
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate. It is to be distinguished (usually) from the county, which may encompass rural territory or numerous small communities such as towns, villages and hamlets.
A local government is a form of public administration which, in a majority of contexts, exists as the lowest tier of administration within a given state. The term is used to contrast with offices at state level, which are referred to as the central government, national government, or federal government and also to supranational government which deals with governing institutions between states. Local governments generally act within powers delegated to them by legislation or directives of the higher level of government. In federal states, local government generally comprises the third tier of government, whereas in unitary states, local government usually occupies the second or third tier of government, often with greater powers than higher-level administrative divisions.

A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages but smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish them vary considerably between different parts of the world.
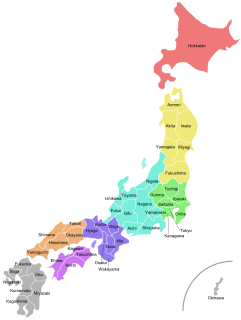
Japan is divided into 47 prefectures, forming the first level of jurisdiction and administrative division. They consist of 43 prefectures proper, two urban prefectures, one "circuit" or "territory" and one "metropolis". In 1868, the Meiji Fuhanken sanchisei administration created the first prefectures to replace the urban and rural administrators in the parts of the country previously controlled directly by the shogunate and a few territories of rebels/shogunate loyalists who had not submitted to the new government such as Aizu/Wakamatsu. In 1871, all remaining feudal domains (han) were also transformed into prefectures, so that prefectures subdivided the whole country. In several waves of territorial consolidation, today's 47 prefectures were formed by the turn of the century. In many instances, these are contiguous with the ancient ritsuryō provinces of Japan.

The administrative divisions of New York are the various units of government that provide local services, "local" meaning "not statewide", in the State of New York. The New York State Constitution standardized the names and functions of these statewide.

For administrative purposes, Egypt is divided into twenty-seven governorates. Egyptian governorates are the top tier of the country's jurisdiction hierarchy. A governorate is administered by a governor, who is appointed by the President of Egypt and serves at the president's discretion. Most governorates have a population density of more than one thousand per km², while the three largest have a population density of less than two per km².

Syria is a unitary state, but for administrative purposes, it is divided into fourteen governorates, also called provinces or counties in English. The governorates are divided into sixty districts, which are further divided into subdistricts. The nawāḥī contain villages, which are the smallest administrative units.
A gram panchayat or village panchayat is the only grassroots-level of panchayati raj formalised local self-governance system in India at the village or small-town level, and has a sarpanch as its elected head.
A village hall is a public building in a village used for various things such as:
A Union Council forms the second-tier of local government and fifth administrative division in Pakistan. Its structure and responsibilities differ between provinces and territories.

In the United States, the meaning of "village" varies by geographic area and legal jurisdiction. In many areas, "village" is a term, sometimes informal, for a type of administrative division at the local government level. Since the Tenth Amendment to the United States Constitution prohibits the federal government from legislating on local government, the states are free to have political subdivisions called "villages" or not to and to define the word in many ways. Typically, a village is a type of municipality, although it can also be a special district or an unincorporated area. It may or may not be recognized for governmental purposes.

A Village Development Committee (VDC) in Nepal was the lower administrative part of its Ministry of Federal Affairs and Local Development. Each district had several VDCs, similar to municipalities but with greater public-government interaction and administration. There were 3,157 village development committees in Nepal. Each VDC was further divided into several wards depending on the population of the district, the average being nine wards.
Mapoch's Caves is a provincial heritage site in Middelburg in the Mpumalanga province of South Africa.
A tehsil is an administrative division in some countries of the Indian subcontinent. It is an area of land within a city or town that serves as its administrative centre, with possible additional towns, and usually a number of villages. The terms in India have replaced earlier geographical terms, such as pargana and thana.
Roossenekal is a town in Elias Motsoaledi Local Municipality in the Limpopo province of South Africa.

The Panchayat raj is a political system, originating from the Indian subcontinent, found mainly in India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and Nepal. It is the oldest system of local government in the Indian subcontinent, and historical mentions date to the 250 CE period. The word raj means "rule" and panchayat means "assembely”(ayat) of five (panch). Traditionally panchayats consisted of wise and respected elders chosen and accepted by the local community. However, there were varying forms of such assemblies. Traditionally, these assemblies settled disputes between individuals and between villages.

Fort Merensky, also called Fort Wilhelm, stands on a prominent hill in a commanding position near Botshabelo, a former Berlin Mission Station (BMS), 13 kilometers from Middelburg on the road to Groblersdal. It was built in order to protect the mission's convert from attacks by the local Bantu tribes using dry wall construction.

Gaunpalika is the newly formed lower administrative division in Nepal. The Ministry of Federal Affairs and Local Development (Nepal) dissolved the existing village development committees and announced the establishment of this new local body. There are currently 460 rural municipalities.


















