
Eurypterids, often informally called sea scorpions, are a group of extinct arthropods that form the order Eurypterida. The earliest known eurypterids date to the Darriwilian stage of the Ordovician period 467.3 million years ago. The group is likely to have appeared first either during the Early Ordovician or Late Cambrian period. With approximately 250 species, the Eurypterida is the most diverse Paleozoic chelicerate order. Following their appearance during the Ordovician, eurypterids became major components of marine faunas during the Silurian, from which the majority of eurypterid species have been described. The Silurian genus Eurypterus accounts for more than 90% of all known eurypterid specimens. Though the group continued to diversify during the subsequent Devonian period, the eurypterids were heavily affected by the Late Devonian extinction event. They declined in numbers and diversity until becoming extinct during the Permian–Triassic extinction event 251.9 million years ago.

Stylonurina is one of two suborders of eurypterids, a group of extinct arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". Members of the suborder are collectively and informally known as "stylonurine eurypterids" or "stylonurines". They are known from deposits primarily in Europe and North America, but also in Siberia.

Slimonia is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Slimonia have been discovered in deposits of Silurian age in South America and Europe. Classified as part of the family Slimonidae alongside the related Salteropterus, the genus contains three valid species, S. acuminata from Lesmahagow, Scotland, S. boliviana from Cochabamba, Bolivia and S. dubia from the Pentland Hills of Scotland and one dubious species, S. stylops, from Herefordshire, England. The generic name is derived from and honors Robert Slimon, a fossil collector and surgeon from Lesmahagow.

Hughmilleria is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Hughmilleria have been discovered in deposits of the Silurian age in China and the United States. Classified as part of the basal family Hughmilleriidae, the genus contains three species, H. shawangunk from the eastern United States, H. socialis from Pittsford, New York, and H. wangi from Hunan, China. The genus is named in honor of the Scottish geologist Hugh Miller.

Drepanopterus is an extinct genus of eurypterid and the only member of the family Drepanopteridae within the Mycteropoidea superfamily. There are currently three species assigned to the genus. The genus has historically included more species, with nine species having been associated with the genus Drepanopterus. Five of these have since been proven to be synonyms of pre-existing species, assigned to their own genera, or found to be based on insubstantial fossil data. The holotype of one species proved to be a lithic clast.

Nanahughmilleria is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Nanahughmilleria have been discovered in deposits of Devonian and Silurian age in the United States, Norway, Russia, England and Scotland, and have been referred to several different species.

Onychopterella is a genus of predatory eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Onychopterella have been discovered in deposits from the Late Ordovician to the Late Silurian. The genus contains three species: O. kokomoensis, the type species, from the Early Pridoli epoch of Indiana; O. pumilus, from the Early Llandovery epoch of Illinois, both from the United States; and O. augusti, from the Late Hirnantian to Early Rhuddanian stages of South Africa.
Pittsfordipterus is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Pittsfordipterus is classified as part of the family Adelophthalmidae, the only clade in the derived ("advanced") Adelophthalmoidea superfamily of eurypterids. Fossils of the single and type species, P. phelpsae, have been discovered in deposits of Silurian age in Pittsford, New York state. The genus is named after Pittsford, where the two only known specimens have been found.
Salteropterus is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Salteropterus have been discovered in deposits of Late Silurian age in Britain. Classified as part of the family Slimonidae, the genus contains one known valid species, S. abbreviatus, which is known from fossils discovered in Herefordshire, England, and a dubious species, S. longilabium, with fossils discovered in Leintwardine, also in Herefordshire. The generic name honours John William Salter, who originally described S. abbreviatus as a species of Eurypterus in 1859.

Erettopterus is a genus of large predatory eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Erettopterus have been discovered in deposits ranging from Early Silurian to the Early Devonian, and have been referred to several different species. Fossils have been recovered from two continents; Europe and North America. The genus name is composed by the Ancient Greek words ἐρέττω (eréttō), which means "rower", and πτερόν (pterón), which means "wing", and therefore, "rower wing".

Pterygotidae is a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. They were members of the superfamily Pterygotioidea. Pterygotids were the largest known arthropods to have ever lived with some members of the family, such as Jaekelopterus and Acutiramus, exceeding 2 metres (6.6 ft) in length. Their fossilized remains have been recovered in deposits ranging in age from 428 to 372 million years old.

Stylonuridae is a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". The family is one of two families contained in the superfamily Stylonuroidea, which in turn is one of four superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Stylonurina.

The Rhenopteridae are a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". The family is the only family currently contained in the superfamily Rhenopteroidea, one of four superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Stylonurina.

Stylonuroidea is an extinct superfamily of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". It is one of four superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Stylonurina.

The Parastylonuridae are a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". The family is one of two families contained in the superfamily Stylonuroidea, which in turn is one of four superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Stylonurina.
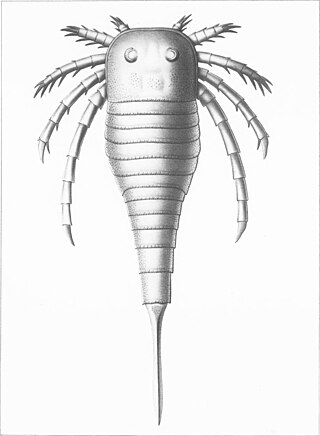
The Kokomopteridae are a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". The family is one of two families contained in the superfamily Kokomopteroidea, which in turn is one of four superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Stylonurina.
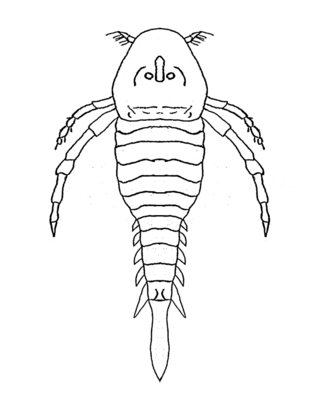
The Hardieopteridae are a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". The family is one of two families contained in the superfamily Kokomopteroidea, which in turn is one of four superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Stylonurina. Hardieopterids have been recovered from deposits of Early Silurian to Late Devonian age in the United States and the United Kingdom.

Adelophthalmidae is a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Adelophthalmidae is the only family classified as part of the superfamily Adelophthalmoidea, which in turn is classified within the infraorder Diploperculata in the suborder Eurypterina.

Mycteropoidea is an extinct superfamily of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". It is one of four superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Stylonurina. Mycteropoids have been recovered from Europe, Russia, South America and South Africa. Mycteropoid specimens are often fragmentary, making it difficult to establish relationships between the included taxa. Only two mycteropoid taxa are known from reasonable complete remains, Hibbertopterus scouleri and H. wittebergensis.

Hughmilleriidae is a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. The hughmilleriids were the most basal members of the superfamily Pterygotioidea, in contrast with the more derived families Pterygotidae and Slimonidae. Despite their classification as pterygotioids, the hughmilleriids possessed several characteristics shared with other eurypterid groups, such as the lanceolate telson.



















