| Ctenopterus Temporal range: | |
|---|---|
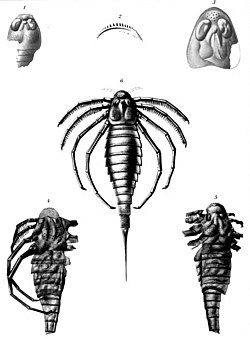 | |
| Restoration and fossils | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Chelicerata |
| Order: | † Eurypterida |
| Family: | † Stylonuridae |
| Subfamily: | † Laurieipterinae |
| Genus: | † Ctenopterus Clarke & Ruedemann, 1912 |
| Species: | †C. cestrotus |
| Binomial name | |
| †Ctenopterus cestrotus (Clarke, 1907) | |
Ctenopterus is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid of the family Stylonuridae. It contains only one species, Ctenopterus cestrotus from the Early Silurian of Otisville, New York, United States. [1]

