
Compsognathus is a genus of small, bipedal, carnivorous theropod dinosaur. Members of its single species Compsognathus longipes could grow to around the size of a chicken. They lived about 150 million years ago, during the Tithonian age of the late Jurassic period, in what is now Europe. Paleontologists have found two well-preserved fossils, one in Germany in the 1850s and the second in France more than a century later. Today, C. longipes is the only recognized species, although the larger specimen discovered in France in the 1970s was once thought to belong to a separate species and named C. corallestris.
Liopleurodon is an extinct genus of carnivorous pliosaurs that lived from the Callovian stage of the Middle Jurassic to the Kimmeridgian stage of the Late Jurassic period. The taxonomic history of the animal is quite complex. The type species L. ferox, which is probably the only valid species, was erected in 1873 by Henri Émile Sauvage from a single tooth discovered near the French commune of Boulogne-sur-Mer, in Pas-de-Calais. Rather, in 1869 Harry Govier Seeley erected a species of Pliosaurus, Pliosaurus pachydeirus, based on a series of cervical vertebrae that had been discovered near the civil parish of Great Gransden, Cambridgeshire, England. In 1960, Lambert Beverly Tarlo moved this species within the genus Liopleurodon. However, its validity as a distinct species has been questioned since the beginning of the 21st century, in particular because its supposed distinctive characteristics would be in fact individual variations, suggesting that it is a probable junior synonym of L .ferox. However, identification of a neotype specimen of L. ferox is necessary to confirm whether this observation is true. Numerous fossil specimens attributed to Liopleurodon, even including numerous skeletons, have been discovered in Europe, Russia and Mexico. Other additional species were even proposed, but these are currently seen as coming from other pliosaurid genera.
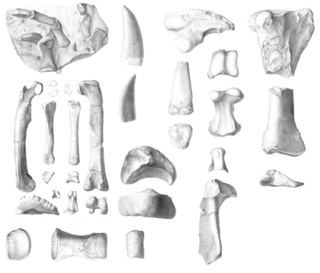
Erectopus is an extinct genus of basal allosauroid theropod from the Early Cretaceous La Penthiève Beds Formation of France and also possibly the Cernavodă Formation of southern Romania. The type species is E. superbus, which was initially known as a species of Megalosaurus.

Halitherium is an extinct dugongid sea cow that arose in the late Eocene, then became extinct during the early Oligocene. Its fossils are common in European shales. Inside its flippers were finger bones that did not stick out. Halitherium also had the remnants of back legs, which did not show externally. However, it did have a basic femur, joined to a reduced pelvis. Halitherium also had elongated ribs, presumably to increase lung capacity to provide fine control of buoyancy. A 2014 review presented the opinion that the genus is dubious.

Sclerorhynchus is an extinct genus of ganopristid sclerorhynchoid that lived during the Late Cretaceous. The genus Ganopristis is considered a junior synonym of Sclerorhynchus. It was a widespread genus, with fossils found in the Middle East, North Africa, Europe, and North America. While it had a long rostrum with large denticles similar to sawfishes and sawsharks, its closest living relatives are actually skates. Complete specimens of S. atavus show that its fin arrangement was similar to skates, with the pectoral and pelvic fins touching, both dorsal fins located behind the pelvic fins, and a reduced caudal fin.

Altmuehlopterus is a genus of pterosaur belonging to the Pterodactyloidea. It lived in the Late Jurassic of what is now Germany. It was formerly known as "Daitingopterus", a nomen nudum, informally coined in 2004.

Palaeoctopus is an extinct genus of octopuses that lived during the Late Cretaceous. It contains one valid species, P. newboldi, which has been found in Lebanon.

Schizorhiza is an extinct genus of schizorhizid sclerorhynchoid that lived during the Late Cretaceous. It contains one valid species, Schizorhiza stromeri. It lived from the Campanian to Maastrichtian, and its fossils have been found in Africa, the Middle East, North America, and South America.
Libanopristis is an extinct genus of ganopristid sclerorhynchoid that lived in Lebanon during the Late Cretaceous. One female specimen with nine embryos preserved in situ represents one of the first fossil evidence of batoid ovoviviparity.

Cretalamna is a genus of extinct otodontid shark that lived from the latest Early Cretaceous to Eocene epoch. It is considered by many to be the ancestor of the largest sharks to have ever lived, such as Otodus angustidens, Otodus chubutensis, and Otodus megalodon.
This list of fossil fishes described in 2013 is a list of new taxa of placoderms, fossil cartilaginous fishes and bony fishess of every kind that have been described during the year 2013. The list only includes taxa at the level of genus or species.

Pseudocorax is an extinct genus of mackerel sharks that lived during the Late Cretaceous. It contains six valid species that have been found in Europe, the Middle East, North Africa, and North America. It was formerly assigned to the family Anacoracidae, but is now placed in its own family Pseudocoracidae along with Galeocorax. The former species "P." australis and "P." primulus have been reidentified as species of Echinorhinus and Squalicorax, respectively.

Sclerorhynchoidei is an extinct suborder of rajiform rays that had long rostra with large denticles similar to sawfishes and sawsharks. This feature was convergently evolved, recently proposed as 'pristification', and their closest living relatives are actually skates. While they are often called "sawfishes", sawskates is a more accurate common name proposed in 2021 for sclerorhynchoids, which has been subsequently used by other researchers.
Plicatoscyllium is an extinct genus of orectolobiform shark known from deposits of Late Cretaceous age in France, Jordan, the Netherlands, Syria and the United States. Remains tentatively referrable to the genus from Cenozoic deposits have been discovered in Saudi Arabia.

Paracestracion is an extinct genus of heterodontiform sharks from Early Jurassic to Early Cretaceous-aged rocks of England, France, Germany and Luxembourg. The genus was first described in 1911 by Ernst Hermann Friedrich von Koken in Karl Alfred von Zittel.
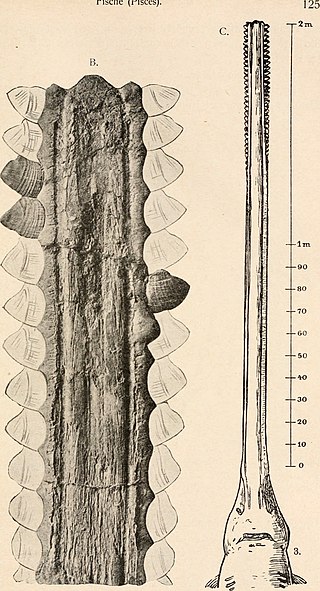
Propristis is an extinct genus of sawfish that lived from the Eocene to the Miocene. It contains two valid species, P. schweinfurthi and P. mayumbensis. It has been found in Egypt, Cabinda, Morocco, Qatar, Spain, the United Kingdom, and the United States. Isolated rostral denticles are the most common remains, but rostra have also been found.
Galeocorax is an extinct genus of mackerel sharks that lived during the Late Cretaceous. It contains a single valid species, G. jaekeli, that has been found in Europe and North America.

Propristiophorus is an extinct genus of sawshark that lived in the Late Cretaceous. It contains a single named species, P. tumidens, from Lebanon. Additional unnamed species have been found in Antarctica, Japan, and Madagascar. Propristiophorus was previously synonymized with Pristiophorus, but more recent authors have considered it a distinct genus.

Pseudastacus is an extinct genus of decapod crustaceans that lived during the Jurassic period in Europe, and possibly the Cretaceous period in Lebanon. Many species have been assigned to it, though the placement of some species remains uncertain and others have been reassigned to different genera. Fossils attributable to this genus were first described by Georg zu Münster in 1839 under the name Bolina pustulosa, but the generic name was changed in 1861 after Albert Oppel noted that it was preoccupied. The genus has been placed into different families by numerous authors, historically being assigned to Nephropidae or Protastacidae. Currently, it is believed to be a member of Stenochiridae.

Protosqualus was a genus of dogfish shark that existed during the Cretaceous. Fossils have been found in Europe, Antarctica, Australia, India and South America. The type species is Protosqualus sigei, which was found around an Albian aged deposit in France. Some species show some level of heterodonty, for example Protosqualus barringtonensis shows a rather high level of heterodonty within its teeth. The oldest specimens are from the Speeton Clay Formation. Protosqualus teeth are quite common in the Grey Chalk deposit of England. The genus went extinct at the end of the Cretaceous during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, with the last species in the genus being Protosqualus argentinensis from southern Argentina as well as possibly being from earlier deposits in India.















