
A salt dome is a type of structural dome formed when salt intrudes into overlying rocks in a process known as diapirism. Salt domes can have unique surface and subsurface structures, and they can be discovered using techniques such as seismic reflection. They are important in petroleum geology as they can function as petroleum traps.

A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about 2,600 meters (8,500 ft) and rises about 2,000 meters (6,600 ft) above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a divergent plate boundary. The rate of seafloor spreading determines the morphology of the crest of the mid-ocean ridge and its width in an ocean basin.
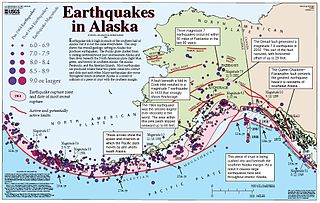
The Queen Charlotte Fault is an active transform fault that marks the boundary of the North American plate and the Pacific plate. It is Canada's right-lateral strike-slip equivalent to the San Andreas Fault to the south in California. The Queen Charlotte Fault forms a triple junction south with the Cascadia subduction zone and the Explorer Ridge. The Queen Charlotte Fault (QCF) forms a transpressional plate boundary, and is as active as other major transform fault systems in terms of slip rates and seismogenic potential. It sustains the highest known deformation rates among continental or continent-ocean transform systems globally, accommodating greater than 50mm/yr dextral offset. The entire approximately 900 km offshore length has ruptured in seven greater than magnitude 7 events during the last century, making the cumulative historical seismic moment release higher than any other modern transform plate boundary system.

The Izu–Bonin–Mariana (IBM) arc system is a tectonic plate convergent boundary in Micronesia. The IBM arc system extends over 2800 km south from Tokyo, Japan, to beyond Guam, and includes the Izu Islands, the Bonin Islands, and the Mariana Islands; much more of the IBM arc system is submerged below sealevel. The IBM arc system lies along the eastern margin of the Philippine Sea Plate in the Western Pacific Ocean. It is the site of the deepest gash in Earth's solid surface, the Challenger Deep in the Mariana Trench.
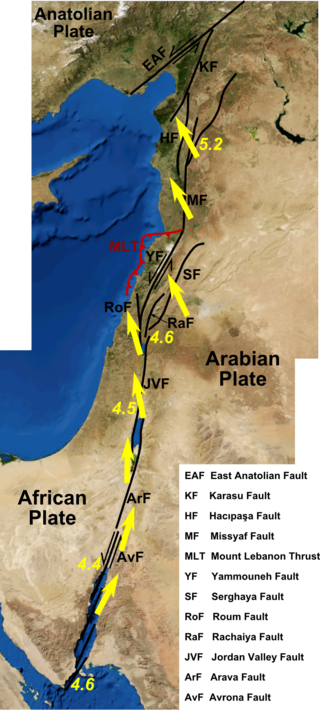
The Dead Sea Transform (DST) fault system, also sometimes referred to as the Dead Sea Rift, is a series of faults that run from the Maras Triple Junction to the northern end of the Red Sea Rift. The fault system forms the transform boundary between the African Plate to the west and the Arabian Plate to the east. It is a zone of left lateral displacement, signifying the relative motions of the two plates. Both plates are moving in a general north-northeast direction, but the Arabian Plate is moving faster, resulting in the observed left lateral motions along the fault of approximately 107 km at its southern end. A component of extension is also present in the southern part of the transform, which has contributed to a series of depressions, or pull-apart basins, forming the Gulf of Aqaba, Dead Sea, Sea of Galilee, and Hula basins. A component of shortening affects the Lebanon restraining bend, leading to uplift on both sides of the Beqaa valley. There is local transtension in the northernmost part of the fault system, forming the Ghab pull-apart basin.

The Nankai Trough is a submarine trough located south of the Nankaidō region of Japan's island of Honshu, extending approximately 900 km (559 mi) offshore. The underlying fault, the Nankai megathrust, is the source of the devastating Nankai megathrust earthquakes, while the trough itself is potentially a major source of hydrocarbon fuel, in the form of methane clathrate.

The Jan Mayen Microcontinent is a fragment of continental crust within the oceanic part of the western Eurasian Plate lying northeast of Iceland. At the onset of separation between the Greenland and Eurasian plates 55 million years ago, it formed part of the eastern margin of the Greenland Plate. Propagation of a new spreading center from the Reykjanes Ridge separated this microcontinent from the Greenland Plate. For a short period it formed a microplate, until the Aegir Ridge became inactive, after which it formed part of the Eurasian Plate. The island of Jan Mayen is a much younger feature, formed of volcanic rock, built up at the northernmost tip of the microcontinent.
Non-volcanic passive margins (NVPM) constitute one end member of the transitional crustal types that lie beneath passive continental margins; the other end member being volcanic passive margins (VPM). Transitional crust welds continental crust to oceanic crust along the lines of continental break-up. Both VPM and NVPM form during rifting, when a continent rifts to form a new ocean basin. NVPM are different from VPM because of a lack of volcanism. Instead of intrusive magmatic structures, the transitional crust is composed of stretched continental crust and exhumed upper mantle. NVPM are typically submerged and buried beneath thick sediments, so they must be studied using geophysical techniques or drilling. NVPM have diagnostic seismic, gravity, and magnetic characteristics that can be used to distinguish them from VPM and for demarcating the transition between continental and oceanic crust.

Paul Gordon Silver was an American seismologist. A member of the research staff at the Department of Terrestrial Magnetism of the Carnegie Institution of Washington since 1982, Paul Silver made a series of important contributions to the investigation of seismic anisotropy and to earthquake research by observing the slow redistribution of stress and strain along fault zones.
The Brawley Seismic Zone (BSZ), also known as the Brawley fault zone, is a predominantly extensional tectonic zone that connects the southern terminus of the San Andreas Fault with the Imperial Fault in Southern California. The BSZ is named for the nearby town of Brawley in Imperial County, California, and the seismicity there is characterized by earthquake swarms.
The Guaymas Fault, named for the city of Guaymas, Sonora, Mexico, is a major right lateral-moving transform fault which runs along the seabed of the Gulf of California. It is an integral part of the Gulf of California Rift Zone, the northern extremity of the East Pacific Rise. The Guaymas Fault runs from the San Pedro Martir Basin located at the southern end of the San Lorenzo Fault, and extends southward to the Guaymas Basin, a heavily sedimented rift which includes both continental and oceanic crust and contains numerous hydrothermal vents.
The Gulf of California Rift Zone (GCRZ) is the northernmost extension of the East Pacific Rise which extends some 1,300 km (800 mi) from the mouth of the Gulf of California to the southern terminus of the San Andreas Fault at the Salton Sink.
The Alarcon Basin is a submarine depression located on the seabed at the southern end of the Gulf of California. The basin results from the activity of the southernmost spreading center in the Gulf. This spreading center has also produced the southernmost oceanic rift in the Gulf of California Rift Zone, the Alarcon Rise. The basin and rise are linked to the Tamayo Fault to the south, and the Pescadero Fault in the north.
The Pescadero Fault is a right lateral-moving transform fault located on the seafloor of the southern Gulf of California. It links the Pescadero Basin to the north with the Alarcon Basin to the south. All these features are part of the Gulf of California Rift Zone, the northern extension of the East Pacific Rise.
The Farallon Basin is a submarine depression located on the seabed at the southern end of the Gulf of California. The basin results from the activity of one of the several spreading centers in the Gulf. The basin is linked to the Atl Fault to the south, and the Farallon Fault in the north.
The Carmen Basin is a submarine depression located on the seabed at the southern end of the Gulf of California. The basin results from the activity of one of the several spreading centers in the Gulf. The basin is linked to the Farallon Fault to the south, and the Carmen Fault in the north.

The Salton Trough is an active tectonic pull-apart basin, or graben. It lies within the Imperial, Riverside, and San Diego counties of southeastern California, United States and extends south of the Mexico–United States border into the state of Baja California, Mexico. The northwestern end of the trough starts at the San Gorgonio Pass in Riverside County, and extends 115 miles (185 km) southeast to the Gulf of California. Major geographical features located in the trough include the Coachella Valley, the Salton Sea, and the Imperial Valley, in the United States, and the western side of the Mexicali Valley, and the Colorado River Delta in Mexico.

Bruce Peter Luyendyk is an American geophysicist and oceanographer, currently professor emeritus of marine geophysics at the University of California, Santa Barbara. His work spans marine geology of the major ocean basins, the tectonics of southern California, marine hydrocarbon seeps, and the tectonics and paleoclimate of Antarctica. His research includes tectonic rotations of the California Transverse Ranges, participation in the discovery of deep-sea hydrothermal vents, quantitative studies of marine hydrocarbon seeps, and geologic exploration of the Ford Ranges in Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica.
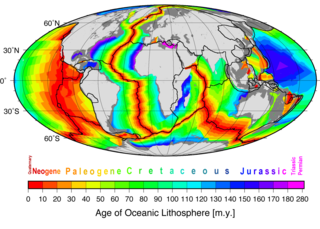
Marine geophysics is the scientific discipline that employs methods of geophysics to study the world's ocean basins and continental margins, particularly the solid earth beneath the ocean. It shares objectives with marine geology, which uses sedimentological, paleontological, and geochemical methods. Marine geophysical data analyses led to the theories of seafloor spreading and plate tectonics.
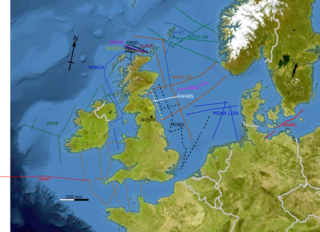
The British Institutions Reflection Profiling Syndicate, better known by its acronym BIRPS, was set up to acquire deep seismic reflection profiles around the United Kingdom Continental Shelf (UKCS). It was formed, initially as BURPS, the British Universities Reflection Profiling Syndicate, involving geophysicists from the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) and British Universities. After the involvement of other institutions the name was changed to BIRPS and by February 1981 NERC had approved funding for a four-year programme. The next ten years saw the collection of 12,000 km of deep seismic profiles around the British Isles. By the time NERC stopped funding the program in 1997, more than 20,000 km of data had been acquired.












