Related Research Articles

The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws and/or nails.

A finger is a prominent digit on the forelimbs of most tetrapod vertebrate animals. Most land vertebrates have five digits (pentadactyly), and short digits are typically referred to as toes, while those that are notably elongated are called fingers. In humans and other primates, the fingers are flexibly articulated and serve as an important organ of tactile sensation and fine movements, which are crucial to the dexterity of the hands and the ability to grasp and manipulate objects.

The thumb is the first digit of the hand, next to the index finger. When a person is standing in the medical anatomical position, the thumb is the outermost digit. The Medical Latin English noun for thumb is pollex, and the corresponding adjective for thumb is pollical.

The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus.
The flexor digitorum profundus is a muscle in the forearm of humans that flexes the fingers. It is considered an extrinsic hand muscle because it acts on the hand while its muscle belly is located in the forearm.

In human anatomy, the ulnar nerve is a nerve that runs near the ulna bone. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest in the human body unprotected by muscle or bone, so injury is common. This nerve is directly connected to the little finger, and the adjacent half of the ring finger, innervating the palmar aspect of these fingers, including both front and back of the tips, perhaps as far back as the fingernail beds.

The upper limbs or upper extremities are the forelimbs of an upright-postured tetrapod vertebrate, extending from the scapulae and clavicles down to and including the digits, including all the musculatures and ligaments involved with the shoulder, elbow, wrist and knuckle joints. In humans, each upper limb is divided into the arm, forearm and hand, and is primarily used for climbing, lifting and manipulating objects.

The phalanges are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones.

The extensor digitorum muscle is a muscle of the posterior forearm present in humans and other animals. It extends the medial four digits of the hand. Extensor digitorum is innervated by the posterior interosseous nerve, which is a branch of the radial nerve.
In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis longus muscle (EPL) is a skeletal muscle located dorsally on the forearm. It is much larger than the extensor pollicis brevis, the origin of which it partly covers and acts to stretch the thumb together with this muscle.
The flexor pollicis longus is a muscle in the forearm and hand that flexes the thumb. It lies in the same plane as the flexor digitorum profundus. This muscle is unique to humans, being either rudimentary or absent in other primates. A meta-analysis indicated accessory flexor pollicis longus is present in around 48% of the population.

In human anatomy, the adductor pollicis muscle is a muscle in the hand that functions to adduct the thumb. It has two heads: transverse and oblique.
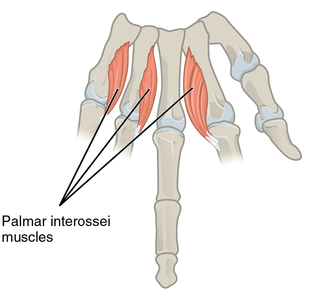
In human anatomy, the palmar or volar interossei are four muscles, one on the thumb that is occasionally missing, and three small, unipennate, central muscles in the hand that lie between the metacarpal bones and are attached to the index, ring, and little fingers. They are smaller than the dorsal interossei of the hand.

In human anatomy, the dorsal interossei (DI) are four muscles in the back of the hand that act to abduct (spread) the index, middle, and ring fingers away from hand's midline and assist in flexion at the metacarpophalangeal joints and extension at the interphalangeal joints of the index, middle and ring fingers.

In human anatomy, the abductor digiti minimi is a skeletal muscle situated on the ulnar border of the palm of the hand. It forms the ulnar border of the palm and its spindle-like shape defines the hypothenar eminence of the palm together with the skin, connective tissue, and fat surrounding it. Its main function is to pull the little finger away from the other fingers.

The interphalangeal joints of the hand are the hinge joints between the phalanges of the fingers that provide flexion towards the palm of the hand.

The interphalangeal joints of the foot are between the phalanx bones of the toes in the feet.
In the human foot, the plantar or volar plates are fibrocartilaginous structures found in the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) and interphalangeal (IP) joints. The anatomy and composition of the plantar plates are similar to the palmar plates in the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) and interphalangeal joints in the hand; the proximal origin is thin but the distal insertion is stout. Due to the weight-bearing nature of the human foot, the plantar plates are exposed to extension forces not present in the human hand.

An ulnar claw, also known as claw hand or 'spinster's claw', is a deformity or an abnormal attitude of the hand that develops due to ulnar nerve damage causing paralysis of the lumbricals. A claw hand presents with a hyperextension at the metacarpophalangeal joints and flexion at the proximal and distal interphalangeal joints of the 4th and 5th fingers. The patients with this condition can make a full fist but when they extend their fingers, the hand posture is referred to as claw hand. The ring- and little finger can usually not fully extend at the proximal interphalangeal joint (PIP).
References
- Stark, HH; Otter, TA; Boyes, JH; Rickard, TA (1979). ""Atavistic contrahentes digitorum" and associated muscle abnormalities of the hand: a cause of symptoms. Report of three cases". J Bone Joint Surg Am. 61 (2): 286–289. doi:10.2106/00004623-197961020-00023. PMID 422616.
- Tubbs, R. Shane; Salter, E. George; Oakes, W. Jerry (26 September 2005). "Contrahentes digitorum muscle". Clinical Anatomy. 18 (8): 606–608. doi:10.1002/ca.20157. PMID 16187298. S2CID 27523606. Archived from the original on 5 January 2013. Retrieved 7 January 2010.
- Wright, Patricia C.; Simons, Elwyn L.; Gursky, Sharon (2003). Tarsiers: past, present, and future. Rutgers University Press. ISBN 9780813532363.
- Yamamoto, Chugo; Murakami, Takuro; Ohtsuka, Aiji (Aug 1988). "Homology of the adductor pollicis and contrahentes muscles: a study of monkey hands" (PDF). Acta Med Okayama. 42 (4): 215–26. PMID 3177007. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-18. Retrieved 2011-03-15.