
Shanxi is a province in North China. Its capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-level cities are Changzhi and Datong. Its one-character abbreviation is 晋, after the state of Jin that existed there during the Spring and Autumn period.

The Wudang Mountains are a mountain range in the northwestern part of Hubei, China. They are home to a famous complex of Taoist temples and monasteries associated with the Lord of the North, Xuantian Shangdi. The Wudang Mountains are renowned for the practice of tai chi and Taoism as the Taoist counterpart to the Shaolin Monastery, which is affiliated with Chan Buddhism. The Wudang Mountains are one of the "Four Sacred Mountains of Taoism" in China, an important destination for Taoist pilgrimages. The monasteries such as the Wudang Garden were made a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1994 because of their religious significance and architectural achievement.

Mount Tai is a mountain of historical and cultural significance located north of the city of Tai'an. It is the highest point in Shandong province, China. The tallest peak is the Jade Emperor Peak, which is commonly reported as being 1,545 meters (5,069 ft) tall.

Mount Lao, or Laoshan, is a mountain located near the East China Sea on the southeastern coastline of the Shandong Peninsula in China. The mountain is culturally significant due to its long affiliation with Taoism and is often regarded as one of the "cradles of Taoism". It is the highest coastal mountain in China and the second highest mountain in Shandong, with the highest peak (Jufeng) reaching 1,132.7 metres (3,716 ft). The mountain lies about 30 kilometres (19 mi) to the northeast of the downtown area of the city of Qingdao and is protected by the Qingdao Laoshan National Park that covers an area of 446 square kilometers.

Mount Wutai, also known by its Chinese name Wutaishan and as Mount Qingliang, is a sacred Buddhist site at the headwaters of the Qingshui in Shanxi Province, China. Its central area is surrounded by a cluster of flat-topped peaks or mesas roughly corresponding to the cardinal directions. The north peak is the highest and is also the highest point in North China.

Mount Hua is a mountain located near the city of Huayin in Shaanxi Province, about 120 kilometres (75 mi) east of Xi'an. It is the "Western Mountain" of the Five Great Mountains of China and has a long history of religious significance. Originally classified as having three peaks, in modern times it is classified as having five main peaks, the highest of which is the South Peak at 2,154.9 metres (7,070 ft).

Mount Qingcheng is a sacred Taoist mountain in Dujiangyan, Chengdu, Sichuan, China.
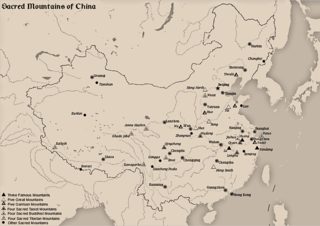
The Sacred Mountains of China are divided into several groups. The Five Great Mountains refers to five of the most renowned mountains in Chinese history, which have been the subjects of imperial pilgrimage by emperors throughout ages. They are associated with the supreme God of Heaven and the five main cosmic deities of traditional Chinese religion. The group associated with Buddhism is referred to as the Four Sacred Mountains of Buddhism, and the group associated with Taoism is referred to as the Four Sacred Mountains of Taoism.

The Wuyi Mountains or Wuyishan are a mountain range located in the prefecture of Nanping, in northern Fujian province near the border with Jiangxi province, China. The highest peak in the area is Mount Huanggang at 2,158 metres (7,080 ft) on the border of Fujian and Jiangxi, making it the highest point of both provinces; the lowest altitudes are around 200 metres (660 ft). Many oolong and black teas are produced in the Wuyi Mountains, including Da Hong Pao and lapsang souchong, and are sold as Wuyi tea. The mountain range is known worldwide for its status as a refugium for several rare and endemic plant species, its dramatic river valleys, and the abundance of important temples and archeological sites in the region, and is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

Mount Jiuhua located in Chizhou, Anhui Province in China is an important Buddhist site and natural scenic spot. It is one of the four famous Buddhist mountains in China, one of the first batch of 5A level scenic spots in China, one of the first batch of natural and cultural heritage sites in China, and the main scenic spot of "two mountains and one lake" tourism development strategy in Anhui Province. The planned area of the scenic spot is 120 square kilometers, and the protected area is 174 square kilometers, which is composed of 11 scenic spots.

Hengshan, also known as Mount Heng, is a mountain in southcentral China's Hunan Province known as the southern mountain of the Five Great Mountains of China. Heng Shan is a mountain range 150 kilometres (93 mi) long with 72 peaks and lies at 27°18′6″N112°41′5″E. The Huiyan Peak is the south end of the peaks, Yuelu Mountain in Changsha City is the north end, and the Zhurong Peak is the highest at 1,300 metres (4,300 ft) above sea level.

The Hanging Temple, also Hengshan Hanging Temple, Hanging Monastery or Xuankong Temple is a temple built into a cliff near Mount Heng in Hunyuan County, Datong City, Shanxi Province, China. The closest city is Datong, 64 kilometres (40 mi) to the northwest. Along with the Yungang Grottoes, the Hanging Temple is one of the main tourist attractions and historical sites in the Datong area. Built more than 1,500 years ago, this temple is notable not only for its location on a sheer precipice but also because as a Buddhist temple it also contains references to the other two of the three Chinese traditional philosophies or religions (三教): Taoism, and Confucianism. The structure is kept in place with oak crossbeams fitted into holes chiseled into the cliffs. The main supportive structure is hidden inside the bedrock. The monastery is located in the small canyon basin, and the body of the building hangs from the middle of the cliff under the prominent summit, protecting the temple from rain erosion and sunlight bake.

Tourism in China is a growing industry that is becoming a significant part of the Chinese economy. The rate of tourism has expanded over the last few decades since the beginning of reform and opening-up. The emergence of a newly rich middle class and an easing of restrictions on movement by the Chinese authorities are both fueling this travel boom. China has become one of world's largest outbound tourist markets. According to Euromonitor International, economic growth and higher incomes in nearby Asian countries will help China to become the world's number one tourist destination by 2030.

Sacred mountains are central to certain religions, and are usually the subjects of many legends. For many, the most symbolic aspect of a mountain is the peak because it is believed that it is closest to heaven or other religious realms. Many religions have traditions centered on sacred mountains, which either are or were considered holy or are related to famous events. In some cases, the sacred mountain is purely mythical, like the Hara Berezaiti in Zoroastrianism. Mount Kailash is believed to be the abode of the deities Shiva and Parvati, and is considered sacred in four religions: Hinduism, Bon, Buddhism, and Jainism. Volcanoes, such as Mount Etna in Italy, were also considered sacred, Mount Etna being believed to have been the home of Vulcan, the Roman god of fire and the forge.

Mount Longhu is located in Yingtan, Jiangxi, China. It is famous for being one of the birthplaces of Taoism, with many Taoist temples built upon the mountainside. It is particularly important to the Zhengyi Dao as the Shangqing Temple and the Mansion of the Taoist Master (天师府) are located here. It is also known as one of the Four Sacred Mountains of Taoism.

Hua Hill (Shandong) (simplified Chinese: 华山; traditional Chinese: 華山; pinyin: Huà Shān) is a solitary cone-shaped hill in the lower Yellow River valley, located at the northeastern edge of the city of Jinan, Shandong Province, China. The hill is known for its cultural and historical significance as well as for its natural environment. It has been an inspiration for Chinese artists for many centuries and was the site of the Battle of An, a major battle fought during the Spring and Autumn period.

Beiyue Temple is a Taoist temple located in Quyang, Hebei Province, China. The temple was used to make sacrifices to Mount Heng by the emperors of the Song dynasty while the mountain was occupied by the Liao dynasty. The Dening Hall of the temple is the largest, earliest and one of the most important extant wooden buildings built in the Yuan dynasty. The temple also contains three gates, an octagonal pavilion and many ancient stelae.

Mount Taibai is a mountain located on the border between Mei, Taibai and Zhouzhi counties in the south west of Shaanxi Province, China. The mount's highest point, Baxian Tower, rises to a height of 3,767 m (12,359 ft) and is the tallest in the Qinling Range, as well as the watershed between the Han River and Wei River. Mount Taibai is also the highest mountain in Eastern China.

Anna Mary Hotchkis RSA was a Scottish artist, writer and lecturer on art. She exhibited in London, Beijing, Hong Kong and at exhibitions in Scotland. She was a member of and exhibited with the Royal Scottish Academy 1915-1968.

Mount Mian, also known by its Chinese name Mianshan, is a mountain in the town of Mianshan in Jiexiu, Jinzhong, in central Shanxi Province in North China. Its official scenic area opened in the year 2000 and covers 75 km2 (29 sq mi), with about 400 attractions grouped into 14 tourist areas.






















