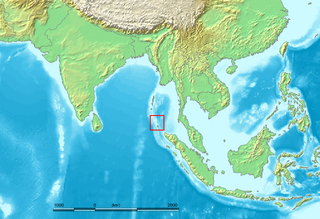
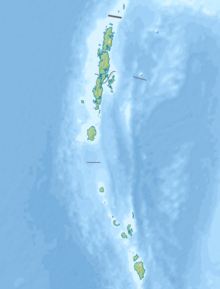
The Nicobar Islands are an archipelagic island chain in the eastern Indian Ocean. They are located in Southeast Asia, 150 kilometres (93 mi) northwest of Aceh on Sumatra, and separated from Thailand to the east by the Andaman Sea. Located 1,300 kilometres (810 mi) southeast of the Indian subcontinent, across the Bay of Bengal, they are part of India, as the Nicobar district within the union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.

According to official estimates in India, 10,749 people were killed, 5,640 people were missing and thousands of people became homeless when a tsunami triggered by the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake near the Indonesian island of Sumatra struck the southern coast on 26 December 2004. The earthquake registered 9.1–9.3 Mw and was the largest in five decades. It was followed by strong aftershocks on the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The death toll of the earthquake was 1,500 people.

North Sentinel Island is one of the Andaman Islands, an Indian archipelago in the Bay of Bengal which also includes South Sentinel Island. It is home to the Sentinelese, an indigenous people in voluntary isolation who have defended, often by force, their protected isolation from the outside world. The island is about 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) long and 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) wide, and its area is approximately 60 square kilometres (23 sq mi).
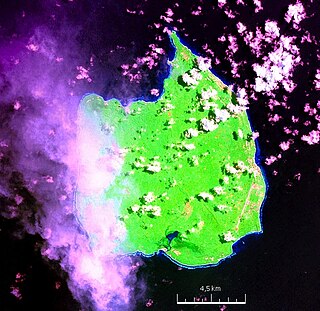
Car Nicobar is the northernmost of the Nicobar Islands. It is also one of three local administrative divisions of the Indian district of Nicobar, part of the Indian union territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Annual rainfall is 2800 millimetres.

Port Blair is the capital city of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a union territory of India in the Bay of Bengal. It is also the local administrative sub-division (tehsil) of the islands, the headquarters for the district of South Andaman and is the territory's only notified town.
Great Nicobar is the southernmost and largest of the Nicobar Islands of India, north of Sumatra.
Indira Point, the southernmost point of India's territory, is a village in the Nicobar district at Great Nicobar Island of Andaman and Nicobar Islands in India. It is located in the Great Nicobar tehsil.

Veer Savarkar International Airport is a domestic airport located 2 km (1.2 mi) south of Port Blair and is the main airport of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Originally known as "Port Blair Airport", it was renamed in 2002 after Vinayak Damodar Savarkar, who had been detained in the Cellular Jail in the city for 11 years during India’s freedom struggle. It operates as a civil enclave, sharing airside facilities with INS Utkrosh of the Indian Navy.

Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar International Airport is an international airport serving the city of Nagpur, Maharashtra, India. The airport is located at Sonegaon, 8 km (5 mi) southwest of Nagpur. The airport covers an area of 1,355 acres. In 2005, it was named after B. R. Ambedkar, the chief architect of the Constitution of India and one of the founding fathers of the Republic of India. The airport handles around 8,500 passengers per day and caters to four domestic airlines and two international airlines connecting Nagpur to Sharjah, Doha, and 14 domestic destinations. The airport spread over 1,460 acres is also home to Nagpur Air Force Station of the Indian Air Force. Growth in passenger traffic is fuelled by passengers traveling to and from the state capital Mumbai, located over 700 km (378 mi) away. The airport has one terminal and has two aerobridges.

Jodhpur Airport is a domestic airport and an Indian Air Force base serving the city of Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India. It is operated by the Airports Authority of India (AAI) and shares its airside with the Jodhpur Air Force Station of the Indian Air Force.
The Andaman and Nicobar Command (ANC) is the only tri-service theater command of the Indian Armed Forces, based at Port Blair in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a Union Territory of India. It was created in 2001 to safeguard India's strategic interests in Southeast Asia and the Strait of Malacca by increasing rapid deployment of military assets in the region. It provides logistical and administrative support to naval ships which are sent on deployment to East Asia and the Pacific Ocean.

Agra Airport or Pandit Deen Dayal Upadhyay Airport, also known as Kheria Airport, is a domestic airport and an Indian Air Force base serving the city of Agra, in the state of Uttar Pradesh, India. The air force station is one of the largest airbases of the Indian Air Force. On 15 August 2007, the airbase celebrated its sixtieth anniversary.

Kalaikunda Air Force Station (ICAO: VEDX) is an Indian Air Force Base in Kharagpur, located in the West Midnapur district of the state of West Bengal. It was the home of No. 18 Squadron IAF, the Flying Bullets. The squadron flew the Indian license-built Mikoyan MiG-27ML till its decommissioning in April 2016. A squadron of Su-30 MKIs is now at the base.
Operation Sea Waves was a disaster relief operation undertaken by the Indian Armed Forces in the aftermath of the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami. Sea Waves was focused on rescue and relief efforts on the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
INS Utkrosh, is an Indian naval air station under the joint-services Andaman and Nicobar Command of the Indian Armed Forces. It is located near naval base INS Jarawa, on Port Blair in the Andaman & Nicobar Islands.

INS Baaz is an Indian naval air station under the joint-services Andaman and Nicobar Command (ANC) of the Indian Armed Forces. It is located near Campbell Bay, on Great Nicobar island in the Andaman & Nicobar Islands. It is the southernmost air station of the Indian Armed Forces. It overlooks the Strait of Malacca as well as the Six Degree channel between Great Nicobar and the Indonesian island of Sumatra.
Carnicobar (Iaf) Code: VOCX* IATA Code: CBD Lat,Lon: 9.1525,92.8196 State: India Elevation: 5 City: Iaf Camp FIR: VOMF Schedule: No