Chinese is a group of related, but in many cases not mutually intelligible, language varieties, forming the Sinitic branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family. Chinese is spoken by the ethnic Chinese majority and many minority ethnic groups in China. About 1.2 billion people speak some form of Chinese as their first language.
Bokmål is an official written standard for the Norwegian language, alongside Nynorsk. Bokmål is the preferred written standard of Norwegian for 85% to 90% of the population in Norway. Unlike, for instance, the Italian language, there is no nationwide standard or agreement on the pronunciation of Bokmål.
Written vernacular Chinese, also known as Baihua, is the forms of written Chinese based on the varieties of Chinese spoken throughout China, in contrast to Classical Chinese, the written standard used during imperial China up to the early twentieth century. A written vernacular based on Mandarin Chinese was used in novels in the Ming and Qing dynasties, and later refined by intellectuals associated with the May Fourth Movement. Since the early 1920s, this modern vernacular form has been the standard style of writing for speakers of all varieties of Chinese throughout mainland China, Taiwan, Malaysia and Singapore as the written form of Modern Standard Chinese. This is commonly called Standard Written Chinese or Modern Written Chinese to avoid ambiguity with spoken vernaculars, with the written vernaculars of earlier eras, and with other written vernaculars such as written Cantonese or written Hokkien.

The Mayan languages form a language family spoken in Mesoamerica and northern Central America. Mayan languages are spoken by at least 6 million Maya peoples, primarily in Guatemala, Mexico, Belize and Honduras. In 1996, Guatemala formally recognized 21 Mayan languages by name, and Mexico recognizes eight more within its territory.

Indigenous languages of the Americas are spoken by indigenous peoples from Alaska, Nunavut, and Greenland to the southern tip of South America, encompassing the land masses that constitute the Americas. These indigenous languages consist of dozens of distinct language families, as well as many language isolates and unclassified languages.

There are some 120 to 187 languages and dialects in the Philippines, depending on the method of classification. Almost all are Malayo-Polynesian languages. A number of Spanish-influenced creole varieties generally called Chavacano are also spoken in certain communities. The 1987 constitution designates Filipino as the national language and an official language along with English.
The Peba–Yaguan language family is located in the northwestern Amazon, but today Yagua is the only remaining spoken language of the family.
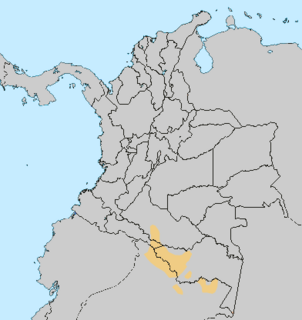
Bora–Witóto is a proposal to unite the Boran and Witotoan language families of southwestern Colombia and neighboring regions of Peru and Brazil. Kaufman (1994) added the Andoque language.
Boran is a small language family, consisting of just two languages:
Bora is an indigenous language of South America spoken in the western region of Amazon rainforest. Bora is a tonal language which, other than the Ticuna language, is a unique trait in the region.
More than 99.2% of Colombians speak the Spanish language; also 65 Amerindian languages, 2 Creole languages and the Romani language are spoken in the country. English has official status in the San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina Islands.
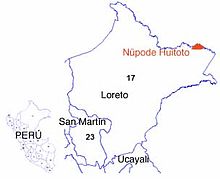
Witoto, or Huitoto, is an indigenous American language or language family spoken in Colombia and Peru.
Minica (Mɨnɨka) Huitoto is one of three indigenous American Huitoto languages of the Witotoan family spoken by a few thousand speakers in western South America.
Murui Huitoto - is an indigenous American Huitoto language of the Witotoan family. Murui is spoken by about 1,100 Murui people along the banks of the Putumayo, Cara-Paraná and Igara-Paraná rivers in Colombia. In Peru it spoken in the North alongside the Ampiyacu and Napo rivers by some 1,000 people. Some Murui speakers live also outside their territories, for instance the vicinity of Leticia, Amazonas, Colombia.
The Andoque language is an aboriginal language spoken by a few hundred Andoque in Colombia, and is in decline. There were 10,000 speakers in 1908, down to 370 a century later, of which at most 50 are monolingual. The remaining speakers live in the area of the Anduche River, downstream from Aracuara, Amazonas, Colombia; the language is no longer spoken in Peru. 80% of speakers are proficient in Spanish.
Ocaina is an indigenous American language spoken in western South America.

The Witoto people are an indigenous people in southeastern Colombia and northern Peru.

SIL International is a U.S.-based, worldwide, Christian non-profit organization, whose main purpose is to study, develop and document languages, especially those that are lesser-known, in order to expand linguistic knowledge, promote literacy, translate the Christian Bible into local languages, and aid minority language development.

The International Standard Book Number (ISBN) is a numeric commercial book identifier which is intended to be unique. Publishers purchase ISBNs from an affiliate of the International ISBN Agency.