| Mormoopidae Temporal range: Oligocene to Recent | |
|---|---|
 | |
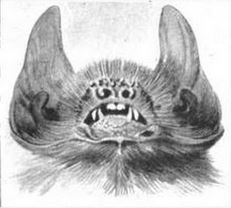
| Antillean ghost-faced bat's (Mormoops blainvillii) face by Ernst Haeckel (1904) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Superfamily: | Noctilionoidea |
| Family: | Mormoopidae Saussure, 1860 |
| Type genus | |
| Mormoops Leach, 1821 | |
| Genera | |
The family Mormoopidae contains bats known generally as mustached bats, ghost-faced bats, and naked-backed bats. They are found in the Americas from the Southwestern United States to Southeastern Brazil.
They are distinguished by the presence of a leaf-like projection from their lips, instead of the nose-leaf found in many other bat species. In some species, the wing membranes join over the animal's back, making it appear hairless. The tail projects only a short distance beyond the membrane that stretches between the hind legs. They are brownish in colour, with short, dense fur. [1] Their dental formula is:
| Dentition |
|---|
| 2.1.2.3 |
| 2.1.3.3 |
Mormoopid bats roost in caves and tunnels in huge colonies that may include hundreds of thousands of members, producing enough guano to allow commercial mining. They do not hibernate as some other bats do since they live in the tropics. They feed on insects found close to, or on, bodies of water. [1]