Related Research Articles
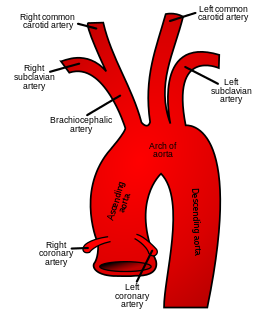
The brachiocephalic artery is an artery of the mediastinum that supplies blood to the right arm and the head and neck.

Aortic dissection (AD) occurs when an injury to the innermost layer of the aorta allows blood to flow between the layers of the aortic wall, forcing the layers apart. In most cases, this is associated with a sudden onset of severe chest or back pain, often described as "tearing" in character. Also, vomiting, sweating, and lightheadedness may occur. Other symptoms may result from decreased blood supply to other organs, such as stroke or mesenteric ischemia. Aortic dissection can quickly lead to death from not enough blood flow to the heart or complete rupture of the aorta.

In human anatomy, the subclavian arteries are paired major arteries of the upper thorax, below the clavicle. They receive blood from the aortic arch. The left subclavian artery supplies blood to the left arm and the right subclavian artery supplies blood to the right arm, with some branches supplying the head and thorax. On the left side of the body, the subclavian comes directly off the aortic arch, while on the right side it arises from the relatively short brachiocephalic artery when it bifurcates into the subclavian and the right common carotid artery.
An aneurysm is an outward bulging, likened to a bubble or balloon, caused by a localized, abnormal, weak spot on a blood vessel wall. Aneurysms may be a result of a hereditary condition or an acquired disease. Aneurysms can also be a nidus for clot formation (thrombosis) and embolization. The word is from Greek: ἀνεύρυσμα, aneurysma, "dilation", from ἀνευρύνειν, aneurynein, "to dilate". As an aneurysm increases in size, the risk of rupture increases, leading to uncontrolled bleeding. Although they may occur in any blood vessel, particularly lethal examples include aneurysms of the Circle of Willis in the brain, aortic aneurysms affecting the thoracic aorta, and abdominal aortic aneurysms. Aneurysms can arise in the heart itself following a heart attack, including both ventricular and atrial septal aneurysms. There are congenital atrial septal aneurysms, a rare heart defect.

An aortic aneurysm is an enlargement (dilatation) of the aorta to greater than 1.5 times normal size. They usually cause no symptoms except when ruptured. Occasionally, there may be abdominal, back, or leg pain.

A thoracic aortic aneurysm is an aortic aneurysm that presents primarily in the thorax.
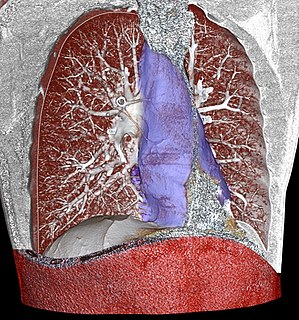
The mediastinum is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by loose connective tissue, as an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax. The mediastinum contains the heart and its vessels, the esophagus, the trachea, the phrenic and cardiac nerves, the thoracic duct, the thymus and the lymph nodes of the central chest.

In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) are arteries that supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood; they divide in the neck to form the external and internal carotid arteries.

The aortic arch, arch of the aorta, or transverse aortic arch is the part of the aorta between the ascending and descending aorta. The arch travels backward, so that it ultimately runs to the left of the trachea.

The ascending aorta (AAo) is a portion of the aorta commencing at the upper part of the base of the left ventricle, on a level with the lower border of the third costal cartilage behind the left half of the sternum.

The aortic arches or pharyngeal arch arteries are a series of six paired embryological vascular structures which give rise to the great arteries of the neck and head. They are ventral to the dorsal aorta and arise from the aortic sac.

Aberrant subclavian artery, or aberrant subclavian artery syndrome, is a rare anatomical variant of the origin of the right or left subclavian artery. This abnormality is the most common congenital vascular anomaly of the aortic arch, occurring in approximately 1% of individuals.
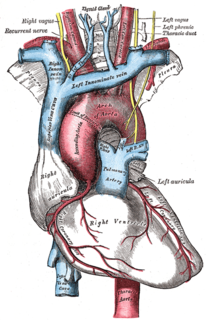
Ortner's syndrome is a rare cardiovocal syndrome and refers to recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy from cardiovascular disease. It was first described by Norbert Ortner (1865–1935), an Austrian physician, in 1897.
Cardarelli's sign is an abnormal pulsation of the trachea that may be found in patients with a dilation or aneurysm of the aortic arch.

Interrupted aortic arch is a very rare heart defect in which the aorta is not completely developed. There is a gap between the ascending and descending thoracic aorta. In a sense it is the complete form of a coarctation of the aorta. Almost all patients also have other cardiac anomalies, including a ventricular septal defect (VSD), aorto-pulmonary window, and truncus arteriosus. There are three types of interrupted aortic arch, with type B being the most common. Interrupted aortic arch is often associated with DiGeorge syndrome.
A vascular ring is a congenital defect in which there is an abnormal formation of the aorta and/or its surrounding blood vessels. The trachea and esophagus are completely encircled and sometimes compressed by a "ring" formed by these vessels, which can lead to breathing and digestive difficulties.

Traumatic aortic rupture, also called traumatic aortic disruption or transection, is a condition in which the aorta, the largest artery in the body, is torn or ruptured as a result of trauma to the body. The condition is frequently fatal due to the profuse bleeding that results from the rupture. Since the aorta branches directly from the heart to supply blood to the rest of the body, the pressure within it is very great, and blood may be pumped out of a tear in the blood vessel very rapidly. This can quickly result in shock and death. Thus traumatic aortic rupture is a common killer in automotive accidents and other traumas, with up to 18% of deaths that occur in automobile collisions being related to the injury. In fact, aortic disruption due to blunt chest trauma is the second leading cause of injury death behind traumatic brain injury.
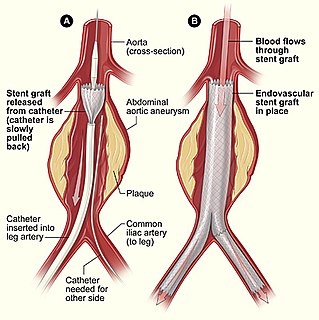
Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR), is a type of minimally-invasive endovascular surgery used to treat pathology of the aorta, most commonly an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). When used to treat thoracic aortic disease, the procedure is then specifically termed TEVAR for "thoracic endovascular aortic/aneurysm repair." The procedure involves the placement of an expandable stent graft within the aorta to treat aortic disease without operating directly on the aorta. In 2003, EVAR surpassed open aortic surgery as the most common technique for repair of AAA, and in 2010, EVAR accounted for 78% of all intact AAA repair in the United States.
Double aortic arch is a relatively rare congenital cardiovascular malformation. DAA is an anomaly of the aortic arch in which two aortic arches form a complete vascular ring that can compress the trachea and/or esophagus. Most commonly there is a larger (dominant) right arch behind and a smaller (hypoplastic) left aortic arch in front of the trachea/esophagus. The two arches join to form the descending aorta which is usually on the left side. In some cases the end of the smaller left aortic arch closes and the vascular tissue becomes a fibrous cord. Although in these cases a complete ring of two patent aortic arches is not present, the term ‘vascular ring’ is the accepted generic term even in these anomalies.

Right-sided aortic arch is a rare anatomical variant in which the aortic arch is on the right side rather than on the left. During normal embryonic development, the aortic arch is formed by the left fourth aortic arch and the left dorsal aorta. In people with a right-sided aortic arch, instead the right dorsal aorta persists and the distal left aorta disappears.
References
- ↑ Dennis, Mark; Bowen, William Talbot; Cho, Lucy (2016). Mechanisms of Clinical Signs - EPub3. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 153. ISBN 9780729585613 . Retrieved 7 March 2018.