
The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. The term "carpus" and "carpal" is derived from the Latin carpus and the Greek καρπός (karpós), meaning "wrist". In human anatomy, the main role of the carpal bones is to articulate with the radial and ulnar heads to form a highly mobile condyloid joint, to provide attachments for thenar and hypothenar muscles, and to form part of the rigid carpal tunnel which allows the median nerve and tendons of the anterior forearm muscles to be transmitted to the hand and fingers.

The thumb is the first digit of the hand, next to the index finger. When a person is standing in the medical anatomical position, the thumb is the outermost digit. The Medical Latin English noun for thumb is pollex, and the corresponding adjective for thumb is pollical.

The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial compartment of the forearm and the associated joints and overlying skin.

The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus.

In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius and the carpus and; (3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as wrist joints. This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, bracelet lines, the flexor retinaculum, and the extensor retinaculum.

The thenar eminence is the mound formed at the base of the thumb on the palm of the hand by the intrinsic group of muscles of the thumb. The skin overlying this region is the area stimulated when trying to elicit a palmomental reflex. The word thenar comes from Ancient Greek θέναρ (thenar) 'palm of the hand'.

The extensor carpi radialis longus is one of the five main muscles that control movements at the wrist. This muscle is quite long, starting on the lateral side of the humerus, and attaching to the base of the second metacarpal bone.

The upper limbs or upper extremities are the forelimbs of an upright-postured tetrapod vertebrate, extending from the scapulae and clavicles down to and including the digits, including all the musculatures and ligaments involved with the shoulder, elbow, wrist and knuckle joints. In humans, each upper limb is divided into the shoulder, arm, elbow, forearm, wrist and hand, and is primarily used for climbing, lifting and manipulating objects. In anatomy, just as arm refers to the upper arm, leg refers to the lower leg.
In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis longus muscle (EPL) is a skeletal muscle located dorsally on the forearm. It is much larger than the extensor pollicis brevis, the origin of which it partly covers and acts to stretch the thumb together with this muscle.

The flexor pollicis brevis is a muscle in the hand that flexes the thumb. It is one of three thenar muscles. It has both a superficial part and a deep part.
In human anatomy, the abductor pollicis longus (APL) is one of the extrinsic muscles of the hand. Its major function is to abduct the thumb at the wrist. Its tendon forms the anterior border of the anatomical snuffbox.

In human anatomy, the adductor pollicis muscle is a muscle in the hand that functions to adduct the thumb. It has two heads: transverse and oblique.

In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) is a skeletal muscle on the dorsal side of the forearm. It lies on the medial side of, and is closely connected with, the abductor pollicis longus. The extensor pollicis brevis belongs to the deep group of the posterior fascial compartment of the forearm. It is a part of the lateral border of the anatomical snuffbox.
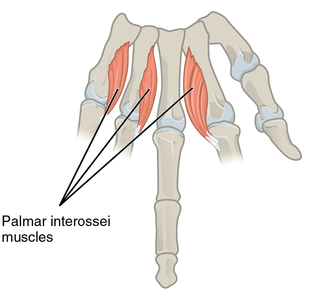
In human anatomy, the palmar or volar interossei are four muscles, one on the thumb that is occasionally missing, and three small, unipennate, central muscles in the hand that lie between the metacarpal bones and are attached to the index, ring, and little fingers. They are smaller than the dorsal interossei of the hand.

The opponens pollicis is a small, triangular muscle in the hand, which functions to oppose the thumb. It is one of the three thenar muscles. It lies deep to the abductor pollicis brevis and lateral to the flexor pollicis brevis.

In human anatomy, the abductor digiti minimi is a skeletal muscle situated on the ulnar border of the palm of the hand. It forms the ulnar border of the palm and its spindle-like shape defines the hypothenar eminence of the palm together with the skin, connective tissue, and fat surrounding it. Its main function is to pull the little finger away from the other fingers.
The posterior compartment of the forearm contains twelve muscles which primarily extend the wrist and digits. It is separated from the anterior compartment by the interosseous membrane between the radius and ulna.

The cervical spinal nerve 8 (C8) is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment.

The muscles of the hand are the skeletal muscles responsible for the movement of the hand and fingers. The muscles of the hand can be subdivided into two groups: the extrinsic and intrinsic muscle groups. The extrinsic muscle groups are the long flexors and extensors. They are called extrinsic because the muscle belly is located on the forearm. The intrinsic group are the smaller muscles located within the hand itself. The muscles of the hand are innervated by the radial, median, and ulnar nerves from the brachial plexus.

The extrinsic extensor muscles of the hand are located in the back of the forearm and have long tendons connecting them to bones in the hand, where they exert their action. Extrinsic denotes their location outside the hand. Extensor denotes their action which is to extend, or open flat, joints in the hand. They include the extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL), extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB), extensor digitorum (ED), extensor digiti minimi (EDM), extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU), abductor pollicis longus (APL), extensor pollicis brevis (EPB), extensor pollicis longus (EPL), and extensor indicis (EI).




















