| Teres minor muscle | |
|---|---|
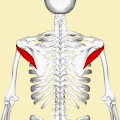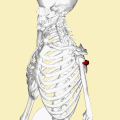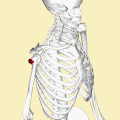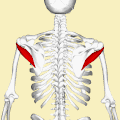
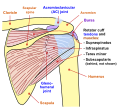
 Teres minor muscle (shown in red), seen from behind. | |
 Muscles on the dorsum of the left scapula, and the Triceps brachii muscle: #3 is Latissimus dorsi muscle #5 is Teres major muscle #6 is Teres minor muscle #7 is Supraspinatus muscle #8 is Infraspinatus muscle #13 is long head of Triceps brachii muscle | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Lateral border of the scapula |
| Insertion | Inferior facet of greater tubercle of the humerus |
| Artery | Posterior circumflex humeral artery and the circumflex scapular artery |
| Nerve | Axillary nerve (C5-C6) |
| Actions | Laterally rotates the arm, stabilizes humerus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus teres minor |
| TA98 | A04.6.02.010 |
| TA2 | 2459 |
| FMA | 32550 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
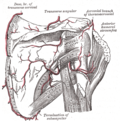
The teres minor (Latin teres meaning 'rounded') is a narrow, elongated muscle of the rotator cuff. The muscle originates from the lateral border and adjacent posterior surface of the corresponding right or left scapula and inserts at both the greater tubercle of the humerus and the posterior surface of the joint capsule. [1]
Contents
- Structure
- Relations
- Innervation
- Variation
- Function
- Clinical significance
- Injury
- Imaging
- Additional images
- See also
- References
- External links
The primary function of the teres minor is to modulate the action of the deltoid, preventing the humeral head from sliding upward as the arm is abducted. It also functions to rotate the humerus laterally. The teres minor is innervated by the axillary nerve. [2]