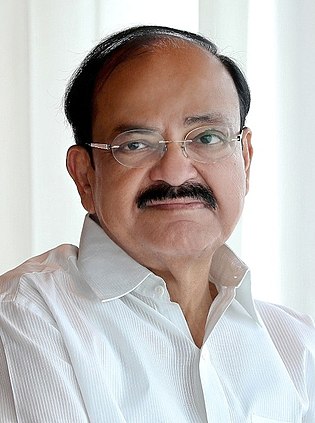A head of state is the public persona who officially embodies a state in its unity and legitimacy. Depending on the country's form of government and separation of powers, the head of state may be a ceremonial figurehead or concurrently the head of government and more.

Impeachment is the process by which a legislative body or other legally constituted tribunal initiates charges against a public official for misconduct. Impeachment may be understood as a unique process involving both political and legal elements.
Sovereign immunity, or crown immunity, is a legal doctrine whereby a sovereign or state cannot commit a legal wrong and is immune from civil suit or criminal prosecution, strictly speaking in modern texts in its own courts. A similar, stronger rule as regards foreign courts is named state immunity.

Article One of the United States Constitution establishes the legislative branch of the federal government, the United States Congress. Under Article One, Congress is a bicameral legislature consisting of the House of Representatives and the Senate. Article One grants Congress various enumerated powers and the ability to pass laws "necessary and proper" to carry out those powers. Article One also establishes the procedures for passing a bill and places various limits on the powers of Congress and the states from abusing their powers.

Article Two of the United States Constitution establishes the executive branch of the federal government, which carries out and enforces federal laws. Article Two vests the power of the executive branch in the office of the president of the United States, lays out the procedures for electing and removing the president, and establishes the president's powers and responsibilities.

The President of India, officially the President of the Republic of India, is the ceremonial head of state of India and the Commander-in-chief of the Indian Armed Forces.
A pocket veto is a legislative maneuver that allows a president or another official with veto power to exercise that power over a bill by taking no action instead of affirmatively vetoing it. This depends on the laws of each country; the common alternative is that if the president takes no action a bill automatically becomes law.

The governor of the State of South Carolina is the chief executive of South Carolina serving as its head of state and head of the executive of the government of South Carolina. The governor is the ex officio commander-in-chief of the National Guard when not called into federal service. The governor's responsibilities include making yearly "State of the State" addresses to the South Carolina General Assembly, submitting an executive budget, and ensuring that state laws are enforced.
The Lok Sabha, or House of the People, is the lower house of India's bicameral Parliament, with the upper house being the Rajya Sabha. Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by an adult universal suffrage and a first-past-the-post system to represent their respective constituencies, and they hold their seats for five years or until the body is dissolved by the President on the advice of the council of ministers. The house meets in the Lok Sabha Chambers of the Sansad Bhavan, New Delhi.

The President of Pakistan, is the ceremonial head of state of Pakistan and the Commander-in-Chief of Pakistan Armed Forces.

The prime minister of Pakistan is the head of government of Pakistan and designated as the "Chief Executive of the Islamic Republic".
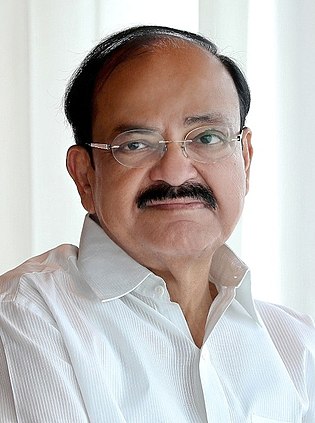
The Vice President of India is the second-highest constitutional office in India after the President. Article 63 of Indian Constitution states that "There shall be a Vice President of India." The Vice President acts as President in the absence of the president due to death, resignation, impeachment, or other situations.
The Constitution of the State of Tennessee defines the form, structure, activities, character, and fundamental rules of the U.S. State of Tennessee.

Impeachment in the United States is the process by which a legislature's lower house brings charges against a civil federal officer, the Vice President, or the President for misconduct alleged to have been committed. Impeachment may also occur at the state level if the state or commonwealth has provisions for it under its constitution. The federal House of Representatives can impeach a party with a simple majority of the House members present or such other criteria as the House adopts in accordance with Article One, Section 2, Clause 5 of the United States Constitution. Most state legislatures can impeach state officials, including the governor, in accordance with their respective state constitution.

The Union Public Service Commission, commonly abbreviated as UPSC, is India's premier central recruiting agency for public servants. It is responsible for appointments to and examinations for All India services and group A & group B posts under civil services cadre and defence services cadre of central government. While Department of Personnel and Training is the central personnel agency in India.
The Governors of the states of India have similar powers and functions at the state level as those of the President of India at Union level. Governors exist in the states while lieutenant governors or administrator exist in union territories including National Capital Territory of Delhi. The governor acts as the nominal head whereas the real power lies with the Chief ministers of the states and his/her councils of ministers. Although, in union territories, the real power lies with the lieutenant governor or administrator, except in NCT of Delhi and Puducherry where he/she shares power with a council of ministers headed by a chief minister. Most, if not all governors are not local to the state that they are appointed to govern.
The law of the Republic of China as applied in Taiwan is based on civil law with its origins in the modern Japanese and German legal systems. The main body of laws are codified into the Six Codes:
Part XI of the Constitution of India – consists of Articles on Relations between the Union and States. Article 352 will be implemented by president of india War national emergency Article 352 The president of india exercise this power during the year the period of war external aggression or armed rebellion. He declare emergency if he is satisfied

The president of Nepal, officially the President of the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal is the head of state of Nepal and the Commander-in-chief of the Nepali Army.
The Public Service Commission, West Bengal or PSCWB is the state agency authorized to conduct the Civil Services Examination for entry-level appointments to the various Civil Services of state of West Bengal in India.