Related Research Articles

The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. The term "carpus" and "carpal" is derived from the Latin carpus and the Greek καρπός (karpós), meaning "wrist". In human anatomy, the main role of the carpal bones is to articulate with the radial and ulnar heads to form a highly mobile condyloid joint, to provide attachments for thenar and hypothenar muscles, and to form part of the rigid carpal tunnel which allows the median nerve and tendons of the anterior forearm muscles to be transmitted to the hand and fingers.

The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus.

In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius and the carpus and; (3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as wrist joints. This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, bracelet lines, the flexor retinaculum, and the extensor retinaculum.
The flexor digitorum profundus or flexor digitorum communis profundus is a muscle in the forearm of humans that flexes the fingers. It is considered an extrinsic hand muscle because it acts on the hand while its muscle belly is located in the forearm.

In anatomy, flexor carpi radialis is a muscle of the human forearm that acts to flex and (radially) abduct the hand. The Latin carpus means wrist; hence flexor carpi is a flexor of the wrist.

Wrist drop is a medical condition in which the wrist and the fingers cannot extend at the metacarpophalangeal joints. The wrist remains partially flexed due to an opposing action of flexor muscles of the forearm. As a result, the extensor muscles in the posterior compartment remain paralyzed.

The radius or radial bone is one of the two large bones of the forearm, the other being the ulna. It extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist and runs parallel to the ulna. The ulna is longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. The radius is a long bone, prism-shaped and slightly curved longitudinally.

The upper limbs or upper extremities are the forelimbs of an upright-postured tetrapod vertebrate, extending from the scapulae and clavicles down to and including the digits, including all the musculatures and ligaments involved with the shoulder, elbow, wrist and knuckle joints. In humans, each upper limb is divided into the shoulder, arm, elbow, forearm, wrist and hand, and is primarily used for climbing, lifting and manipulating objects. In anatomy, just as arm refers to the upper arm, leg refers to the lower leg.
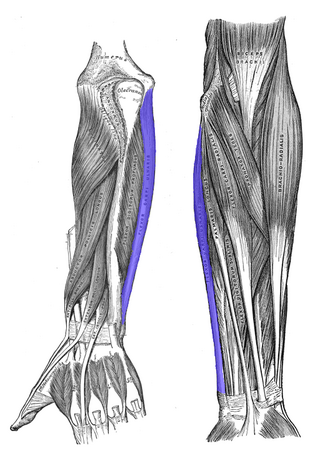
The flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) is a muscle of the forearm that flexes and adducts at the wrist joint.
In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis longus muscle (EPL) is a skeletal muscle located dorsally on the forearm. It is much larger than the extensor pollicis brevis, the origin of which it partly covers and acts to stretch the thumb together with this muscle.
The pronator teres is a muscle that, along with the Pronator quadratus muscle pronator quadratus, serves to pronate the forearm. It has two origins, at the medial humeral supracondylar ridge and the medial side of the coronoid process of the ulna and inserts near the middle of the radius.

The palmaris longus is a muscle visible as a small tendon located between the flexor carpi radialis and the flexor carpi ulnaris, although it is not always present. Reviews report rates of absence in the general population ranging from 10–20%; however, the rate varies in different ethnic groups. Absence of the palmaris longus does not have an effect on grip strength. The lack of palmaris longus muscle does result in decreased pinch strength in fourth and fifth fingers. The absence of palmaris longus muscle is more prevalent in females than males.

The flexor retinaculum is a fibrous band on the palmar side of the hand near the wrist. It arches over the carpal bones of the hands, covering them and forming the carpal tunnel.
The medial epicondyle of the humerus is an epicondyle of the humerus bone of the upper arm in humans. It is larger and more prominent than the lateral epicondyle and is directed slightly more posteriorly in the anatomical position. In birds, where the arm is somewhat rotated compared to other tetrapods, it is called the ventral epicondyle of the humerus. In comparative anatomy, the more neutral term entepicondyle is used.
Golfer's elbow, or medial epicondylitis, is tendinosis of the medial common flexor tendon on the inside of the elbow. It is similar to tennis elbow, which affects the outside of the elbow at the lateral epicondyle. The tendinopathy results from overload or repetitive use of the arm, causing an injury similar to ulnar collateral ligament injury of the elbow in "pitcher's elbow".
The common extensor tendon is a tendon that attaches to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus.
The posterior compartment of the forearm contains twelve muscles which primarily extend the wrist and digits. It is separated from the anterior compartment by the interosseous membrane between the radius and ulna.

In the human body, the carpal tunnel or carpal canal is a flattened body cavity on the flexor (palmar/volar) side of the wrist, bounded by the carpal bones and flexor retinaculum. It forms the passageway that transmits the median nerve and the tendons of the extrinsic flexor muscles of the hand from the forearm to the hand. The median artery is an anatomical variant. When present it lies between the radial artery, and the ulnar artery and runs with the median nerve supplying the same structures innervated.
Upper-limb surgery in tetraplegia includes a number of surgical interventions that can help improve the quality of life of a patient with tetraplegia.

The extrinsic extensor muscles of the hand are located in the back of the forearm and have long tendons connecting them to bones in the hand, where they exert their action. Extrinsic denotes their location outside the hand. Extensor denotes their action which is to extend, or open flat, joints in the hand. They include the extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL), extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB), extensor digitorum (ED), extensor digiti minimi (EDM), extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU), abductor pollicis longus (APL), extensor pollicis brevis (EPB), extensor pollicis longus (EPL), and extensor indicis (EI).
References
- ↑ Standring, Susan (2008). Gray's Anatomy : The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (fortieth ed.). London: Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0-443-06684-9.