Stylonurina is one of two suborders of eurypterids, a group of extinct arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". Members of the suborder are collectively and informally known as "stylonurine eurypterids" or "stylonurines". They are known from deposits primarily in Europe and North America, but also in Siberia.

Hughmilleria is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Hughmilleria have been discovered in deposits of the Silurian age in China and the United States. Classified as part of the basal family Hughmilleriidae, the genus contains three species, H. shawangunk from the eastern United States, H. socialis from Pittsford, New York, and H. wangi from Hunan, China. The genus is named in honor of the Scottish geologist Hugh Miller.

Brachyopterus is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid of the family Rhenopteridae. It is one of the earliest known eurypterids, having been recovered from Middle Ordovician deposits in Montgomeryshire, Wales. Though other species have been assigned to it in the past, Brachyopterus is today recognized as containing one valid species, B. stubblefieldi.

Drepanopterus is an extinct genus of eurypterid and the only member of the family Drepanopteridae within the Mycteropoidea superfamily. There are currently three species assigned to the genus. The genus has historically included more species, with nine species having been associated with the genus Drepanopterus. Five of these have since been proven to be synonyms of pre-existing species, assigned to their own genera, or found to be based on insubstantial fossil data. The holotype of one species proved to be a lithic clast.

Dorfopterus is a genus of eurypterid, a group of extinct aquatic arthropods. Only one fossil of the single and type species, D. angusticollis, has been discovered in deposits of the Early Devonian period in the Beartooth Butte Formation in Wyoming, in the United States. The first half of the name of the genus honors the discoverer of this formation, Erling Dorf, while the second half consists in the Ancient Greek word πτερόν (pteron), meaning "wing". The species name angusticollis is composed by the Latin words angustus ("narrow") and collum ("neck").
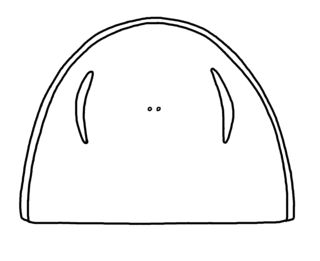
Pittsfordipterus is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Pittsfordipterus is classified as part of the family Adelophthalmidae, the only clade in the derived ("advanced") Adelophthalmoidea superfamily of eurypterids. Fossils of the single and type species, P. phelpsae, have been discovered in deposits of Silurian age in Pittsford, New York state. The genus is named after Pittsford, where the two only known specimens have been found.

Parahughmilleria is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Parahughmilleria have been discovered in deposits of the Devonian and Silurian age in the United States, Canada, Russia, Germany, Luxembourg and Great Britain, and have been referred to several different species. The first fossils of Parahughmilleria, discovered in the Shawangunk Mountains in 1907, were initially assigned to Eurypterus. It would not be until 54 years later when Parahughmilleria would be described.

The Rhenopteridae are a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". The family is the only family currently contained in the superfamily Rhenopteroidea, one of four superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Stylonurina.

Mycteroptidae are a family of eurypterids, a group of extinct chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". The family is one of three families contained in the superfamily Mycteropoidea, which in turn is one of four superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Stylonurina.

Stylonuroidea is an extinct superfamily of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". It is one of four superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Stylonurina.

The Parastylonuridae are a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". The family is one of two families contained in the superfamily Stylonuroidea, which in turn is one of four superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Stylonurina.
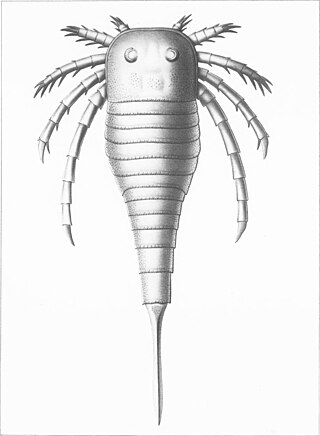
Kokomopteroidea is an extinct superfamily of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". It is one of four superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Stylonurina. Kokomopteroids have been recovered from deposits of Early Silurian to Late Devonian age in the United States and the United Kingdom.

The Kokomopteridae are a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". The family is one of two families contained in the superfamily Kokomopteroidea, which in turn is one of four superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Stylonurina.
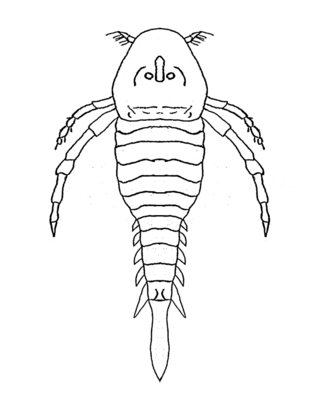
The Hardieopteridae are a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". The family is one of two families contained in the superfamily Kokomopteroidea, which in turn is one of four superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Stylonurina. Hardieopterids have been recovered from deposits of Early Silurian to Late Devonian age in the United States and the United Kingdom.

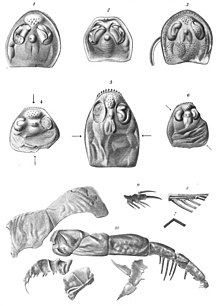
Hibbertopteridae is a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. They were members of the superfamily Mycteropoidea. Hibbertopterids were large, broad and heavy animals unlike virtually every other group of eurypterids, which are commonly streamlined and lightweight. Their bizarre morphology is so unusual that they in the past have been thought to represent an entirely distinct order of chelicerates. Fossils of the family first appear in deposits of Middle Devonian age and the last known fossils representing hibbertopterids are known from deposits of Late Permian age. The hibbertopterids represent the last known living eurypterids, going extinct during the Permian–Triassic extinction event or shortly before.

Adelophthalmidae is a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Adelophthalmidae is the only family classified as part of the superfamily Adelophthalmoidea, which in turn is classified within the infraorder Diploperculata in the suborder Eurypterina.

Eurypterina is one of two suborders of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". Eurypterine eurypterids are sometimes informally known as "swimming eurypterids". They are known from fossil deposits worldwide, though primarily in North America and Europe.

Mycteropoidea is an extinct superfamily of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". It is one of four superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Stylonurina. Mycteropoids have been recovered from Europe, Russia, South America and South Africa. Mycteropoid specimens are often fragmentary, making it difficult to establish relationships between the included taxa. Only two mycteropoid taxa are known from reasonable complete remains, Hibbertopterus scouleri and H. wittebergensis.

Hughmilleriidae is a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. The hughmilleriids were the most basal members of the superfamily Pterygotioidea, in contrast with the more derived families Pterygotidae and Slimonidae. Despite their classification as pterygotioids, the hughmilleriids possessed several characteristics shared with other eurypterid groups, such as the lanceolate telson.

Slimonidae is a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Slimonids were members of the superfamily Pterygotioidea and the family most closely related to the derived pterygotid eurypterids, which are famous for their cheliceral claws and great size. Many characteristics of the Slimonidae, such as their flattened and expanded telsons, support a close relationship between the two groups.