
Debian, also known as Debian GNU/Linux, is a Linux distribution composed of free and open-source software and optionally non-free firmware or software developed by the community-supported Debian Project, which was established by Ian Murdock on August 16, 1993. The first version of Debian (0.01) was released on September 15, 1993, and its first stable version (1.1) was released on June 17, 1996. The Debian Stable branch is the most popular edition for personal computers and servers. Debian is also the basis for many other distributions that have different purposes, like Proxmox for servers, Ubuntu or Linux Mint for desktops, Kali for penetration testing, and Pardus and Astra for government use.

A Linux distribution is an operating system made from a software collection that includes the Linux kernel and often a package management system. They are often obtained from the website of each distribution, which are available for a wide variety of systems ranging from embedded devices and personal computers to servers and powerful supercomputers.

Nmap is a network scanner created by Gordon Lyon. Nmap is used to discover hosts and services on a computer network by sending packets and analyzing the responses.

Ubuntu is a Linux distribution derived from Debian and composed mostly of free and open-source software. Ubuntu is officially released in multiple editions: Desktop, Server, and Core for Internet of things devices and robots. The operating system is developed by the British company Canonical and a community of other developers, under a meritocratic governance model. As of April 2024, the most-recent long-term support release is 24.04.

Kubuntu is an official flavor of the Ubuntu operating system that uses the KDE Plasma Desktop instead of the GNOME desktop environment. As part of the Ubuntu project, Kubuntu uses the same underlying systems. Kubuntu shares the same repositories as Ubuntu and is released regularly on the same schedule as Ubuntu.
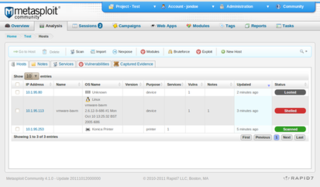
The Metasploit Project is a computer security project that provides information about security vulnerabilities and aids in penetration testing and IDS signature development. It is owned by Boston, Massachusetts-based security company, Rapid7.

BackTrack was a Linux distribution that focused on security, based on the Knoppix Linux distribution aimed at digital forensics and penetration testing use. In March 2013, Khaled Baoween (Kali) & the Offensive Security team rebuilt BackTrack around the Debian distribution and released it under the name Kali Linux.

Linux Mint is a community-driven Linux distribution based on Ubuntu, bundled with a variety of free and open-source applications. It can provide full out-of-the-box multimedia support for those who choose to include proprietary software such as multimedia codecs. Compared to standard Ubuntu, it uses the Cinnamon interface in the most popular edition, using a different, more traditional layout that can be customized by dragging the applets and creating panels. New applets can also be downloaded.

Pentoo is a Live CD and Live USB designed for penetration testing and security assessment. Based on Gentoo Linux, Pentoo is provided both as 32 and 64-bit installable live CD. Pentoo is also available as an overlay for an existing Gentoo installation. It features packet injection patched Wi-Fi drivers, GPGPU cracking software, and many tools for penetration testing and security assessment. The Pentoo kernel includes grsecurity and PAX hardening and extra patches - with binaries compiled from a hardened toolchain with the latest nightly versions of some tools available.

BackBox is a penetration test and security assessment oriented Ubuntu-based Linux distribution providing a network and informatic systems analysis toolkit. It includes a complete set of tools required for ethical hacking and security testing.

Kali Linux is a Linux distribution designed for digital forensics and penetration testing. It is maintained and funded by Offensive Security. The software is based on the Debian Testing branch: most packages Kali uses are imported from the Debian repositories.
Long-term support (LTS) is a product lifecycle management policy in which a stable release of computer software is maintained for a longer period of time than the standard edition. The term is typically reserved for open-source software, where it describes a software edition that is supported for months or years longer than the software's standard edition.
Besides the Linux distributions designed for general-purpose use on desktops and servers, distributions may be specialized for different purposes including computer architecture support, embedded systems, stability, security, localization to a specific region or language, targeting of specific user groups, support for real-time applications, or commitment to a given desktop environment. Furthermore, some distributions deliberately include only free software. As of 2015, over four hundred Linux distributions are actively developed, with about a dozen distributions being most popular for general-purpose use.

Parrot OS is a Linux distribution based on Debian with a focus on security, privacy, and development.
Offensive Security is an American international company working in information security, penetration testing and digital forensics. Operating from around 2007, the company created open source projects, advanced security courses, the ExploitDB vulnerability database, and the Kali Linux distribution. The company was started by Mati Aharoni, and employs security professionals with experience in security penetration testing and system security evaluation. The company has provided security counseling and training to many technology companies.

Snap is a software packaging and deployment system developed by Canonical for operating systems that use the Linux kernel and the systemd init system. The packages, called snaps, and the tool for using them, snapd, work across a range of Linux distributions and allow upstream software developers to distribute their applications directly to users. Snaps are self-contained applications running in a sandbox with mediated access to the host system. Snap was originally released for cloud applications but was later ported to also work for Internet of Things devices and desktop applications.

Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) is a feature of Microsoft Windows that allows developers to run a Linux environment without the need for a separate virtual machine or dual booting. There are two versions of WSL: WSL 1 and WSL 2. WSL is not available to all Windows 10 users by default. It can be installed either by joining the Windows Insider program or manually via Microsoft Store or Winget.
Ubuntu is a Debian-based Linux distribution for personal computers, tablets and smartphones, where the Ubuntu Touch edition is used; and also runs network servers, usually with the Ubuntu Server edition, either on physical or virtual servers or with containers, that is with enterprise-class features.















