In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as R−COOH or R−CO2H, sometimes as R−C(O)OH with R referring to an organyl group, or hydrogen, or other groups. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion.

The citric acid cycle—also known as the Krebs cycle, Szent–Györgyi–Krebs cycle, or TCA cycle —is a series of biochemical reactions to release the energy stored in nutrients through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and alcohol. The chemical energy released is available in the form of ATP. The Krebs cycle is used by organisms that respire to generate energy, either by anaerobic respiration or aerobic respiration. In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids, as well as the reducing agent NADH, that are used in numerous other reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest components of metabolism. Even though it is branded as a "cycle", it is not necessary for metabolites to follow only one specific route; at least three alternative segments of the citric acid cycle have been recognized.

In organic chemistry, an aldehyde is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure R−CH=O. The functional group itself can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group. Aldehydes are a common motif in many chemicals important in technology and biology.

An aldol condensation is a condensation reaction in organic chemistry in which two carbonyl moieties react to form a β-hydroxyaldehyde or β-hydroxyketone, and this is then followed by dehydration to give a conjugated enone.
In organic chemistry, a nitrile is any organic compound that has a −C≡N functional group. The name of the compound is composed of a base, which includes the carbon of the −C≡N, suffixed with "nitrile", so for example CH3CH2C≡N is called "propionitrile". The prefix cyano- is used interchangeably with the term nitrile in industrial literature. Nitriles are found in many useful compounds, including methyl cyanoacrylate, used in super glue, and nitrile rubber, a nitrile-containing polymer used in latex-free laboratory and medical gloves. Nitrile rubber is also widely used as automotive and other seals since it is resistant to fuels and oils. Organic compounds containing multiple nitrile groups are known as cyanocarbons.
Biosynthesis, i.e., chemical synthesis occurring in biological contexts, is a term most often referring to multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed processes where chemical substances absorbed as nutrients serve as enzyme substrates, with conversion by the living organism either into simpler or more complex products. Examples of biosynthetic pathways include those for the production of amino acids, lipid membrane components, and nucleotides, but also for the production of all classes of biological macromolecules, and of acetyl-coenzyme A, adenosine triphosphate, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and other key intermediate and transactional molecules needed for metabolism. Thus, in biosynthesis, any of an array of compounds, from simple to complex, are converted into other compounds, and so it includes both the catabolism and anabolism of complex molecules. Biosynthetic processes are often represented via charts of metabolic pathways. A particular biosynthetic pathway may be located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located across an array of cellular organelles and structures.

Adipic acid or hexanedioic acid is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)4(COOH)2. From an industrial perspective, it is the most important dicarboxylic acid: about 2.5 billion kilograms of this white crystalline powder are produced annually, mainly as a precursor for the production of nylon. Adipic acid otherwise rarely occurs in nature, but it is known as manufactured E number food additive E355. Salts and esters of adipic acid are known as adipates.
Aldaric acids are a group of sugar acids, where the terminal hydroxyl and carbonyl groups of the sugars have been replaced by terminal carboxylic acids, and are characterised by the formula HO2C-(CHOH)n-CO2H. Oxidation of just the aldehyde yields an aldonic acid while oxidation of just the terminal hydroxyl group yields an uronic acid.) Aldaric acids cannot form cyclic hemiacetals like unoxidized sugars, but they can sometimes form lactones.
In organic chemistry, hydrocyanation is a process for conversion of alkenes to nitriles. The reaction involves the addition of hydrogen cyanide and requires a catalyst. This conversion is conducted on an industrial scale for the production of precursors to nylon.
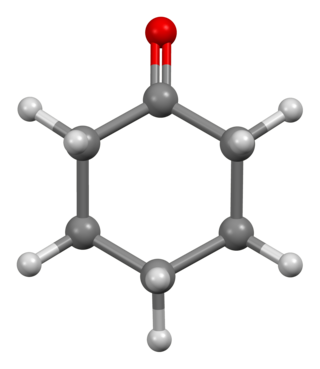
Cyclohexanone is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)5CO. The molecule consists of six-carbon cyclic molecule with a ketone functional group. This colorless oily liquid has a sweet odor reminiscent of benzaldehyde. Over time, samples of cyclohexanone assume a pale yellow color.

Perrhenic acid is the chemical compound with the formula Re2O7(H2O)2. It is obtained by evaporating aqueous solutions of Re2O7. Conventionally, perrhenic acid is considered to have the formula HReO4, and a species of this formula forms when rhenium(VII) oxide sublimes in the presence of water or steam. When a solution of Re2O7 is kept for a period of months, it breaks down and crystals of HReO4·H2O are formed, which contain tetrahedral ReO−4. For most purposes, perrhenic acid and rhenium(VII) oxide are used interchangeably. Rhenium can be dissolved in nitric or concentrated sulfuric acid to produce perrhenic acid.

(E)-Stilbene, commonly known as trans-stilbene, is an organic compound represented by the condensed structural formula C6H5CH=CHC6H5. Classified as a diarylethene, it features a central ethylene moiety with one phenyl group substituent on each end of the carbon–carbon double bond. It has an (E) stereochemistry, meaning that the phenyl groups are located on opposite sides of the double bond, the opposite of its geometric isomer, cis-stilbene. Trans-stilbene occurs as a white crystalline solid at room temperature and is highly soluble in organic solvents. It can be converted to cis-stilbene photochemically, and further reacted to produce phenanthrene.
A pinacol coupling reaction is an organic reaction in which a carbon–carbon bond is formed between the carbonyl groups of an aldehyde or a ketone in presence of an electron donor in a free radical process. The reaction product is a vicinal diol. The reaction is named after pinacol, which is the product of this reaction when done with acetone as reagent. The reaction is usually a homocoupling but intramolecular cross-coupling reactions are also possible. Pinacol was discovered by Wilhelm Rudolph Fittig in 1859.

The Holton Taxol total synthesis, published by Robert A. Holton and his group at Florida State University in 1994, was the first total synthesis of Taxol.
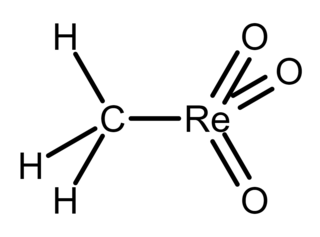
Methylrhenium trioxide, also known as methyltrioxorhenium(VII), is an organometallic compound with the formula CH3−ReO3. It is a volatile, colourless solid that has been used as a catalyst in some laboratory experiments. In this compound, rhenium has a tetrahedral coordination geometry with one methyl and three oxo ligands. The oxidation state of rhenium is +7.

Oxotrichlorobis(triphenylphosphine)rhenium(V) is the chemical compound with the formula ReOCl3(PPh3)2. This yellow, air-stable solid is a precursor to a variety of other rhenium complexes. In this diamagnetic compound, Re has an octahedral coordination environment with one oxo, three chloro and two mutually trans triphenylphosphine ligands. The oxidation state of rhenium is +5 and its configuration is d2.
Metal carbon dioxide complexes are coordination complexes that contain carbon dioxide ligands. Aside from the fundamental interest in the coordination chemistry of simple molecules, studies in this field are motivated by the possibility that transition metals might catalyze useful transformations of CO2. This research is relevant both to organic synthesis and to the production of "solar fuels" that would avoid the use of petroleum-based fuels.

Trichloroacetonitrile is an organic compound with the formula CCl3CN. It is a colourless liquid, although commercial samples often are brownish. It is used commercially as a precursor to the fungicide etridiazole. It is prepared by dehydration of trichloroacetamide. As a bifunctional compound, trichloroacetonitrile can react at both the trichloromethyl and the nitrile group. The electron-withdrawing effect of the trichloromethyl group activates the nitrile group for nucleophilic additions. The high reactivity makes trichloroacetonitrile a versatile reagent, but also causes its susceptibility towards hydrolysis.
Rhenium compounds are compounds formed by the transition metal rhenium (Re). Rhenium can form in many oxidation states, and compounds are known for every oxidation state from -3 to +7 except -2, although the oxidation states +7, +4, and +3 are the most common. Rhenium is most available commercially as salts of perrhenate, including sodium and ammonium perrhenates. These are white, water-soluble compounds. The tetrathioperrhenate anion [ReS4]− is possible.
The stabilization of bismuth's +3 oxidation state due to the inert pair effect yields a plethora of organometallic bismuth-transition metal compounds and clusters with interesting electronics and 3D structures.