 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Tetraammineplatinum(II) tetrachloroplatinate(II) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.034.078 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
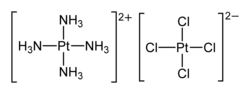
| [Pt(NH3)4][PtCl4] | |
| Molar mass | 600.09 g/mol |
| Appearance | green solid |
| Density | 3.7 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 320 °C (608 °F; 593 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
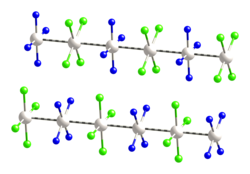
Magnus's green salt is the inorganic compound with the formula [Pt(NH3)4][PtCl4]. This salt is named after Heinrich Gustav Magnus, who, in the early 1830s, first reported the compound. The compound is a linear chain compound, consisting of a chain of platinum atoms. It is dark green, which is unusual for platinum compounds.