
The Mastigoteuthidae, also known as whip-lash squid, are a family of small deep-sea squid. Approximately 20 known species in six genera are represented, with members found in both the mesopelagic and bathypelagic zone of most oceans. Originally described by Verill in 1881, it was later lowered by Chun (1920) to a subfamily (Mastigoteuthinae) of the Chiroteuthidae. However, Roper et al. (1969) raised it back to the family level, and this has not been changed since. The taxonomy of this family is extremely unstable, and there have been at times one genus, two genera and four subgenera(Salcedo-Vargas & Okutani, 1994), two genera and several 'groups', five genera and one species with an uncertain placement, or six genera.

Vitreledonella richardi, also known as the glass octopus, is an incirrate octopus. It is in the genus Vitreledonella and of the family Amphitretidae.

The Octopodidae comprise the family containing the majority of known octopus species.
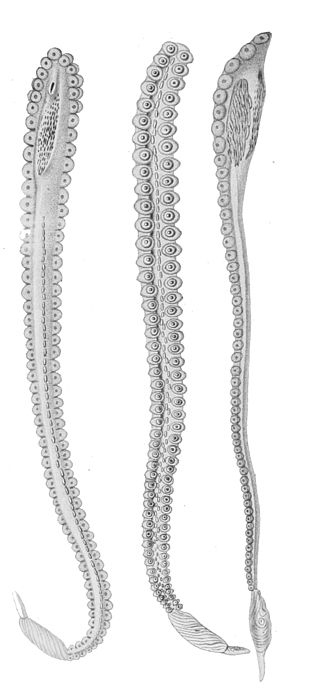
A hectocotylus is one of the arms of male cephalopods that is specialized to store and transfer spermatophores to the female. Structurally, hectocotyli are muscular hydrostats. Depending on the species, the male may use it merely as a conduit to the female, analogously to a penis in other animals, or he may wrench it off and present it to the female.

Enteroctopus is an octopus genus whose members are sometimes known as giant octopuses.

Octopus is the largest genus of octopuses, comprising about 100 species. These species are widespread throughout the world's oceans. Many species formerly placed in the genus Octopus are now assigned to other genera within the family. The octopus has 8 arms, averaging 20 cm (8 in) long for an adult.

Graneledone is a genus of octopuses in the family Octopodidae. The type species is Eledone verrucosaVerrill, 1881.
Thaumeledone is a genus of octopuses in the family Octopodidae found in deep waters in the Southern Hemisphere.

Pteroctopus is a genus of octopuses in the family Octopodidae.

Illex coindetii, commonly known as the southern shortfin squid or broadtail shortfin squid, is a species of neritic squids in the family Ommastrephidae. They are found in the Mediterranean Sea and on both sides of the north Atlantic Ocean.

Macrotritopus defilippi, commonly known as the Lilliput longarm octopus or the Atlantic longarm octopus, is a small species of octopus, a marine cephalopod mollusc of the order Octopoda.

Octopus salutii or the spider octopus is a species of cephalopods in the family Octopodidae. It ranges from 4.0 to 13.0 cm ML in males and 3.5 to 16.5 cm ML in females. Octopus salutii are found at depths ranging from 100 to 700m however, they are most abundant at depths of 250 to 500m.

Neorossia caroli, the Carol bobtail squid, is a species of bobtail squid belonging to the family Sepiolidae.

Megaleledonidae is a family of octopuses in the superfamily Octopodoidea. It was formerly placed in the family Octopodidae sensu lato as the subfamily Megaleledoninae but more recent studies have raised this taxon as a valid family. Megaleledonidae contains about 43 species in 12 genera.
Macrochlaena winckworthi, Winckworth's octopus, is a little known species of octopus, it is the only species in the monotypic genus Macrochlaena, in the family Octopodidae. It was described by the British malacologist Guy Coburn Robson in 1926, the type specimens having been collected in the Gulf of Mannar, off Thoothukudi in Tamil Nadu, southeastern India.
Paroctopus is a small genus of octopuses from the family Octopodidae.

Octopus insularis is a species of octopus described in 2008 from individuals found off the coast of Brazil, with a potentially much larger range.

Opisthoteuthis grimaldii is an octopus found near the Azores.

Amphioctopus aegina, commonly referred to as the marbled octopus or the sandbird octopus, is a bottom dwelling species residing in the coastal zone of the Indo-West Pacific. Planktonic hatchlings and eggs are laid by females predominantly during the months of January and October, however they have been known to reproduce year-round.

Octopus hubbsorum, is an octopus in the family Octopodidae. It is commonly found along tropical waters along the central Pacific Coast of Mexico. Here, they are one of the most commonly caught cephalopods and are commercially extremely important for the economy.

















