See also
| External videos | |
|---|---|
Leonard Hayflick | |
|---|---|
| Born | May 20, 1928 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States |
| Alma mater | |
| Known for |
|
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | |
| Institutions | |
Leonard Hayflick (born 20 May 1928) is a Professor of Anatomy at the UCSF School of Medicine, and was Professor of Medical Microbiology at Stanford University School of Medicine. He is a past president of the Gerontological Society of America and was a founding member of the council of the National Institute on Aging (NIA). The recipient of a number of research prizes and awards, including the 1991 Sandoz Prize for Gerontological Research, he has studied the aging process for more than fifty years. He is known for discovering that normal human cells divide for a limited number of times in vitro [1] (refuting the contention by Alexis Carrel that normal body cells are immortal). This is known as the Hayflick limit. His discoveries overturned a 60-year old dogma that all cultured cells are immortal. Hayflick demonstrated that normal cells have a memory and can remember at what doubling level they have reached. He demonstrated that his normal human cell strains were free from contaminating viruses. His cell strain WI-38 soon replaced primary monkey kidney cells and became the substrate for the production of most of the world's human virus vaccines. Hayflick discovered that the etiological agent of primary atypical pneumonia (also called "walking pneumonia") was not a virus as previously believed. He was the first to cultivate the causative organism called a mycoplasma, the smallest free-living organism, which Hayflick isolated on a unique culture medium that bears his name. He named the organism Mycoplasma pneumoniae .
In 1959, Hayflick developed the first inverted microscope for use in cell culture research. To this day, all inverted microscopes used in cell culture laboratories worldwide are descended from this prototype. His microscope was accessioned by the Smithsonian Institution in 2009.
Hayflick developed the first practical method for producing powdered cell culture media in 1965. This method is now used worldwide for the production of many tons of powdered media annually for use in research laboratories and commercial production facilities. The technique is not patented and Hayflick receives no remuneration from this invention.
Hayflick is the author of the book, How and Why We Age, published in August 1994 by Ballantine Books, New York City and available since 1996 as a paperback. [2] This book has been translated into nine languages and is published in Brazil, the Czech Republic, Germany, Hungary, Israel, Japan, Poland, Russia, and Spain. It was a selection of the Book of the Month Club and has sold over 50,000 copies worldwide.
Hayflick and his associates have vehemently condemned "anti-aging medicine" and criticized organizations such as the American Academy of Anti-Aging Medicine. [3] Hayflick has written numerous articles criticizing both the feasibility and desirability of human life extension, [4] [5] which have provoked responses critical of his views. [6]
Leonard Hayflick was born 20 May 1928 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He received his Ph.D. at the University of Pennsylvania in 1956. After receiving a post-doctoral fellowship for study at the University of Texas Medical Branch in Galveston under the tutelage of the renowned cell culturist Charles M. Pomerat (1905–1964), [7] he returned to Philadelphia, where he spent ten years as an Associate Member of the Wistar Institute and two years as an Assistant Professor of Research Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
In 1968, Hayflick was appointed Professor of Medical Microbiology at the Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California. Hayflick resigned from Stanford in 1976 in protest to the behavior of a few of its administrators who were later shown to have wrongly accepted the beliefs of an NIH accountant who was unable to understand the unique concept of title to a self-duplicating biological system. Hayflick sued the NIH, who later agreed that the issue was in dispute. [8] [9] The behavior of Stanford and the NIH was later condemned by 85 prominent biologists who viewed him as having been "exonerated" by subsequent events. [10] [11] In 1982 he moved to the University of Florida, Gainesville, where he became Director of the Center for Gerontological Studies and Professor of Zoology in the College of Liberal Arts and Sciences and Professor of Microbiology and Immunology in the College of Medicine.
In 1988, Hayflick joined the faculty of the University of California, San Francisco, where he is currently Professor of Anatomy. Hayflick is a member of numerous national and international scientific and public boards of directors and committees. He is now, or has been, on the Editorial Boards of more than ten professional journals. Hayflick was Editor-in-Chief of the international journal "Experimental Gerontology" for 13 years.
He is a member of twenty scientific and professional societies in which he has held several high offices including President of the Gerontological Society of America from 1982 to 1983. He was a founding member of the Council of the National Institute on Aging, NIH, and chairman of its executive committee. He was a consultant to the National Cancer Institute and the World Health Organization, and is now a member of several scientific advisory boards. He was Chairman of the Scientific Review Board of the American Federation for Aging Research where he was also a vice president and a Member of the board of directors. He was also recruited by Michael D. West, founder of Geron (Nasdaq : GERN) and current CEO of BioTime, to join the company's Scientific and Clinical Advisory Board, on which he served from 1991–2000. Hayflick was also a consultant at Genentech from a year after its founding and for the next 25 years. He developed their technology for growing animal cells in fermentation tanks in which most of their products were produced.
Hayflick is one of several prominent biologists featured in the 1995 science documentary Death by Design: The Life and Times of Life and Times.
Hayflick is known for his research in cell biology, virus vaccine development, and mycoplasmology. In 1962 he discovered that, contrary to the prevailing belief at the time, cultured normal human and animal cells have a limited capacity for replication. This discovery, known as the Hayflick limit, overturned a long-held belief bolstered by Alexis Carrel's work in the early 20th century that claimed that normal cells would proliferate continuously in culture. Hayflick found that only cancer cells are immortal and that normal cells have a mechanism for remembering what replication level they are at. He interpreted his finding that normal cells are mortal, to be an indication of aging at the cellular level. Hayflick demonstrated for the first time that mortal (normal) and immortal (malignant) mammalian cells existed.
Hayflick developed the first normal human diploid cell strains for studies on human aging and for research use throughout the world. Prior to his seminal research, all cultured cell lines were immortal and aneuploid. One of these new cell strains, developed by Hayflick and his colleague Paul Moorhead at the Wistar Institute in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, called WI-38, has become the most widely used and highly characterized normal human cell population in the world. Hayflick had found that his normal cell strain WI-38 was capable of growing all of the then known human viruses. He hypothesized that because WI-38 was free from contaminating viruses, it could replace the then widely used primary monkey kidney cells, which contained several dangerous contaminating viruses. Indeed, WI-38 became used worldwide for human virus vaccine manufacture, to the benefit of billions of people. [12]
Hayflick produced the first oral polio vaccine ever made on his normal human cell strain WI-38. WI-38 is now used for the production of all of the Rubella Virus vaccine used in the Western Hemisphere. WI-38, or new diploid cell strains, are used today for the manufacture of most human virus vaccines produced throughout the world including those for poliomyelitis, rubella, rubeola, varicella, mumps, rabies, adenoviruses and hepatitis A. Over one billion vaccinees have received vaccines produced on WI-38 or foreign versions of Hayflick's original WI-38. [12]
Hayflick is also known for his discovery of the cause of primary atypical pneumonia ("walking pneumonia") in humans. [13] The etiological agent was first thought to be a virus, but Hayflick showed that it was, in fact, a mycoplasma, a member of the smallest free-living class of microorganisms. The etiological agent was named by him as Mycoplasma pneumoniae , and was first grown by Hayflick on a medium he developed and that bears his name. It is now used worldwide for mycoplasma isolation and research.
Hayflick is the recipient of more than twenty-five major awards including the $20,000 Brookdale Award and the Kleemeier Award from the Gerontological Society of America, the Biomedical Sciences and Aging Award from the University of Southern California, The Karl August Forster Lectureship of the Academy of Sciences and Literature and the University of Mainz, Germany, the Samuel Roberts Noble Foundation Research Recognition Award, the Lifetime Achievement Award of the Society for In Vitro Biology, the Sandoz Prize from the International Association of Gerontology, and the Presidential Award from The International Organization for Mycoplasmology. Hayflick, together with Paul Moorhead, were awarded the prestigious John Scott Award in 2014. This is the oldest scientific award in the United States, established in 1823 in honor of Benjamin Franklin.
In the mid-1990s, Hayflick was recruited by Geron founder Michael D. West to join the company's Scientific Advisory Board. [14] In 1997, Hayflick was elected Academician and Foreign Member of the Ukrainian Academy of Medical Sciences. In 1998 he was elected corresponding member of the Société de Biologie of France. In 1999, he was presented with the van Weezel Award by the European Society for Animal Cell Technology and the Lord Cohen of Birkenhead Medal by the British Society for Research on Ageing. The American Aging Association established an Annual Hayflick Lectureship in 1997. A second Annual Hayflick Lecture was established by the University of Alabama at Birmingham in 2000. Hayflick was the recipient of the 2001, $10,000 Life Extension Prize and Laureate Diploma from the Regenerative Medicine Secretariat for his "...discovery of the finite replicative capacity of normal human diploid cells..." A third Annual Hayflick Lecture was established at the Friedrich Schiller University in 2013.
Hayflick is a Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science, an Honorary Member of the Tissue Culture Association and, according to the Institute of Scientific Information, is one of the most cited contemporary scientists in the world in the fields of biochemistry, biophysics, cell biology, enzymology, genetics and molecular biology. Hayflick is the author of over 275 scientific papers, book chapters and edited books of which four papers are among the 100 most cited scientific papers of the two million papers published in the basic biomedical sciences from 1961 to 1978.
The inverted microscope that Hayflick modified for use in his tissue culture and mycoplasma work and on which all other such microscopes have been modeled has been acquired by the Smithsonian National Museum of American History.
| External videos | |
|---|---|

HeLa is an immortalized cell line used in scientific research. It is the oldest human cell line and one of the most commonly used. The line is derived from cervical cancer cells taken on 8 February, 1951, from Henrietta Lacks, a 31-year-old African-American mother of five, who died of cancer on 4 October 1951, and after whom they are named. The cell line is durable and prolific, allowing it to be used extensively in scientific study.
Mycoplasma pneumoniae is a very small bacterium in the class Mollicutes. It is a human pathogen that causes the disease mycoplasma pneumonia, a form of atypical bacterial pneumonia related to cold agglutinin disease. M. pneumoniae is characterized by the absence of a peptidoglycan cell wall and resulting resistance to many antibacterial agents. The persistence of M. pneumoniae infections even after treatment is associated with its ability to mimic host cell surface composition.

Hilary Koprowski was a Polish virologist and immunologist active in the United States who demonstrated the world's first effective live polio vaccine. He authored or co-authored over 875 scientific papers and co-edited several scientific journals.
Biological immortality is a state in which the rate of mortality from senescence is stable or decreasing, thus decoupling it from chronological age. Various unicellular and multicellular species, including some vertebrates, achieve this state either throughout their existence or after living long enough. A biologically immortal living being can still die from means other than senescence, such as through injury, poison, disease, predation, lack of available resources, or changes to environment.

The Hayflick limit, or Hayflick phenomenon, is the number of times a normal somatic, differentiated human cell population will divide before cell division stops. However, this limit does not apply to stem cells.

Stanley Alan Plotkin is an American physician who works as a consultant to vaccine manufacturers, such as Sanofi Pasteur, as well as biotechnology firms, non-profits and governments. In the 1960s, he played a pivotal role in discovery of a vaccine against rubella virus while working at Wistar Institute in Philadelphia. Plotkin was a member of Wistar’s active research faculty from 1960 to 1991. Today, in addition to his emeritus appointment at Wistar, he is emeritus professor of Pediatrics at the University of Pennsylvania. His book, Vaccines, is the standard reference on the subject. He is an editor with Clinical and Vaccine Immunology, which is published by the American Society for Microbiology in Washington, D.C.

The Wistar Institute is an independent, nonprofit research institution in biomedical science with special focuses in oncology, immunology, infectious disease and vaccine research. Located on Spruce Street in Philadelphia’s University City neighborhood, Wistar was founded in 1892 as a nonprofit institution to focus on biomedical research and training.
Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae is a species of bacteria known to cause the disease porcine enzootic pneumonia, a highly contagious and chronic disease affecting pigs. As with other mollicutes, M. hyopneumoniae is small in size (400–1200 nm), has a small genome and lacks a cell wall. It is difficult to grow in laboratories due to its complex nutritional requirements and the high chances of contamination associated with mycoplasma culture. To successfully grow the bacterium, an environment of 5–10% carbon dioxide is required, and the medium should demonstrate an acid colour shift.

Robert Charles Gallo is an American biomedical researcher. He is best known for his role in establishing the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) as the infectious agent responsible for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) and in the development of the HIV blood test, and he has been a major contributor to subsequent HIV research.
The rabies vaccine is a vaccine used to prevent rabies. There are several rabies vaccines available that are both safe and effective. Vaccinations must be administered prior to rabies virus exposure or within the latent period after exposure to prevent the disease. Transmission of rabies virus to humans typically occurs through a bite or scratch from an infectious animal, but exposure can occur through indirect contact with the saliva from an infectious individual.

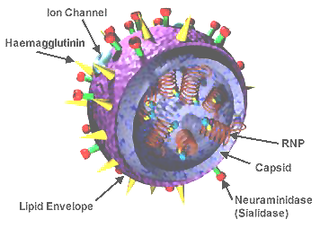
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms begin from one to four days after exposure to the virus and last for about 2–8 days. Diarrhea and vomiting can occur, particularly in children. Influenza may progress to pneumonia, which can be caused by the virus or by a subsequent bacterial infection. Other complications of infection include acute respiratory distress syndrome, meningitis, encephalitis, and worsening of pre-existing health problems such as asthma and cardiovascular disease.
Rubella vaccine is a vaccine used to prevent rubella. Effectiveness begins about two weeks after a single dose and around 95% of people become immune. Countries with high rates of immunization no longer see cases of rubella or congenital rubella syndrome. When there is a low level of childhood immunization in a population it is possible for rates of congenital rubella to increase as more women make it to child-bearing age without either vaccination or exposure to the disease. Therefore, it is important for more than 80% of people to be vaccinated. By introducing rubella containing vaccines, rubella has been eradicated in 81 nations, as of mid-2020.

Karl Maramorosch was an Austrian-born American virologist, entomologist, and plant pathologist. A centenarian and polyglot, he conducted research on viruses, mycoplasmas, rickettsiae, and other micro-organisms; and their transmission to plants through insect vectors in many parts of the world. He is the co-author of a textbook on techniques in virology and is the author of numerous papers on the biology and ecology of plant viruses, their hosts, and vectors. He received the Wolf Prize in Agriculture in 1980 for his contribution to the study of crop pathogens.

Robert Merritt Chanock was an American pediatrician and virologist who made major contributions to the prevention and treatment of childhood respiratory infections in more than 50 years spent at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.

WI-38 is a diploid human cell line composed of fibroblasts derived from lung tissue of a 3-month-gestation female fetus. The fetus came from the elective abortion of a Swedish woman in 1963. The cell line was isolated by Leonard Hayflick the same year, and has been used extensively in scientific research, with applications ranging from developing important theories in molecular biology and aging to the production of most human virus vaccines. The uses of this cell line in human virus vaccine production is estimated to have saved the lives of millions of people.
Jay A. Levy is an American AIDS and cancer research physician. He is a professor of medicine with specialties in virology and immunology at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF).
A universal flu vaccine is a flu vaccine that is effective against all influenza strains regardless of the virus sub type, antigenic drift or antigenic shift. Hence it should not require modification from year to year. As of 2021 no universal flu vaccine had been approved for general use, several were in development, and one was in clinical trial.

MRC-5 is a diploid cell culture line composed of fibroblasts, originally developed from the lung tissue of a 14-week-old aborted Caucasian male fetus. The cell line was isolated by J.P. Jacobs and colleagues in September 1966 from the seventh population doubling of the original strain, and MRC-5 cells themselves are known to reach senescence in around 45 population doublings.
Barrie Patrick Marmion was an English microbiologist who spent the majority of his career in Australia. He is known for his work on Q fever, and led the team that developed the first vaccine against the bacteria that causes it.

John R. Mascola is an American physician-scientist, immunologist and infectious disease specialist. He was the director of the Vaccine Research Center (VRC), part of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), National Institutes of Health (NIH). He also served as a principal advisor to Anthony Fauci, director of NIAID, on vaccines and biomedical research affairs. Mascola is the current Chief Scientific Officer for ModeX Therapeutics.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)