
The brachioradialis is a muscle of the forearm that flexes the forearm at the elbow. It is also capable of both pronation and supination, depending on the position of the forearm. It is attached to the distal styloid process of the radius by way of the brachioradialis tendon, and to the lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus.

The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial compartment of the forearm and the associated joints and overlying skin.

The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus.

A fascial compartment is a section within the body that contains muscles and nerves and is surrounded by deep fascia. In the human body, the limbs can each be divided into two segments – the upper limb can be divided into the arm and the forearm and the sectional compartments of both of these – the fascial compartments of the arm and the fascial compartments of the forearm contain an anterior and a posterior compartment. Likewise, the lower limbs can be divided into two segments – the leg and the thigh – and these contain the fascial compartments of the leg and the fascial compartments of the thigh.
The flexor digitorum profundus or flexor digitorum communis profundus is a muscle in the forearm of humans that flexes the fingers. It is considered an extrinsic hand muscle because it acts on the hand while its muscle belly is located in the forearm.
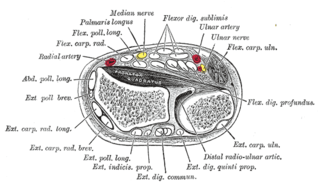
Flexor digitorum superficialis or flexor digitorum communis sublimis is an extrinsic flexor muscle of the fingers at the proximal interphalangeal joints.
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus.

In anatomy, flexor carpi radialis is a muscle of the human forearm that acts to flex and (radially) abduct the hand. The Latin carpus means wrist; hence flexor carpi is a flexor of the wrist.

In human anatomy, the fibularis longus is a superficial muscle in the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body (eversion) and to extend the foot downward away from the body at the ankle.

The ulnar nerve is a nerve that runs near the ulna, one of the two long bones in the forearm. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest in the human body unprotected by muscle or bone, so injury is common. This nerve is directly connected to the little finger, and the adjacent half of the ring finger, innervating the palmar aspect of these fingers, including both front and back of the tips, perhaps as far back as the fingernail beds.

A fascia is a generic term for macroscopic membranous bodily structures. Fasciae are classified as superficial, visceral or deep, and further designated according to their anatomical location.

The upper limbs or upper extremities are the forelimbs of an upright-postured tetrapod vertebrate, extending from the scapulae and clavicles down to and including the digits, including all the musculatures and ligaments involved with the shoulder, elbow, wrist and knuckle joints. In humans, each upper limb is divided into the shoulder, arm, elbow, forearm, wrist and hand, and is primarily used for climbing, lifting and manipulating objects. In anatomy, just as arm refers to the upper arm, leg refers to the lower leg.

The ulnar artery is the main blood vessel, with oxygenated blood, of the medial aspects of the forearm. It arises from the brachial artery and terminates in the superficial palmar arch, which joins with the superficial branch of the radial artery. It is palpable on the anterior and medial aspect of the wrist.
In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis longus muscle (EPL) is a skeletal muscle located dorsally on the forearm. It is much larger than the extensor pollicis brevis, the origin of which it partly covers and acts to stretch the thumb together with this muscle.

In human anatomy, the supinator is a broad muscle in the posterior compartment of the forearm, curved around the upper third of the radius. Its function is to supinate the forearm.

The gracilis muscle is the most superficial muscle on the medial side of the thigh. It is thin and flattened, broad above, narrow and tapering below.

The fascial compartments of arm refers to the specific anatomical term of the compartments within the upper segment of the upper limb of the body. The upper limb is divided into two segments, the arm and the forearm. Each of these segments is further divided into two compartments which are formed by deep fascia – tough connective tissue septa (walls). Each compartment encloses specific muscles and nerves.
The posterior compartment of the forearm contains twelve muscles which primarily extend the wrist and digits. It is separated from the anterior compartment by the interosseous membrane between the radius and ulna.

A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala are often described as having "hands" instead of paws on their front limbs. The raccoon is usually described as having "hands" though opposable thumbs are lacking.

Anatomical Terminology is a specialized system of terms used by anatomists, zoologists, and health professionals, such as doctors, surgeons, and pharmacists, to describe the structures and functions of the body.

















