
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase catalyzes the ATP-dependent synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate from glutamine or ammonia and bicarbonate. This enzyme catalyzes the reaction of ATP and bicarbonate to produce carboxy phosphate and ADP. Carboxy phosphate reacts with ammonia to give carbamic acid. In turn, carbamic acid reacts with a second ATP to give carbamoyl phosphate plus ADP.
The crotonase family comprises mechanistically diverse proteins that share a conserved trimeric quaternary structure, the core of which consists of 4 turns of a (beta/beta/alpha)n superhelix.
In enzymology, a 4-deoxy-L-threo-5-hexosulose-uronate ketol-isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an arabinose isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glucuronate isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a L-arabinose isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a L-rhamnose isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a L-ribulose-5-phosphate 4-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the interconversion of ribulose 5-phosphate and xylulose 5-phosphate in the oxidative phase of the Pentose phosphate pathway.

In enzymology, a phosphoribosylanthranilate isomerase (PRAI) is an enzyme that catalyzes the third step of the synthesis of the amino acid tryptophan.
In enzymology, a S-methyl-5-thioribose-1-phosphate isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a phenylalanine—tRNA ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In Enzymology, a dUTP diphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.23) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The aldo-keto reductase family is a family of proteins that are subdivided into 16 categories; these include a number of related monomeric NADPH-dependent oxidoreductases, such as aldehyde reductase, aldose reductase, prostaglandin F synthase, xylose reductase, rho crystallin, and many others.

In molecular biology, chaperone DnaJ, also known as Hsp40, is a molecular chaperone protein. It is expressed in a wide variety of organisms from bacteria to humans.
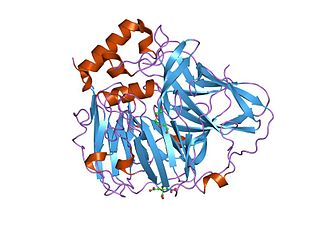
In molecular biology, multicopper oxidases are enzymes which oxidise their substrate by accepting electrons at a mononuclear copper centre and transferring them to a trinuclear copper centre; dioxygen binds to the trinuclear centre and, following the transfer of four electrons, is reduced to two molecules of water. There are three spectroscopically different copper centres found in multicopper oxidases: type 1, type 2 and type 3. Multicopper oxidases consist of 2, 3 or 6 of these homologous domains, which also share homology with the cupredoxins azurin and plastocyanin. Structurally, these domains consist of a cupredoxin-like fold, a beta-sandwich consisting of 7 strands in 2 beta-sheets, arranged in a Greek-key beta-barrel. Multicopper oxidases include:
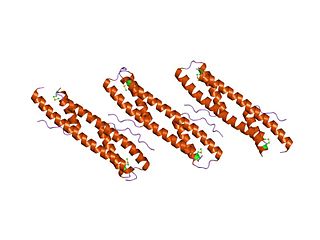
The enzyme exodeoxyribonuclease VII is a bacterial exonuclease enzyme. It is composed of two nonidentical subunits; one large subunit and 4 small ones. that catalyses exonucleolytic cleavage in either 5′- to 3′- or 3′- to 5′-direction to yield nucleoside 5′-phosphates. The large subunit also contains an N-terminal OB-fold domain that binds to nucleic acids.

In molecular biology the FGGY carbohydrate kinase family is a family of evolutionarily related carbohydrate kinase enzymes. These enzymes include L-fuculokinase EC 2.7.1.51 ; gluconokinase EC 2.7.1.12 ; glycerol kinase EC 2.7.1.30 ; xylulokinase EC 2.7.1.17 ; D-ribulose kinase EC 2.7.1.47 ; and L-xylulose kinase EC 2.7.1.53. These enzymes are proteins of from 480 to 520 amino acid residues.

In molecular biology, the KduI/IolB isomerase family is a family of isomerase enzymes that includes 4-deoxy-L-threo-5-hexosulose-uronate ketol-isomerase (KduI) and 5-deoxy-glucuronate isomerase (IolB).

Fumarate reductase (quinol) (EC 1.3.5.4, QFR,FRD, menaquinol-fumarate oxidoreductase, quinol:fumarate reductase) is an enzyme with systematic name succinate:quinone oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyzes the following chemical reaction:
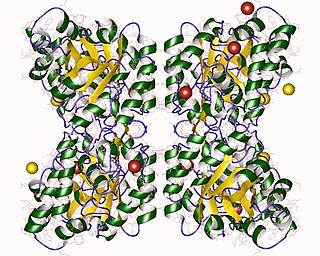
4-Hydroxy-tetrahydrodipicolinate synthase (EC 4.3.3.7, dihydrodipicolinate synthase, dihydropicolinate synthetase, dihydrodipicolinic acid synthase, L-aspartate-4-semialdehyde hydro-lyase (adding pyruvate and cyclizing), dapA (gene)) is an enzyme with the systematic name L-aspartate-4-semialdehyde hydro-lyase (adding pyruvate and cyclizing; (4S)-4-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-(2S)-dipicolinate-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

















