Anatomy
The lobates have a pair of lobes, which are muscular, cuplike extensions of the body that project beyond the mouth. Their inconspicuous tentacles originate from the corners of the mouth, running in convoluted grooves and spreading out over the inner surface of the lobes (rather than trailing far behind, as in the Cydippida). Between the lobes on either side of the mouth, many species of lobates have four auricles, gelatinous projections edged with cilia that produce water currents that help direct microscopic prey toward the mouth. This combination of structures enables lobates to feed continuously on suspended planktonic prey. [4]
Lobates have eight comb-rows, originating at the aboral pole and usually not extending beyond the body to the lobes; in species with (four) auricles, the cilia edging the auricles are extensions of cilia in four of the comb rows. Most lobates are quite passive when moving through the water, using the cilia on their comb rows for propulsion, [4] although Leucothea has long and active auricles whose movements also contribute to propulsion. Members of the lobate genera Bathocyroe and Ocyropsis can escape from danger by clapping their lobes, so that the jet of expelled water drives them backwards very quickly. [5]
Unlike cydippids, the movements of lobates' combs are coordinated by nerves rather than by water disturbances created by the cilia, and combs on the same row beat together rather than in Mexican wave style. This may have enabled lobates to grow larger than cydippids and to have shapes that are less egg-like. [6]

Ctenophora comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming, and they are the largest animals to swim with the help of cilia.

Beroidae is a family of ctenophores or comb jellies more commonly referred to as the beroids. It is the only known family within the monotypic order Beroida and the class Nuda. They are distinguished from other comb jellies by the complete absence of tentacles, in both juvenile and adult stages. Species of the family Beroidae are found in all the world's oceans and seas and are free-swimmers that form part of the plankton.

Bathocyroe fosteri is a species of lobate ctenophore found at intermediate depths in all the world's oceans. The species is very common and abundant near the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. It is bioluminescent, and is typically observed hanging motionlessly in an upright or inverted posture although it can flap its oral lobes to swim. This deep-sea comb jelly is named for Alvin (DSV-2) pilot Dudley Foster, who collected the first specimens.

Mnemiopsis leidyi, the warty comb jelly or sea walnut, is a species of tentaculate ctenophore. It is native to western Atlantic coastal waters, but has become established as an invasive species in European and western Asian regions. Three species have been named in the genus Mnemiopsis, but they are now believed to be different ecological forms of a single species M. leidyi by most zoologists.

Phacellophora, commonly known as the fried egg jellyfish or egg-yolk jellyfish, is a very large jellyfish in the monotypic family Phacellophoridae containing a single species Phacellophora camtschatica. This genus can be easily identified by the yellow coloration in the center of its body which closely resembles an egg yolk, hence its common name. Some individuals can have a bell close to 60 cm (2 ft) in diameter, and most individuals have 16 clusters of up to a few dozen tentacles, each up to 6 m (20 ft) long. A smaller jellyfish, Cotylorhiza tuberculata, typically found in warmer water, particularly in the Mediterranean Sea, is also popularly called a fried egg jellyfish. Also, P. camtschatica is sometimes confused with the Lion's mane jellyfish.
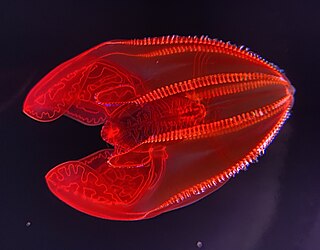
Lampocteis is a monotypic genus of comb jellies, the only genus in family Lampoctenidae. The sole species in this new genus is Lampocteis cruentiventer, the bloodybelly comb jelly. This ctenophore was first collected in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego, California, in 1979. It was described in 2001. The generic name was formed from the Ancient Greek lampós and kteís ("comb"), referring to the iridescence of its "combs"; the specific epithet was formed from the Latin cruentus ("blood-red") and venter ("belly"). Two morphological differences separating it from previously known comb jellies warranted the naming of a new family for this animal. These jellies are typically found at a depth of 250-1,500 meters deep in the North Pacific Ocean.

Chrysaora colorata (Russell), commonly known as the purple-striped jelly or purple-striped sea nettle, is a species of jellyfish that exists primarily off the coast of California from Bodega Bay to San Diego. The bell (body) of the jellyfish is up to 70 cm (2.3 ft) in diameter, typically with a radial pattern of stripes. The tentacles vary with the age of the individual, consisting typically of eight marginal long dark arms, and four central frilly oral arms. It is closely studied by scientists due to not much being known about their eating habits. A 15-foot-long specimen has been seen.

Ocyropsis, a genus within the comb jelly phylum Ctenophora, belonging to the family of Ocyropsidae, are characterized by their prominent muscular lobes and four auricles. These pale, translucent organisms inhabit a wide range of oceanic environments, from warm tropical waters to the cold depths. Unlike many other ctenophores, which are relatively slow-moving, Ocyropsis species are agile predators, utilizing their powerful lobes for rapid propulsion. Additionally, they possess the ability to secrete bioluminescent mucus, a defense mechanism that can disorient and deter potential threats. To capture prey, Ocyropsis employ their muscular lobes to seize and manipulate food items, subsequently transferring them to their prehensile mouths for ingestion.

Cydippida is an order of comb jellies. They are distinguished from other comb jellies by their spherical or oval bodies, and the fact their tentacles are branched, and can be retracted into pouches on either side of the pharynx. The order is not monophyletic, that is, more than one common ancestor is believed to exist.

Pleurobrachia bachei is a member of the phylum Ctenophora and is commonly referred to as the Pacific sea gooseberry. These comb jellies are often mistaken for medusoid Cnidaria, but lack stinging cells.

Mertensia ovum, also known as the Arctic comb jelly or sea nut, is a cydippid comb jelly or ctenophore first described as Beroe ovum by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1780. It is the only species in the genus Mertensia. Unusually among ctenophores, which normally prefer warmer waters, it is found in the Arctic and adjacent polar seas, mostly in surface waters down to 50 metres (160 ft).

The benthic comb jelly is a comb jelly living in the Ryukyu Trench near Japan. Found at a depth of 7,217 metres (23,700 ft), it is the deepest dwelling ctenophore discovered. Since its discovery, similar comb jellies have been found in the New Britain and Yap trenches.

Leucothea is a genus of ctenophores in the monotypic family Leucotheidae.

Beroe ovata is a comb jelly in the family Beroidae. It is found in the South Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea and has been introduced into the Black Sea, the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Azov and the Caspian Sea. It was first described by the French physician and zoologist Jean Guillaume Bruguière in 1789.

Bolinopsis infundibulum, commonly known as the common northern comb jelly, is a species of comb jelly in the family Bolinopsidae. It is found in the northern Atlantic Ocean and was first described by the Danish naturalist Otto Friedrich Müller in 1776.

Pleurobrachia pileus is a species of comb jelly, commonly known as a sea gooseberry. It is found in open water in the northern Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the Baltic Sea and the Black Sea, and was first described by the Danish zoologist Otto Friedrich Müller in 1776.

Thalassocalyce is a genus of ctenophore, or comb jellies, known from the California Coast, Gulf of Mexico, and west north Atlantic. It is represented by a single species, Thalassocalyce inconstans, which is the only species in the family Thalassocalycidae and the order Thalassocalycida. T. inconstans is a pelagic ctenophore typically occurring in upper-mesopelagic depths, but has been observed at depths up to 3,500 m in Monterey Canyon.

Beroe abyssicola is a species of beroid ctenophore, or comb jelly. It is largely found in deep waters in the North Pacific Ocean, and is common in Japan and the Arctic Ocean. A predator, B. abyssicola feeds mostly on other ctenophores by swallowing them whole. Like other ctenophores, B. abyssicola has a simple nervous system in the form of a nerve net, which it uses to direct its movement, feeding, and hunting behaviors.
Euplokamis is a genus of ctenophores, or comb jellies, belonging to the monotypic family Euplokamididae. It shares the common name sea gooseberry with species of the genus Pleurobrachia. After being originally described by Chun (1879), the family Euplokamididae was expanded by Mills (1987) due to the discovery of a new species, Euplokamis dunlapae. Further research indicated that Euplokamis should be identified from Mertensiidae due to the rows of combs and some compression. They may also be distinguished from the genus Pleurobrachia due to their more elongated shape. Additionally, various adaptations of Euplokamis have been observed such as the use of tentacles for movement/feeding, a complex nervous system, and bioluminescent capabilities. Other characteristics including a defined mesoderm, lack of stinging cells, developmental differences, and symmetry supported the reclassification of these organisms.
Beroe gracilis is a species of comb jelly in the family Beroidae. It is a free-swimming species found in the North Sea, the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.



















