
Rolf Singer was a German mycologist and taxonomist of gilled mushrooms (agarics).

Agaricus bisporus, commonly known as the cultivated mushroom, is a basidiomycete mushroom native to grasslands in Eurasia and North America. It is cultivated in more than 70 countries and is one of the most commonly and widely consumed mushrooms in the world. It has two color states while immature – white and brown – both of which have various names, with additional names for the mature state, such as chestnut, portobello, portabellini, button and champignon de Paris.

Amanita porphyria, also known as the grey veiled amanita or the porphyry amanita, is a fairly common, inedible mushroom of the genus Amanita found in Europe and North America.

Suillus granulatus is a pored mushroom of the genus Suillus in the family Suillaceae. It is similar to the related S. luteus, but can be distinguished by its ringless stalk. Like S. luteus, it is an edible mushroom that often grows in a symbiosis (mycorrhiza) with pine. It has been commonly known as the weeping bolete, or the granulated bolete. Previously thought to exist in North America, that species has now been confirmed to be the rediscovered Suillus weaverae.

Caloboletus calopus, commonly known as the bitter bolete, bitter beech bolete or scarlet-stemmed bolete, is a fungus of the bolete family, found in Asia, Northern Europe and North America. Appearing in coniferous and deciduous woodland in summer and autumn, the stout fruit bodies are attractively coloured, with a beige to olive cap up to 15 cm (6 in) across, yellow pores, and a reddish stipe up to 15 cm (6 in) long and 5 cm (2 in) wide. The pale yellow flesh stains blue when broken or bruised.

Neoboletus luridiformis, also previously known as Boletus luridiformis and (invalidly) as Boletus erythropus, is a fungus of the bolete family, all of which produce mushrooms with tubes and pores beneath their caps. It is found in Northern Europe and North America, and is commonly known as the scarletina bolete, for its red pores, which are yellow when young. Other common names include the red foot bolete, dotted stemmed bolete, or dotted stem bolete.

Hygrophoropsis aurantiaca, commonly known as the false chanterelle, is a species of fungus in the family Hygrophoropsidaceae. It is found across several continents, growing in woodland and heathland, and sometimes on woodchips used in gardening and landscaping. Fruit bodies (mushrooms) are yellow–orange, with a funnel-shaped cap up to 8 cm across that has a felt-like surface. The thin, often forked gills on the underside of the cap run partway down the length of the otherwise smooth stipe. Reports on the mushroom's edibility vary – it is considered poisonous, but has historically been eaten in parts of Europe and the Americas.

Narcisse Théophile Patouillard was a French pharmacist and mycologist.

Lacrymaria is a genus of fungi in the family Psathyrellaceae. A 2008 estimate placed 14 species in the widespread genus.

Lactifluus volemus, formerly known as Lactarius volemus, and commonly known as the weeping milk cap or bradley, is a species of fungus in the family Russulaceae. Phylogenetic analysis suggests that L. volemus represents several species or subspecies, rather than a single taxon.
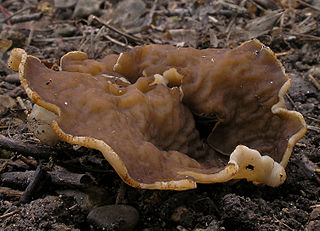
Disciotis venosa, commonly known as the bleach cup, veiny cup fungus, or the cup morel is a species of fungus in the family Morchellaceae. Fruiting from April, they are often difficult to locate because of their nondescript brown color.

Agaricus silvaticus, otherwise known as the scaly wood mushroom, blushing wood mushroom, or pinewood mushroom, is a species of mushroom often found in groups in coniferous forests from early summer, or September through to November in Europe, North Africa and North America.

Cyanoboletus pulverulentus, commonly known as the ink stain bolete, is an edible bolete mushroom. It is found in deciduous and mixed forests, particularly on moist soil on slopes and under beech and oak trees. A common species, it is found in northern Asia, Europe, North Africa, Central and northern South America, and eastern North America. All parts of the mushroom will stain dark bluish-black after handling. A recent study has revealed this mushroom hyperaccumulates arsenic and therefore it's consumption should be limited.

Protostropharia semiglobata, commonly known as the dung roundhead, the halfglobe mushroom, or the hemispherical stropharia, is an agaric fungus of the family Strophariaceae. A common and widespread species with a cosmopolitan distribution, the fungus produces mushrooms on the dung of various wild and domesticated herbivores. The mushrooms have hemispherical straw yellow to buff-tan caps measuring 1–4 cm (0.4–1.6 in), greyish gills that become dark brown in age, and a slender, smooth stem 3–12 cm (1.2–4.7 in) long with a fragile ring.

Cortinarius iodes, commonly known as the spotted cort or the viscid violet cort, is a species of agaric fungus in the family Cortinariaceae. The fruit bodies have small, slimy, purple caps up to 6 cm (2.4 in) in diameter that develop yellowish spots and streaks in maturity. The gill color changes from violet to rusty or grayish brown as the mushroom matures. The species range includes eastern North America, Central America, northern South America, and northern Asia, where it grows on the ground in a mycorrhizal association with deciduous trees. The mushroom is not recommended for consumption. Cortinarius iodeoides, one of several potential lookalike species, can be distinguished from C. iodes by its bitter-tasting cap cuticle.

Morchella deliciosa is a species of edible fungus in the family Morchellaceae. It was first described scientifically by Elias Magnus Fries in 1822. It is a European species, although the name has erroneously been applied to morphologically similar North American morels.

Leucoagaricus rubrotinctus, commonly known as the red-eyed parasol, is a widespread species of fungus in the family Agaricaceae. It was described as new to science in 1884 by American mycologist Charles Horton Peck as Agaricus rubrotinctus. Rolf Singer transferred it to the genus Leucoagaricus in 1948. The fungus may be a complex of several closely related species. It is inedible.

Imleria badia, commonly known as the bay bolete, is an edible, pored mushroom found in Eurasia and North America, where it grows in coniferous or mixed woods on the ground or on decaying tree stumps, sometimes in prolific numbers. Both the common and scientific names refer to the bay- or chestnut-coloured cap, which is almost spherical in young specimens before broadening and flattening out to a diameter up to 15 cm (6 in). On the cap underside are small yellowish pores that turn dull blue-grey when bruised. The smooth, cylindrical stipe, measuring 4–9 cm long by 1–2 cm thick, is coloured like the cap, but paler. Some varieties have been described from eastern North America, differing from the main type in both macroscopic and microscopic morphology.

Gloioxanthomyces nitidus, commonly known as the shining waxcap, is a species of fungus in the family Hygrophoraceae.

Phlebia tremellosa, commonly known as trembling Merulius or jelly rot, is a species of fungus in the family Meruliaceae. It is a common and widely distributed wood-decay fungus that grows on the rotting wood of both hardwood and conifer plants.




















