This article contains lists of notable salmon canneries, cannery companies, cannery owners and salmon canning settlements
| Canneries |
|---|
|
| Cannery companies |
|---|
| Cannery owners |
|---|
|
This article contains lists of notable salmon canneries, cannery companies, cannery owners and salmon canning settlements
| Canneries |
|---|
|
| Cannery companies |
|---|
| Cannery owners |
|---|
|

Dillingham, also known as Curyung, is a city in Dillingham Census Area, Alaska, United States. Incorporated in 1963, it is an important commercial fishing port on Nushagak Bay. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 2,249, down from 2,329 in 2010.
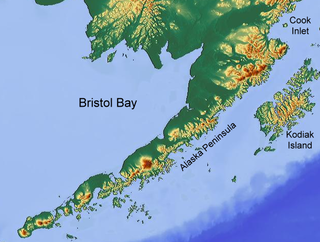
Bristol Bay is the easternmost arm of the Bering Sea, at 57° to 59° North 157° to 162° West in Southwest Alaska. Bristol Bay is 400 km (250 mi) long and 290 km (180 mi) wide at its mouth. A number of rivers flow into the bay, including the Cinder, Egegik, Igushik, Kvichak, Meshik, Nushagak, Naknek, Togiak, and Ugashik.
Steveston, founded in the 1880s, is a neighbourhood of Richmond in Metro Vancouver. On the southwest tip of Lulu Island, the village is a historic port and salmon canning centre at the mouth of the South Arm of the Fraser River. The early 1900s style architecture attracts both the film and tourism industries.

The Alagnak River is a 64-mile (103 km) tributary of the Kvichak River in the U.S. state of Alaska. It has a catchment area of approximately 1400 square mi (3600 km2). It is located in central Lake and Peninsula Borough.
Rivers Inlet is a fjord in the Central Coast region of the Canadian province of British Columbia, its entrance off Fitz Hugh Sound, about 125 km (78 mi) southwest of the community of Bella Coola and about 65 km (40 mi) north of the northern tip of Vancouver Island and the western entrance of the Queen Charlotte Strait.

The Egegik River is a waterway in the U.S. state of Alaska. A biological survey was conducted at the base of the Alaska Peninsula in 1902 by Wilfred Hudson Osgood, which included the Egegik River.

The Gulf of Georgia Cannery is a National Historic Site of Canada located in Steveston village in Richmond, British Columbia.

The Alaska Packers' Association (APA) was a San Francisco-based manufacturer of Alaska canned salmon founded in 1891 and sold in 1982. As the largest salmon packer in Alaska, the member canneries of APA were active in local affairs, and had considerable political influence. The Alaska Packers' Association is best known for operating the "Star Fleet," the last fleet of commercial sailing vessels on the West Coast of North America, as late as 1927.

The Kake Cannery is a historic fish processing facility near Kake, Alaska. Operated by a variety of companies between 1912 and 1977, the cannery was one of many which operated in Southeast Alaska, an area historically rich in salmon. The cannery's surviving buildings are among the best-preserved of the period, and provide a window into the labor practices of the cannery operators, which emphasized production over working conditions, and made significant use of immigrant contract workers. It was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1997.

Tallheo is the location of a former village of the Nuxalk known as Talyu, and is a former cannery town near Bella Coola, British Columbia, Canada, on North Bentinck Arm. Tallheo is also the name of the dialect of the Nuxalk language spoken by the Talhyumc, the particular subgroup of the Nuxalk who live there.

Samuel Elmore Cannery was a U.S. National Historic Landmark in Astoria, Oregon that was designated in 1966 but was delisted in 1993.
Crescent Porter Hale (1872–1937) was an American industrialist who was involved in the canned salmon industry in Bristol Bay, Alaska throughout his adult life.

North of the Great Divide is a 1950 American western film directed by William Witney and starring Roy Rogers, Penny Edwards and Gordon Jones.

A salmon cannery is a factory that commercially cans salmon. It is a fish-processing industry that became established on the Pacific coast of North America during the 19th century, and subsequently expanded to other parts of the world that had easy access to salmon.

Canned or tinned fish are food fish which have been processed, sealed in an airtight container such as a sealed tin can, and subjected to heat. Canning is a method of preserving food, and provides a typical shelf life ranging from one to five years. They are usually opened via a can opener, but sometimes have a pull-tab so that they can be opened by hand. In the past it was common for many cans to have a key that would be turned to peel the lid of the tin off; most predominately sardines, among others.
The Marshall J. Kinney Cannery, located in Uniontown, Astoria, Oregon, United States, between Fifth and Seventh streets, was constructed in 1879 and became one of the city's longest-running salmon canneries. Run by the Astoria Packing Company, of which Marshall J. Kinney was president, the complex quickly became the "largest and most extensive salmon-packing establishment on the Pacific Coast". In 1894, the cannery was completely rebuilt after being burned to the ground. Five years later Kinney became part of the Columbia River Packers Association, joining several other canneries and packing companies. By 1904, the complex supported three production lines; Kinney continued cannery operations until the 1920s when it was primarily used as a central machine shop and warehouse for the Columbia River Packers Association. In 1954, a cargo ship ran into the complex, part of which was lost. Intact portions were used for storage until 1980 and today house shops and small businesses. The cannery was added to the National Register of Historic Places on June 30, 1989, but was delisted on September 8, 1997.
Kildonan is an unincorporated community in the Alberni Inlet-Barkley Sound region of the west coast of southern Vancouver Island, British Columbia. The former steamboat landing and ferry dock is on the east shore of Uchuchklesit Inlet, which branches northwest of the lower reaches of Alberni Inlet. Adjacent to Pacific Rim National Park Reserve, the locality is by road and ferry about 120 kilometres (75 mi) southwest of Port Alberni.

A cannery tender was a type of commercial fishing vessel operated by salmon canneries in the early to mid- 20th century. Most commonly used in the Pacific Northwest and Alaska, cannery tenders transported fish from cannery-owned fish traps to canneries. Cannery tenders also transported men and supplies to set up and maintain the fish traps and patrolled the area around fish traps to protect them from fish pirates.