Related Research Articles
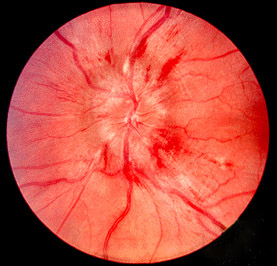
Papilledema or papilloedema is optic disc swelling that is caused by increased intracranial pressure due to any cause. The swelling is usually bilateral and can occur over a period of hours to weeks. Unilateral presentation is extremely rare.
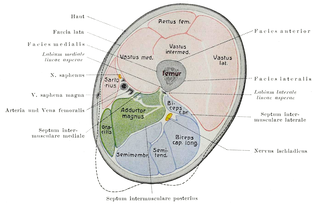
In human anatomy, the thigh is the area between the hip (pelvis) and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb.

An air embolism, also known as a gas embolism, is a blood vessel blockage caused by one or more bubbles of air or other gas in the circulatory system. Air embolisms may also occur in the xylem of vascular plants, especially when suffering from water stress. Air can be introduced into the circulation during surgical procedures, lung over-expansion injury, decompression, and a few other causes.

The jugular venous pressure is the indirectly observed pressure over the venous system via visualization of the internal jugular vein. It can be useful in the differentiation of different forms of heart and lung disease. Classically three upward deflections and two downward deflections have been described.

Caput medusae is the appearance of distended and engorged superficial epigastric veins, which are seen radiating from the umbilicus across the abdomen. The name caput medusae originates from the apparent similarity to Medusa's head, which had venomous snakes in place of hair. It is also a sign of portal hypertension. It is caused by dilation of the paraumbilical veins, which carry oxygenated blood from mother to fetus in utero and normally close within one week of birth, becoming re-canalised due to portal hypertension caused by liver failure.

The atrium is the upper chamber through which blood enters the ventricles of the heart. There are two atria in the human heart – the left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary (lung) circulation, and the right atrium receives blood from the venae cavae. The atria receive blood while relaxed (diastole), then contract (systole) to move blood to the ventricles. All animals with a closed circulatory system have at least one atrium. Humans have two atria.
In medicine, the cardiac examination, also precordial exam, is performed as part of a physical examination, or when a patient presents with chest pain suggestive of a cardiovascular pathology. It would typically be modified depending on the indication and integrated with other examinations especially the respiratory examination.
Pulsus paradoxus, also paradoxic pulse or paradoxical pulse, is an abnormally large decrease in stroke volume, systolic blood pressure and pulse wave amplitude during inspiration. The normal fall in pressure is less than 10 mmHg. When the drop is more than 10 mmHg, it is referred to as pulsus paradoxus. Pulsus paradoxus is not related to pulse rate or heart rate, and it is not a paradoxical rise in systolic pressure. The normal variation of blood pressure during breathing/respiration is a decline in blood pressure during inhalation and an increase during exhalation. Pulsus paradoxus is a sign that is indicative of several conditions, including cardiac tamponade, chronic sleep apnea, croup, and obstructive lung disease.
The abdominojugular test, also known as abdominojugular reflux (AJR), is a physical examination test useful in diagnosing right ventricle dysfunction, particularly right ventricular failure.
A peripheral vascular examination is a medical examination to discover signs of pathology in the peripheral vascular system. It is performed as part of a physical examination, or when a patient presents with leg pain suggestive of a cardiovascular pathology.

Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) is the presence of a blood clot in the dural venous sinuses, which drain blood from the brain. Symptoms may include headache, abnormal vision, any of the symptoms of stroke such as weakness of the face and limbs on one side of the body, and seizures.

Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) is a medical condition in which blood pools in the veins, straining the walls of the vein. The most common cause of CVI is superficial venous reflux which is a treatable condition. As functional venous valves are required to provide for efficient blood return from the lower extremities, this condition typically affects the legs. If the impaired vein function causes significant symptoms, such as swelling and ulcer formation, it is referred to as chronic venous disease. It is sometimes called chronic peripheral venous insufficiency and should not be confused with post-thrombotic syndrome in which the deep veins have been damaged by previous deep vein thrombosis.
Bancroft's sign, also known as Moses' sign, is a clinical sign found in patients with deep vein thrombosis of the lower leg involving the posterior tibial veins. The sign is positive if pain is elicited when the calf muscle is compressed forwards against the tibia, but not when the calf muscle is compressed from side to side. Like other clinical signs for deep vein thrombosis, such as Homans sign and Lowenberg's sign, this sign is neither sensitive nor specific for the presence of thrombosis.
Lowenberg's sign is a clinical sign found in patients with deep vein thrombosis of the lower leg. The sign is positive when pain is elicited rapidly when a blood pressure cuff is placed around the calf and inflated to 80mmHg. Like other signs of deep vein thrombosis, such as Homans sign and Bancroft's sign, this sign is neither sensitive nor specific for the presence of thrombosis.
Louvel's sign is a clinical sign found in patients with deep vein thrombosis. The sign is defined as pain in the distribution of the affected vein which occurs during coughing or sneezing, and which disappears when the vein is compressed proximally.
Rose's sign is a clinical sign in which the skin of one leg feels warm and stiff when pinched. It can occur in people with deep vein thrombosis due to oedema in the affected leg.
The cardiovascular examination is a portion of the physical examination that involves evaluation of the cardiovascular system. The exact contents of the examination will vary depending on the presenting complaint but a complete examination will involve the heart, lungs, belly and the blood vessels.

Computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis is an application of computed tomography (CT) and is a sensitive method for diagnosis of abdominal diseases. It is used frequently to determine stage of cancer and to follow progress. It is also a useful test to investigate acute abdominal pain. Renal stones, appendicitis, pancreatitis, diverticulitis, abdominal aortic aneurysm, and bowel obstruction are conditions that are readily diagnosed and assessed with CT. CT is also the first line for detecting solid organ injury after trauma.

Ultrasonography of suspected or previously confirmed chronic venous insufficiency of leg veins is a risk-free, non-invasive procedure. It gives information about the anatomy, physiology and pathology of mainly superficial veins. As with heart ultrasound (echocardiography) studies, venous ultrasonography requires an understanding of hemodynamics in order to give useful examination reports. In chronic venous insufficiency, sonographic examination is of most benefit; in confirming varicose disease, making an assessment of the hemodynamics, and charting the progression of the disease and its response to treatment. It has become the reference standard for examining the condition and hemodynamics of the lower limb veins. Particular veins of the deep venous system (DVS), and the superficial venous system (SVS) are looked at. The great saphenous vein (GSV), and the small saphenous vein (SSV) are superficial veins which drain into respectively, the common femoral vein and the popliteal vein. These veins are deep veins. Perforator veins drain superficial veins into the deep veins. Three anatomic compartments are described, (N1) containing the deep veins, (N2) containing the perforator veins, and (N3) containing the superficial veins, known as the saphenous compartment. This compartmentalisation makes it easier for the examiner to systematize and map. The GSV can be located in the saphenous compartment where together with the Giacomini vein and the accessory saphenous vein (ASV) an image resembling an eye, known as the 'eye sign' can be seen. The ASV which is often responsible for varicose veins, can be located at the 'alignment sign', where it is seen to align with the femoral vessels.
Sickle cell retinopathy is a major ocular complication of the sickle cell disease (SCD) which causes permanent loss of vision. Retinopathy can occur in sickling hemoglobinopathies like sickle cell disease, sickle cell C disease, and sickle cell thalassaemia disease.
References
| | This medical sign article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |