Related Research Articles

Sidon or Saida is the third-largest city in Lebanon. It is located on the Mediterranean coast in the South Governorate, of which it is the capital. Tyre, to the south, and the Lebanese capital of Beirut, to the north, are both about 40 kilometres away. Sidon has a population of about 80,000 within the city limits, while its metropolitan area has more than a quarter-million inhabitants.

Tyre is a city in Lebanon, one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, though in medieval times for some centuries by just a small population. It was one of the earliest Phoenician metropolises and the legendary birthplace of Europa, her brothers Cadmus and Phoenix, as well as Carthage's founder Dido (Elissa). The city has many ancient sites, including the Tyre Hippodrome, and was added as a whole to the list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites in 1984. The historian Ernest Renan noted that "One can call Tyre a city of ruins, built out of ruins".

Tripoli is the largest and most important city in northern Lebanon and the second-largest city in the country. Situated 81 km (50 mi) north of the capital Beirut, it is the capital of the North Governorate and the Tripoli District. Tripoli overlooks the eastern Mediterranean Sea, and it is the northernmost seaport in Lebanon. The city is predominantly inhabited by Sunni Muslims, with smaller populations of Alawites and Christians, including Maronites and Armenians among others.

Arwad, the classical Aradus, is a town in Syria on an eponymous island in the Mediterranean Sea. It is the administrative center of the Arwad Subdistrict (nahiyah), of which it is the only locality. It is the only inhabited island in Syria. It is located 3 km (1.9 mi) from Tartus, Syria's second-largest port.

El-Mina or El Mina, is a coastal independent town that neighbors Tripoli, Northern Lebanon. El-Mina occupies the location of the old Phoenician city of Tripolis. It acts as the harbor city for the neighboring Tripoli, Lebanon's second-largest city, situated 5 km to the east.

Our Lady of Mantara is a Melkite Greek Catholic Marian shrine in Maghdouché, Lebanon, discovered on 8 September 1721 by a young shepherd. The grotto, which according to a legend dates to ancient times, was subsequently cared after by Monsignor Eftemios Saïfi, Melkite Catholic bishop of the Melkite Greek Catholic Archeparchy of Sidon. The shrine consists of a tower crowned with the statue of the Virgin and Child, a cathedral, a cemetery and a sacred cave believed to be the one where the Virgin Mary rested while she waited for Jesus while he was in Tyre and Sidon. Since its discovery, it has been steadily visited by families particularly each year on the occasion of the feast of the Nativity of Mary on 8 September.

Maghdouché is a town in the South Governorate of Lebanon. It is located 50 km south of Beirut and 8 km southeast of Sidon. The village lies 3 km inland from the Mediterranean, occupying a hill with elevation ranging between 200 and 229 meters above sea level.
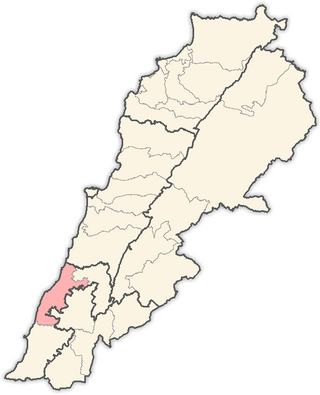
The Sidon District is a district within the South Governorate of Lebanon.

The tourism industry in Lebanon has been important to the local economy historically and comprises a major source of revenue for the country.

The Palm Islands Nature Reserve consists of three flat, rocky islands of eroded limestone and the surrounding sea area, located 5.5 kilometres (3.4 mi) offshore and northwest of the city of Mina El Mina, Lebanon, to the west of Tripoli, Lebanon.

Phoenicia, or Phœnicia, was an ancient Semitic thalassocratic civilization originating in the coastal strip of the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenicians expanded and contracted throughout history, with the core of their culture stretching from Arwad in modern Syria to Mount Carmel in modern Israel. Beyond their homeland, the Phoenicians extended through trade and colonization throughout the Mediterranean, from Cyprus to the Iberian Peninsula.

Melkite Greek Catholic Archeparchy of Tyre is a metropolitan see of the Melkite Greek Catholic Church. In 2009 there were 3,100 baptized. It is currently governed by an Apostolic Administrator, Archbishop Elie Bechara Haddad, B.S., because of the 31 January 2021 removal of Archeparch Michael Abrass, BA.
Melkite Greek Catholic Archeparchy of Tripoli is a diocese of the Melkite Greek Catholic Church suffragan of the Melkite Greek Catholic Archeparchy of Tyre. It is governed by Archeparch Eduard Daher, BC.
Melkite Greek Catholic Archeparchy of Sidon is a diocese of the Melkite Greek Catholic Church suffragan of the Melkite Greek Catholic Archeparchy of Tyre. It is governed by Archeparch Elie Bechara Haddad. The territory is made up of 53 parishes and, as of 2010, 32,000 Melkite Catholics.

Maronite Catholic Archeparchy of Tyre is an Archeparchy of the Maronite Church immediately subject to the Maronite Patriarch of Antioch. In 2014 there were 42,500 baptized. It is currently ruled by Archeparch Charbel Abdallah.
The Maronite Catholic Archeparchy of Tripoli is a non-Metropolitan Archeparchy of the Maronite Church in the north-west of Lebanon.

El-Assaad or Al As'ad is an Arab feudal political family who originated from Najd and is a main branch of the Anizah tribe. Unrelated to Syrian or Palestinian al-Assads, the El-Assaad dynasty that ruled most of South Lebanon for three centuries and whose lineage defended the local people of the Jabal Amel principality – today southern Lebanon – for 36 generations, they also held influence in Balqa in Jordan, Nablus in Palestine, and Homs in Syria during Ottomans rule.
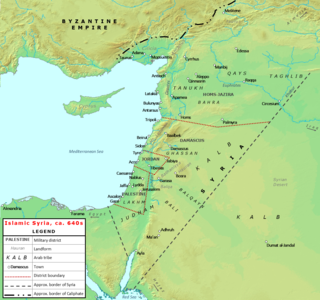
This article lists historical events that occurred between 601–700 in modern-day Lebanon or regarding its people.

This article lists historical events that occurred between 901–1000 in modern-day Lebanon or regarding its people.
References
- ↑ Lebanon, Cultural Landscape Palm Islands, medomed.org; Retrieved 20 December 2018.
- ↑ Tripoli's Palm Islands Natural Preserve Archived 5 July 2018 at the Wayback Machine ; Retrieved 20 December 2018.
- ↑ Palm Islands Nature Reserve, moe.gov.lb; Retrieved 20 December 2018.
- ↑ PALM ISLANDS, TRIPOLI; Retrieved 20 December 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 PALM ISLAND NATURE RESERVE; Retrieved 20 December 2018.
- ↑ El Bellâne; Retrieved 20 December 2018.
- 1 2 3 The Islands of Tripoli Archived 11 October 2017 at the Wayback Machine ; Retrieved 20 December 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 SUMMER ON THE COAST; Retrieved 20 December 2018.
- ↑ Get a map, Lebanon (Beirut) / (le02) / Ez Zîré, getamap.net, Retrieved 20 December 2018.
- ↑ Albawaba, published 30 July 2018, Lebanon's Sidon Sees Largest Underwater ‘Garden’ in Med, albawaba.com; Retrieved 20 December 2018.
- ↑ "Tyre | Ancient City & Historical Site | Britannica". 17 August 2024.