
Opossums are members of the marsupial order Didelphimorphia endemic to the Americas. The largest order of marsupials in the Western Hemisphere, it comprises 126 species in 18 genera. Opossums originated in South America and entered North America in the Great American Interchange following the connection of North and South America.

The water opossum, also locally known as the yapok, is a marsupial of the family Didelphidae. It is the only living member of its genus, Chironectes. This semiaquatic creature is found in and near freshwater streams and lakes from Mexico through Central and South America to Argentina and is the most aquatic living marsupial. It is also the only living marsupial in which both sexes have a pouch. The thylacine, commonly referred to as the Tasmanian tiger, also exhibited this trait, but it is now extinct.

The gray four-eyed opossum is an opossum species from Central and South America, ranging from southern Mexico to Peru, Bolivia and southwestern Brazil, at altitudes from sea level to 1600 m, but generally below 1,000 metres (3,300 ft). Its habitats include primary, secondary and disturbed forest. It is one of many opossum species in the order Didelphimorphia and the family Didelphidae.

The bare-tailed woolly opossum is an opossum from South America. It was first described by Swedish zoologist Carl Linnaeus in 1758. The bare-tailed woolly opossum is characterized by a gray head, brown to gray coat, orange to gray underside and a partially naked tail. It is nocturnal and solitary; there is hardly any social interaction except between mother and juveniles and in mating pairs. The opossum constructs nests in tree cavities, and its litter size ranges from one to seven. Gestation lasts 25 days, and the juveniles exit the pouch after three months; weaning occurs a month later. The bare-tailed woolly opossum inhabits subtropical forests, rainforests, secondary forests, and plantations; its range extends from northern Venezuela to northeastern and southcentral Brazil. The IUCN classifies this opossum as least concern.

The brown-eared woolly opossum, also known as the western woolly opossum, is an opossum from South America. It was first described by German naturalist Ignaz von Olfers in 1818. The opossum is characterized by a brown to reddish brown coat and similarly colored limbs, yellow to orange underbelly, hairless, brown ears with a hint of pink, and a tail furred on the back for up to half of its length. The brown-eared woolly opossum is nocturnal, solitary and omnivorous. The IUCN lists it as least concern.

The big lutrine opossum, also called little water opossum, thick-tailed opossum and coligrueso, is a long-tailed, otter-like mammal native to grasslands of South America. It generally lives near water and is active at night, dawn or dusk. It eats mice, insects and crabs. Like all opossums, it is a marsupial and carries its young in a pouch.

The black-shouldered opossum, also known as the white-eared opossum, is an opossum known from western Brazil and southeastern Peru. It was first described by Colin Campbell Sanborn, curator of Field Museum of Natural History, in 1951. The black-shouldered opossum is characterized by a gray coat, gray underbelly, and broad black stripes that extend from the forefeet, meet on the shoulders, run along the midline of the back and then split into parallel stripes that run down the hind feet. Little is known of the behavior of the black-shouldered opossum. It is nocturnal and arboreal. It is known to feed on fruits and rodents. The opossum inhabits humid forests. The IUCN classifies it as least concern.

Monodelphis is a genus of marsupials in the family Didelphidae, commonly referred to as short-tailed opossums. They are found throughout South America. As of January 2019, the most recently described species is M. vossi.

The gray short-tailed opossum is a small South American member of the family Didelphidae. Unlike most other marsupials, the gray short-tailed opossum does not have a true pouch. The scientific name Monodelphis is derived from Greek and means "single womb" and the Latin word domestica which means "domestic". It was the first marsupial to have its genome sequenced. The gray short-tailed opossum is used as a research model in science, and is also frequently found in the exotic pet trade. It is also known as the Brazilian opossum, rainforest opossum and in a research setting the laboratory opossum.

The yellow-sided opossum is an opossum species from South America. It is found in Argentina, Brazil and Uruguay. They have grey or black fur on their dorsal side with yellowish fur on the lateral side that continues down to the feet. They are the most mysterious of all the Monodelphis that is found specifically in the Pampean region or Pampa of Argentina. It is suspected to be a once-in-a-lifetime breeder as seen in a three-year observational study of one population in the marshy grasslands of the Pampean region. Maintaining their native grasslands is important for them to keep a stable population. They show sexual dimorphism in overall size: adult males are typically 100-150 g whereas adult females are 30-70 g.
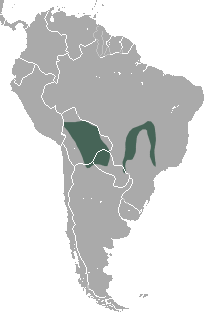
The pygmy short-tailed opossum, scientifically named Monodelphis kunsi, is an opossum species from South America. M. kunsi is a marsupial from the family Didelphidae of the order Didelphimorphia. Although it is a marsupial, it lacks the characteristic pouch that is often associated with this order. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil and Paraguay. M. kunsi is considered a smaller species within the family Didelphidae, which is why it is named a pygmy opossum. The young are referred to as 'joeys'. The females are referred to as 'Jill,' and the males 'jack'. It was thought to have been endangered in 2001, but has since been moved to least concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature.

Marmosops is a genus of Neotropical opossums of the family Didelphidae. The genus was originally treated as a subgenus from the genus Marmosa rather than having their own classification. This was changed in 1989 by Gardner and Crieghton, who officially separated the group and made them their own genus. The mix-up between to genera Marmosa and Marmosops was common due to the similar appearances including size and other external features. However, the two groups differ significantly in their integument and in the arrangement of their skull and dentition. The dentition is similar in morphology between the two groups, with the exception of the deciduous lower third premolar varying from one genus to the next. The similarity between the two continues to cause the genus Marmosops to be frequently misidentified due to the lack of knowledge regarding the species along with the overlooked traits that help separate them from other opossums. The Marmosops are also commonly confused with the genus Gracilinanus, but this is quickly ruled out by a large number of differing characteristics. These differences include the arrangement of their digits, caudal scales, and the central hair on the scales changing from a three hairs per follicle to many more. This causes the hair of the Gracilinanus to be thicker and has also found to be heavily pigmented. The last group commonly confused with Marmosops is known as the genus Thylamys. These animals have a contrasting dorsal body pelage and the taxa are actually quite different.

Derby's woolly opossum, or the Central American woolly opossum, is an opossum found in deciduous and moist evergreen forests of Central America, from southern Mexico to western Ecuador and Colombia. It was first described by English naturalist George Robert Waterhouse, and named in honor of Edward Smith-Stanley, 13th Earl of Derby. Derby's woolly opossum is the largest in its genus, with a total length of 60 to 70 centimetres and weight between 200 and 400 grams. The coat is brown and the underside white-buff to golden-brown. The opossum is nocturnal, arboreal (tree-living) and solitary. Diet consists of fruits, nectar, small invertebrates and vertebrates. The time when breeding takes place varies geographically. The litter size ranges from one to six. The IUCN classifies this opossum as least concern.

The grayish or gray mouse opossum is a diminutive species of opossum in the family Didelphidae, endemic to Mexico. It is the sole species of its monotypic genus, Tlacuatzin.

The elegant fat-tailed mouse opossum, also known as the Chilean mouse opossum, is an opossum from central Chile. The type species of Thylamys, it was first described by English naturalist George Robert Waterhouse in 1839. This medium-sized opossum is characterized by black rings around the eyes, white limbs, gray to light brown coat, lighter flanks and underbelly and a thick 12.7–14.6 centimetres (5.0–5.7 in) long tail covered with hairs. It is crepuscular and lives in nests in tree hollows or under rocks and roots. This opossum feeds mainly on arthropods and larvae apart from fruits. Litter size is typically between 11 and 13. The elegant fat-tailed opossum can occur in a variety of habitats – from cloud forests to chaparrals. The IUCN classifies the opossum as least concern.

The white-bellied fat-tailed mouse opossum is a species of opossum in the family Didelphidae. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Chile and Peru.

Gracilinanus is a genus of opossum in the family Didelphidae. It was separated from the genus Marmosa in 1989, and has since had the genera Cryptonanus, Chacodelphys, and Hyladelphys removed from it.

The Didelphinae are a subfamily of opossums consisting of 15 genera and 123 species. Specimens have been collected throughout the Americas, but are predominant in South and Central America.

The Amazonian red-sided opossum is a South American opossum species of the family Didelphidae, formerly viewed as part of M. brevicaudata. It is found in Bolivia, Brazil and Peru, where it inhabits the Amazon rainforest. It is omnivorous, nocturnal, and primarily nonarboreal.





















