
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the British Virgin Islands:
Contents
- General reference
- Geography of the British Virgin Islands
- Environment of the British Virgin Islands
- Demography of the British Virgin Islands
- Government and politics of the British Virgin Islands
- Branches of the government of the British Virgin Islands
- Foreign relations of the British Virgin Islands
- Law and order in the British Virgin Islands
- Military of the British Virgin Islands
- Local government in the British Virgin Islands
- History of the British Virgin Islands
- Culture of the British Virgin Islands
- Art in the British Virgin Islands
- Literature
- Sports in the British Virgin Islands
- Economy and infrastructure of the British Virgin Islands
- Education in the British Virgin Islands
- See also
- References
- External links
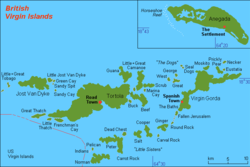
British Virgin Islands (BVI) – British overseas territory located in the eastern portion of the Virgin Islands Archipelago in the Caribbean Sea. [1] The Virgin Islands are part of the Leeward Islands of the Lesser Antilles. The United States Virgin Islands comprises the western portion of the archipelago. Technically the name of the Territory is simply the "Virgin Islands", but in practice since 1917 they have been almost universally referred to as the "British Virgin Islands" to distinguish the islands from the American Territory. [2] To add to the regional confusion, the Puerto Rican islands of Culebra, Vieques and surrounding islands began referring to themselves as the "Spanish Virgin Islands" as part of a tourism drive in the early 2000s.
The British Virgin Islands consist of the main islands of Tortola, Virgin Gorda, Anegada and Jost Van Dyke, along with over fifty other smaller islands and cays. Approximately fifteen of the islands are inhabited. The largest island, Tortola, is approximately 20 km (approx. 12 mi) long and 5 km (approx. 3 mi) wide. The islands have a total population of about 22,000, of whom approximately 18,000 live on Tortola. Road Town, the capital, is situated on Tortola.



