
Felix Heinrich Wankel was a German mechanical engineer and inventor after whom the Wankel engine was named.

Mazda Motor Corporation, also known as simply Mazda, is a Japanese multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Fuchū, Hiroshima, Japan. The company was founded on January 30, 1920, as Toyo Cork Kogyo Co., Ltd., a cork-making factory, by Jujiro Matsuda. The company then acquired Abemaki Tree Cork Company. It changed its name to Toyo Kogyo Co., Ltd. in 1927 and started producing vehicles in 1931.
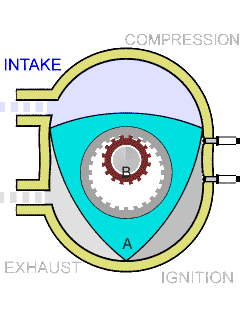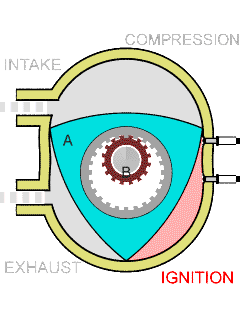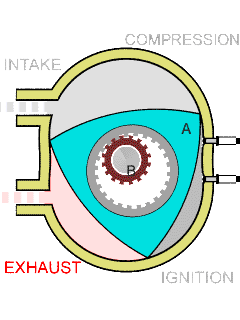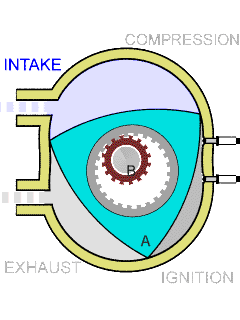
The Wankel engine is a type of internal combustion engine using an eccentric rotary design to convert pressure into rotating motion. The concept was proven by German engineer Felix Wankel, followed by a commercially feasible engine designed by German engineer Hanns-Dieter Paschke. The Wankel engine's rotor, which creates the turning motion, is similar in shape to a Reuleaux triangle, with the sides having less curvature. The rotor spins inside a figure-eight-like epitrochoidal housing around a fixed-toothed gearing. The midpoint of the rotor moves in a circle around the output shaft, rotating the shaft via a cam.

The Mazda RX-7 is a front-engine, rear-wheel-drive, rotary engine-powered sports car that was manufactured and marketed by Mazda from 1978 until 2002 across three generations, all of which made use of a compact, lightweight Wankel rotary engine.

The Mazda RX-8 is a sports car manufactured by Japanese automobile manufacturer Mazda between 2003 and 2012. It was first shown in 2001 at the North American International Auto Show. It is the direct successor to the RX-7. Like its predecessors in the RX range, it is powered by a rotary Wankel engine. The RX-8 was available for the 2003 model year in most parts of the world.

The Mazda Cosmo is an automobile which was produced by Mazda from 1967 until 1996. Throughout its history, the Cosmo served as a "halo" vehicle for Mazda, with the first Cosmo successfully launching the Mazda Wankel engine. The final generation of Cosmo served as Mazda's flagship vehicle in Japan, being sold as the Eunos Cosmo through its luxury Eunos division in Japan.

The Mazda Luce is an executive car that was produced by Mazda in Japan from 1966 until 1991. It was widely exported as the Mazda 929 from 1973 to 1991 as Mazda's largest sedan. Later generations were installed with luxury items and interiors as the Luce became the flagship offering. The Luce was replaced by the Sentia in 1991 which was also exported under the 929 nameplate.

The Mazda Wankel engines are a family of Wankel rotary combustion car engines produced by Mazda.

Mazda North American Operations (MNAO), which includes Mazda Motor of America, Inc., is Mazda Motor Corporation's North American arm, and constitutes the largest component of that company outside Japan. The company has its headquarters in Irvine, California and is headed by Jeffrey Guyton.
Hydrogen technologies are technologies that relate to the production and use of hydrogen as a part hydrogen economy. Hydrogen technologies are applicable for many uses.
Hybrid vehicle drivetrains transmit power to the driving wheels for hybrid vehicles. A hybrid vehicle has multiple forms of motive power, and can come in many configurations. For example, a hybrid may receive its energy by burning gasoline, but switch between an electric motor and a combustion engine.

The Mazda Premacy Hydrogen RE Hybrid or Mazda5 Hydrogen RE Hybrid was a hydrogen powered hybrid car produced by Mazda. Later models were also called the Mazda Hydrogen RE Plug in Hybrid. The first car was unveiled in 2005, with an improved version shown at the 2007 Tokyo Motor Show. Mazda planned for the car to enter production and leased a few cars to end users in 2009 in 2010.
The Mazda RX-01 was a concept car produced by Mazda that debuted at the 1995 Tokyo Motor Show.

A range extender is a fuel-based auxiliary power unit (APU) that extends the range of a battery electric vehicle by driving an electric generator that charges the vehicle's battery. This arrangement is known as a series hybrid drivetrain. The most commonly used range extenders are internal combustion engines, but fuel-cells or other engine types can be used.

The Mazda Premacy is a passenger minivan that was built by the Japanese manufacturer Mazda from 1999 to 2018.
Skyactiv is a brand name for a series of automobile technologies developed by Mazda that increase fuel efficiency and engine output. The initial announcement of the Skyactiv technologies included new engines, transmissions, body, and chassis, which appeared in Mazda products from 2011 onwards.

The Mazda HR-X was the first hydrogen powered concept car produced by Mazda. The car was unveiled at the Tokyo Motor Show in 1991. The car seated four passengers in a plastic shell and was powered by a two rotor Wankel engine which propelled it to 130 km/h (81 mph). The hydrogen was stored in a cooled metal hydride tank and 3.32 kilograms (7.3 lb) provided a range of 190 km (120 mi). It was the first in a series of demonstration hydrogen internal combustion engine vehicles produced by Mazda.

The Mazda MX-30 is a subcompact crossover SUV produced by Mazda and sold as a battery electric (BEV), plug-in hybrid (PHEV) or mild hybrid (MHEV) variant. Based on the CX-30, it was unveiled at the 2019 Tokyo Motor Show. Production of the vehicle, which is Mazda's first mass-produced electric car, began at their Ujina factory on 19 May 2020.

The Mazda 2 is a subcompact/supermini (B-segment) car manufactured and marketed by Mazda since 2002, currently in its third generation. An entry-level model of the brand in markets outside Japan, the Mazda2 is positioned below the Mazda3. The Mazda2 has also been marketed as the Mazda Demio, while its direct predecessor was exported as the Mazda 121.
















