The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. The terms "carpus" and "carpal" are derived from the Latin carpus and the Greek καρπός (karpós), meaning "wrist". In human anatomy, the main role of the carpal bones is to articulate with the radial and ulnar heads to form a highly mobile condyloid joint, to provide attachments for thenar and hypothenar muscles, and to form part of the rigid carpal tunnel which allows the median nerve and tendons of the anterior forearm muscles to be transmitted to the hand and fingers.

The thumb is the first digit of the hand, next to the index finger. When a person is standing in the medical anatomical position, the thumb is the outermost digit. The Medical Latin English noun for thumb is pollex, and the corresponding adjective for thumb is pollical.

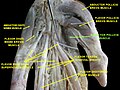
The ulnar nerve is a nerve that runs near the ulna, one of the two long bones in the forearm. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest in the human body unprotected by muscle or bone, so injury is common. This nerve is directly connected to the little finger, and the adjacent half of the ring finger, innervating the palmar aspect of these fingers, including both front and back of the tips, perhaps as far back as the fingernail beds.
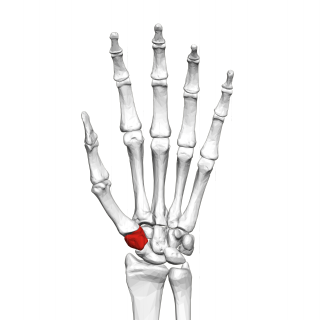
The trapezium bone is a carpal bone in the hand. It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel.

The upper limbs or upper extremities are the forelimbs of an upright-postured tetrapod vertebrate, extending from the scapulae and clavicles down to and including the digits, including all the musculatures and ligaments involved with the shoulder, elbow, wrist and knuckle joints. In humans, each upper limb is divided into the shoulder, arm, elbow, forearm, wrist and hand, and is primarily used for climbing, lifting and manipulating objects. In anatomy, just as arm refers to the upper arm, leg refers to the lower leg.
In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis longus muscle (EPL) is a skeletal muscle located dorsally on the forearm. It is much larger than the extensor pollicis brevis, the origin of which it partly covers and acts to stretch the thumb together with this muscle.

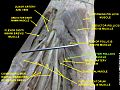
The flexor pollicis brevis is a muscle in the hand that flexes the thumb. It is one of three thenar muscles. It has both a superficial part and a deep part.
The flexor pollicis longus is a muscle in the forearm and hand that flexes the thumb. It lies in the same plane as the flexor digitorum profundus. This muscle is unique to humans, being either rudimentary or absent in other primates. A meta-analysis indicated accessory flexor pollicis longus is present in around 48% of the population.
In human anatomy, the abductor pollicis longus (APL) is one of the extrinsic muscles of the hand. Its major function is to abduct the thumb at the wrist. Its tendon forms the anterior border of the anatomical snuffbox.

In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) is a skeletal muscle on the dorsal side of the forearm. It lies on the medial side of, and is closely connected with, the abductor pollicis longus. The extensor pollicis brevis belongs to the deep group of the posterior fascial compartment of the forearm. It is a part of the lateral border of the anatomical snuffbox.
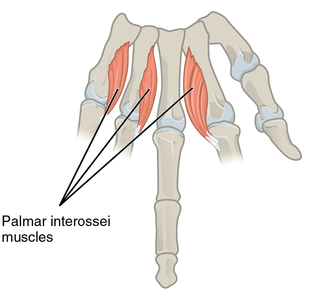
In human anatomy, the palmar or volar interossei are four muscles, one on the thumb that is occasionally missing, and three small, unipennate, central muscles in the hand that lie between the metacarpal bones and are attached to the index, ring, and little fingers. They are smaller than the dorsal interossei of the hand.

The opponens pollicis is a small, triangular muscle in the hand, which functions to oppose the thumb. It is one of the three thenar muscles. It lies deep to the abductor pollicis brevis and lateral to the flexor pollicis brevis.

The carpometacarpal (CMC) joints are five joints in the wrist that articulate the distal row of carpal bones and the proximal bases of the five metacarpal bones.

In human anatomy, the dorsal interossei (DI) are four muscles in the back of the hand that act to abduct (spread) the index, middle, and ring fingers away from the hand's midline and assist in flexion at the metacarpophalangeal joints and extension at the interphalangeal joints of the index, middle and ring fingers.

The palmar aponeurosis invests the muscles of the palm, and consists of central, lateral, and medial portions.

The deep palmar arch is an arterial network found in the palm. It is usually primarily formed from the terminal part of the radial artery. The ulnar artery also contributes through an anastomosis. This is in contrast to the superficial palmar arch, which is formed predominantly by the ulnar artery.

The princeps pollicis artery, or principal artery of the thumb, arises from the radial artery just as it turns medially towards the deep part of the hand; it descends between the first dorsal interosseous muscle and the oblique head of the adductor pollicis, along the medial side of the first metacarpal bone to the base of the proximal phalanx, where it lies beneath the tendon of the flexor pollicis longus muscle and divides into two branches.

The deep branch of the ulnar nerve is a terminal, primarily motor branch of the ulnar nerve. It is accompanied by the deep palmar branch of ulnar artery.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The muscles of the thumb are nine skeletal muscles located in the hand and forearm. The muscles allow for flexion, extension, adduction, abduction and opposition of the thumb. The muscles acting on the thumb can be divided into two groups: The extrinsic hand muscles, with their muscle bellies located in the forearm, and the intrinsic hand muscles, with their muscles bellies located in the hand proper.