
Cytisus scoparius, the common broom or Scotch broom, is a deciduous leguminous shrub native to western and central Europe. In Britain and Ireland, the standard name is broom; this name is also used for other members of the Genisteae tribe, such as French broom or Spanish broom; and the term common broom is sometimes used for clarification. In other English-speaking countries, the most common name is "Scotch broom" ; however, it is known as English broom in Australia.

Pinus pumila, commonly known as the Siberian dwarf pine, dwarf Siberian pine, dwarf stone pine, Japanese stone pine, or creeping pine, is a tree in the family Pinaceae native to northeastern Asia and the Japanese isles. It shares the common name creeping pine with several other plants.

Pyrus calleryana, or the Callery pear, is a species of pear tree native to China and Vietnam, in the family Rosaceae. It is most commonly known for its cultivar 'Bradford' and its offensive odor, widely planted throughout the United States and increasingly regarded as an invasive species.

Lespedeza is a genus of some 45 species of flowering plants in the pea family (Fabaceae), commonly known as bush clovers or Japanese clovers (hagi). The genus is native to warm temperate to subtropical regions of eastern North America, eastern and southern Asia and Australasia.

Camellia japonica, known as common camellia, or Japanese camellia, is a species of Camellia, a flowering plant genus in the family Theaceae. There are thousands of cultivars of C. japonica in cultivation, with many colors and forms of flowers. In the U.S. it is sometimes called japonica. In the wild, it is found in mainland China, Taiwan, southern Korea and southwestern Japan. It grows in forests, at altitudes of around 300–1,100 metres (980–3,600 ft).

Weigela is a genus of between six and 38 species of deciduous shrubs in the family Caprifoliaceae, growing to 1–5 m (3–15′) tall. All are natives of eastern Asia. The genus is named after the German scientist Christian Ehrenfried Weigel.

Spartium junceum, known as Spanish broom, rush broom, or weaver's broom, it is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae and the sole species in the genus Spartium. It is closely related to the other brooms.

Ulex europaeus, the gorse, common gorse, furze or whin, is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae, native to the British Isles and Western Europe.

Desmanthus is a genus of flowering plants in the mimosoid clade of the subfamily Caesalpinioideae of the pea family, Fabaceae. The name is derived from the Greek words δεσμός (desmos), meaning "bundle", and ἄνθος (anthos), meaning "flower". It contains about 24 species of herbs and shrubs that are sometimes described as being suffruiticose and have bipinnate leaves. Desmanthus is closely related to Leucaena and in appearance is similar to Neptunia. Like Mimosa and Neptunia, Desmanthus species fold their leaves in the evening. They are native to Mexico and North, Central and South America. Members of the genus are commonly known as bundleflowers. Donkey beans is another common name and originated in Central America, where Desmanthus species are highly regarded as fodder for these domestic draught animals.

Spiraea japonica, the Japanese meadowsweet or Japanese spiraea, is a plant in the family Rosaceae.

Cytisus multiflorus is a species of legume known by the common names white broom, white spanishbroom and Portuguese broom.

Symphoricarpos albus is a species of flowering plant in the honeysuckle family known by the common name common snowberry. Native to North America, it is browsed by some animals and planted for ornamental and ecological purposes, but is poisonous to humans.

Lespedeza leptostachya is a rare species of flowering plant in the legume family known by the common names prairie lespedeza and prairie bush-clover. It occurs in the Upper Midwest region of the United States. The flowers are creamy-white to purplish and arranged into a narrow terminal spikes.

Lespedeza cuneata is a species of flowering plant in the legume family known by the common names Chinese bushclover and sericea lespedeza, or just sericea. It is native to Asia and eastern Australia and it is present elsewhere as an introduced species and sometimes an invasive plant.

Eragrostis curvula is a species of grass known by the common name weeping lovegrass. Other common names include Boer lovegrass, curved lovegrass, Catalina lovegrass, and African lovegrass.

Elaeagnus pungens is a species of flowering plant in the family Elaeagnaceae, known by the common names thorny olive, spiny oleaster and silverthorn; also by the family name "oleaster". It is native to Asia, including China and Japan. It is present in the southeastern United States as an introduced species, a common landscaping and ornamental plant, and sometimes an invasive species.

Vaccinium pallidum is a species of flowering plant in the heath family known by the common names hillside blueberry, Blue Ridge blueberry, late lowbush blueberry, and early lowbush blueberry. It is native to central Canada (Ontario) and the central and eastern United States plus the Ozarks of Missouri, Arkansas, southeastern Kansas and eastern Oklahoma.

Lespedeza capitata is a species of flowering plant in the Fabaceae, or legume family, and is known by the common name roundhead bushclover, or roundhead lespedeza. It is native to eastern North America, including eastern Canada and the eastern half of the United States.

Lespedeza thunbergii is a species of flowering plant in the legume family known by the common names Thunberg's bushclover, Thunberg's lespedeza, and shrub lespedeza. It is native to the eastern Himalayas, China, Korea, and Japan.
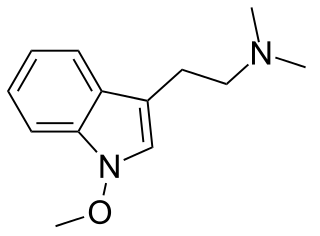
Lespedamine is an indole alkaloid and substituted tryptamine present in the plant Lespedeza bicolor. The alkaloid bears a close structural resemblance to the psychedelic alkaloid dimethyltryptamine and was speculated to have psychoactivity by Alexander Shulgin. No reports on lespedamine's biological activity have been published.




















