
Cardamom, sometimes cardamon or cardamum, is a spice made from the seeds of several plants in the genera Elettaria and Amomum in the family Zingiberaceae. Both genera are native to the Indian subcontinent and Indonesia. They are recognized by their small seed pods: triangular in cross-section and spindle-shaped, with a thin, papery outer shell and small, black seeds; Elettaria pods are light green and smaller, while Amomum pods are larger and dark brown.

Tamarind is a leguminous tree bearing edible fruit that is indigenous to tropical Africa and naturalized in Asia. The genus Tamarindus is monotypic, meaning that it contains only this species. It belongs to the family Fabaceae.

Kalimpong is a town and the headquarters of an eponymous district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is located at an average elevation of 1,250 metres (4,101 ft). The town is the headquarters of the Kalimpong district. The region comes under Gorkhaland Territorial Administration which is an autonomous governing body within the state of West Bengal. The Indian Army's 27 Mountain Division is located on the outskirts of the city.

Cinnamomum tamala, Indian bay leaf, also known as tejpat, tejapatta,Malabar leaf, Indian bark, Indian cassia, or malabathrum, is a tree in the family Lauraceae that is native to India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, and China. It can grow up to 20 m (66 ft) tall. Its leaves have a clove-like aroma with a hint of peppery taste; they are used for culinary and medicinal purposes. It is thought to have been one of the major sources of the medicinal plant leaves known in classic and medieval times as malabathrum.

Bauhinia purpurea is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae, native to the Indian subcontinent and Myanmar, and widely introduced elsewhere in tropical and subtropical areas of the world. Common names include orchid tree, purple bauhinia, camel's foot, butterfly tree, and Hawaiian orchid tree.
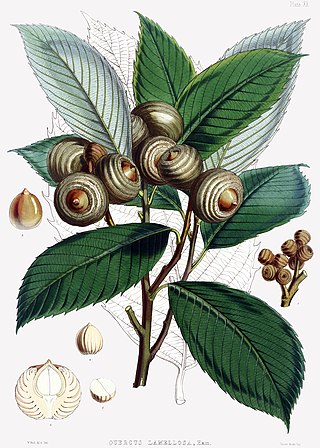
Quercus lamellosa is a species of oak (Quercus) native to the Himalaya and adjoining mountains from Tibet and Nepal east as far as Guangxi and northern Thailand, growing at altitudes of 1300–2500 m. The Lepcha of Sikkim call it book koong. It is placed in subgenus Cerris, section Cyclobalanopsis.

The Indian grey mongoose or Asian grey mongoose is a mongoose species native to the Indian subcontinent and West Asia. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List.

The genus Tylosema is in the plant family Fabaceae and encompasses four accepted species of perennial legumes native to southern and central Africa. These are semi-woody viniferous plants broadly distributed from Sudan and Ethiopia south to Angola and South Africa. Coetzer and Ross originally described four Tylosema species:

Pithecellobium dulce, commonly known as Manila tamarind, Madras thorn, monkeypod tree or camachile, is a species of flowering plant in the pea family, Fabaceae, that is native to the Pacific Coast and adjacent highlands of Mexico, Central America, and northern South America. It is also sometimes known as monkeypod, but that name is also used for several other plants, including Samanea saman. It is an introduced species and extensively naturalized in the Caribbean and Florida, as well as the Philippines and Guam via the Manila galleons. It has also been introduced to Cambodia, Thailand and South Asia, It is considered an invasive species in Hawaii.

The barred cuckoo-dove is a bird species in the family Columbidae. It is native to South and Southeast Asia, and listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List.
Fish toxins or fish stupefying plants have historically been used by many hunter gatherer cultures to stun fish, so they become easy to collect by hand. Some of these toxins paralyse fish, which can then be easily collected. The process of documenting many fish toxins and their use is ongoing, with interest in potential uses from medicine, agriculture, and industry.

Zanthoxylum armatum, also called winged prickly ash or rattan pepper in English, is a species of plant in the family Rutaceae. It is an aromatic, deciduous, spiny shrub growing to 3.5 metres (11 ft) in height, endemic from Pakistan across to Southeast Asia and up to Korea and Japan. It is one of the sources of the spice Sichuan pepper, and also used in folk medicine, essential oil production and as an ornamental garden plant.
Mun or Munism is the traditional polytheistic, animist, shamanistic and syncretic religion of the Lepcha people. It predates the 7th century Lepcha conversion to Lamaistic Buddhism, and since that time, the Lepcha have practiced it together with Buddhism. Since the arrival of Christian missionaries in the nineteenth century, Mun traditions have been followed alongside that religion as well. The traditional religion permits incorporation of Buddha and Jesus Christ as deities, depending on household beliefs.

Phanera is a genus of flowering plants in the legume subfamily Cercidoideae and the tribe Bauhinieae. This genus differs from Bauhinia in being vines or lianas, generally with tendrils and a lobed rather than spathaceous calyx, and from Schnella in having only three fertile stamens rather than ten, and being native to the Indomalayan realm and the Australasian realm rather than the Americas. The subsection Corymbosae was recently segregated into a new genus, Cheniella. It has been suggested that the genus Lasiobema should be reduced to a section within Phanera.

Clematis gouriana, or Indian Traveller's Joy, is a liana found in Asia which belongs to the buttercup family (Ranunculaceae). It was described by Roxb. ex DC. and published in Regni Vegetabilis Systema Naturale 1: 138-139, in 1818.
Calamus flagellum is an Asian species of tropical forest rattan liana in the family Arecaceae, with a native range from Assam to southern China and Indo-China. Its name in Vietnamese is mây song, while the Lepcha of Sikkim call it rim.

Phanera scandens is a species of 'monkey ladder' lianas in the subfamily Cercidoideae and the tribe Bauhinieae, the genus having been separated from Bauhinia and the discontinued genus Lasiobema. Under its synonym, Bauhinia scandens, records exist from the Indian subcontinent, Indo-China and Malesia. Under the name Bauhinia scandens var. horsfieldii its Vietnamese name is móng bò leo.
Phanera cardinalis is a species of lianas in the subfamily Cercidoideae and the tribe Bauhinieae, the genus having been separated from Bauhinia and also placed in the defunct genus Lasiobema. Under its synonym, Bauhinia cardinalis, records exist from Vietnam, where it is called móng bò đỏ, mấu hang or mấu tràm; no subspecies were listed in the Catalogue of Life.

Cheniella is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae. It belongs to the subfamily Cercidoideae and tribe Bauhinieae. It includes ten species which range from the eastern Himalayas through Indochina and China to Taiwan, Peninsular Malaysia, Sumatra, and Java. This genus differs from Phanera in having a hypanthium that is equal in length or longer than the sepals, indehiscent fruit, many-seeded fruit, and the funicle extending most of the circumference of the seed.

Phanera coccinea is the type species of the genus Phanera: a "climbing shrub" in the subfamily Cercidoideae and the tribe Bauhinieae, the genus having been separated from Bauhinia. Under its synonym Bauhinia coccinea, its Vietnamese names include "quạch" and "mấu". Records of distribution exist from the subtropical and tropical forests of Indochina and South-central China.

















