Opossums are members of the marsupial order Didelphimorphia endemic to the Americas. The largest order of marsupials in the Western Hemisphere, it comprises 126 species in 18 genera. Opossums originated in South America and entered North America in the Great American Interchange following the connection of North and South America.

Alston's mouse opossum, also known as Alston's opossum, is a medium-sized pouchless marsupial of the family Didelphidae. It is arboreal and nocturnal, inhabiting forests from Belize to northern Colombia. The main components of its diet are insects and fruits, but it may also eat small rodents, lizards, and bird eggs. It was formerly assigned to the genus Micoureus, which was made a subgenus of Marmosa in 2009.

The white-bellied woolly mouse opossum is a small pouchless marsupial of the family Didelphidae. It was formerly assigned to the genus Micoureus, which was made a subgenus of Marmosa in 2009. The specific epithet was given in honour of Constance Sladen, wife of the naturalist Percy Sladen. She funded the 1902 expedition which collected the type specimen.

Linnaeus's mouse opossum, also known as the common or murine mouse opossum, is a South American marsupial of the family Didelphidae.

The Chacoan pygmy opossum is a recently described genus and species of didelphimorph marsupial. The only species in Chacodelphys, C. formosa, was known until 2004 from only one specimen collected in 1920 in the Chaco of Formosa Province, Argentina. The species is gaining popularity as a pocket pet.

The bushy-tailed opossum is an opossum from South America. It was first described by English zoologist Oldfield Thomas in 1912. It is a medium-sized opossum characterized by a large, oval, dark ears, fawn to cinnamon coat with a buff to gray underside, grayish limbs, and a furry tail. Little is known of the behavior of the bushy-tailed opossum; less than 25 specimens are known. It appears to be arboreal (tree-living), nocturnal and solitary. The diet probably comprises insects, eggs and plant material. This opossum has been captured from heavy, humid, tropical forests; it has been reported from Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador and Peru. The IUCN classifies it as least concern.

The bare-tailed woolly opossum is an opossum from South America. It was first described by Swedish zoologist Carl Linnaeus in 1758. The bare-tailed woolly opossum is characterized by a gray head, brown to gray coat, orange to gray underside and a partially naked tail. It is nocturnal and solitary; there is hardly any social interaction except between mother and juveniles and in mating pairs. The opossum constructs nests in tree cavities, and its litter size ranges from one to seven. Gestation lasts 25 days, and the juveniles exit the pouch after three months; weaning occurs a month later. The bare-tailed woolly opossum inhabits subtropical forests, rainforests, secondary forests, and plantations; its range extends from northern Venezuela to northeastern and southcentral Brazil. The IUCN classifies this opossum as least concern.

The black-shouldered opossum, also known as the white-eared opossum, is an opossum known from western Brazil and southeastern Peru. It was first described by Colin Campbell Sanborn, curator of Field Museum of Natural History, in 1951. The black-shouldered opossum is characterized by a gray coat, gray underbelly, and broad black stripes that extend from the forefeet, meet on the shoulders, run along the midline of the back and then split into parallel stripes that run down the hind feet. Little is known of the behavior of the black-shouldered opossum. It is nocturnal and arboreal. It is known to feed on fruits and rodents. The opossum inhabits humid forests. The IUCN classifies it as least concern.

The 27 species in the genus Marmosa are relatively small Neotropical members of the family Didelphidae. This genus is one of three that are known as mouse opossums. The others are Thylamys and Tlacuatzin, the grayish mouse opossum. Members of the genus Marmosops used to be called "slender mouse opossums", but are now just called "slender opossums". The thirteen members of the Marmosa subgenus Micoureus, known as woolly mouse opossums, were formerly considered to be a separate genus, but were moved into Marmosa in 2009. Based on a comparison of sequences of one mitochondrial and three nuclear genes, three new subgenera, Eomarmosa, Exulomarmosa and Stegomarmosa, were recognized by Voss et al. in 2014. Eomarmosa and Exulomarmosa, as well as Marmosa and Micoureus, are thought to be sister taxa, while Stegomarmosa is viewed as sister to Marmosa plus Micoureus. Exulomarmosa is a mostly trans-Andean clade.
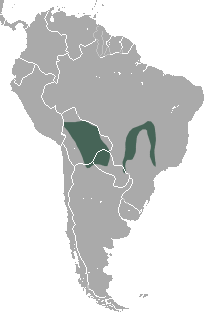
The pygmy short-tailed opossum, scientifically named Monodelphis kunsi, is an opossum species from South America. M. kunsi is a marsupial from the family Didelphidae of the order Didelphimorphia. Although it is a marsupial, it lacks the characteristic pouch that is often associated with this order. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil and Paraguay. M. kunsi is considered a smaller species within the family Didelphidae, which is why it is named a pygmy opossum. The young are referred to as 'joeys'. The females are referred to as 'Jill,' and the males 'jack'. It was thought to have been endangered in 2001, but has since been moved to least concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature.

Marmosops is a genus of Neotropical opossums of the family Didelphidae. The genus was originally treated as a subgenus from the genus Marmosa rather than having their own classification. This was changed in 1989 by Gardner and Crieghton, who officially separated the group and made them their own genus. The mix-up between to genera Marmosa and Marmosops was common due to the similar appearances including size and other external features. However, the two groups differ significantly in their integument and in the arrangement of their skull and dentition. The dentition is similar in morphology between the two groups, with the exception of the deciduous lower third premolar varying from one genus to the next. The similarity between the two continues to cause the genus Marmosops to be frequently misidentified due to the lack of knowledge regarding the species along with the overlooked traits that help separate them from other opossums. The Marmosops are also commonly confused with the genus Gracilinanus, but this is quickly ruled out by a large number of differing characteristics. These differences include the arrangement of their digits, caudal scales, and the central hair on the scales changing from a three hairs per follicle to many more. This causes the hair of the Gracilinanus to be thicker and has also found to be heavily pigmented. The last group commonly confused with Marmosops is known as the genus Thylamys. These animals have a contrasting dorsal body pelage and the taxa are actually quite different.

The heavy-browed mouse opossum, or Anderson's mouse opossum, is a species of opossum in the family Didelphidae. It is endemic to a restricted range in southern Peru. This opossum inhabits forests; it is nocturnal and probably arboreal.

Robinson's mouse opossum is a species of opossum in the family Didelphidae. It is found in Belize, Colombia, Ecuador, Grenada, Honduras, Panama, Peru, Trinidad and Tobago, and Venezuela.

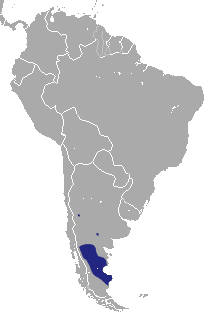
The elegant fat-tailed mouse opossum, also known as the Chilean mouse opossum, is an opossum from central Chile. The type species of Thylamys, it was first described by English naturalist George Robert Waterhouse in 1839. This medium-sized opossum is characterized by black rings around the eyes, white limbs, gray to light brown coat, lighter flanks and underbelly and a thick 12.7–14.6 centimetres (5.0–5.7 in) long tail covered with hairs. It is crepuscular and lives in nests in tree hollows or under rocks and roots. This opossum feeds mainly on arthropods and larvae apart from fruits. Litter size is typically between 11 and 13. The elegant fat-tailed opossum can occur in a variety of habitats – from cloud forests to chaparrals. The IUCN classifies the opossum as least concern.

The white-bellied fat-tailed mouse opossum is a species of opossum in the family Didelphidae. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Chile and Peru.

Gracilinanus is a genus of opossum in the family Didelphidae. It was separated from the genus Marmosa in 1989, and has since had the genera Cryptonanus, Chacodelphys, and Hyladelphys removed from it.

The buff-bellied fat-tailed mouse opossum is a species of opossum in the family Didelphidae. It is found in the transitional and humid forests of northern Argentina and southern Bolivia. Its dorsal fur is cinnamon brown. Most of its ventral fur is gray-based, but its chest, throat, and the thoracic midline are not gray-based. The postorbital ridges are absent in the young and weakly developed in adults.

The chacoan gracile opossum is a species of opossum in the family Didelphidae. It is native to Argentina, Brazil and Paraguay. Its habitat is seasonally flooded grasslands and forests in and near the Gran Chaco.

Cryptonanus is a genus of opossums from South America. It includes five species found from Bolivia to Uruguay and eastern Brazil, one of which is now extinct. Although the first species were discovered in 1931, the genus was not recognized as distinct from Gracilinanus until 2005. It includes small opossums with generally grayish, sometimes reddish, fur that are mainly distinguished from other opossums by characters of the skull.

Peradectes is an extinct genus of small metatherian mammals known from the latest Cretaceous to Eocene of North and South America and Europe. The first discovered fossil of P. elegans, was one of 15 Peradectes specimens described in 1921 from the Mason pocket fossil beds in Colorado. The monophyly of the genus has been questioned.