
Bellastraea aurea, common name the golden small star, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Turbinidae, the turban snails.
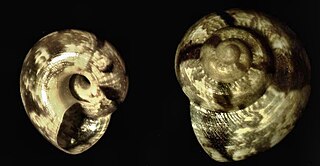
Ethminolia vitiliginea, common name the depressed top shell, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Trochidae, the top snails.

Phasianotrochus is a genus of sea snails. They are marine gastropod molluscs in the family Trochidae, the top snails.

Prothalotia pulcherrima, common name the beautiful jewel top shell, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Trochidae, the top snails.

Phasianotrochus bellulus, common name the necklace shell, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Trochidae, the top snails.
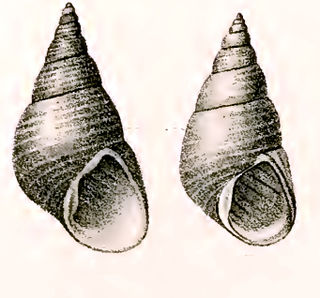
Phasianotrochus eximius, common name the kelp shell or true kelp, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Trochidae, the top snails.

Phasianotrochus rutilus, common name the pink-tipped kelp shell, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Trochidae, the top snails.
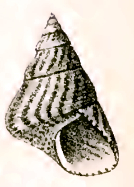
Prothalotia lehmanni, common name Lehmann's top shell, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Trochidae, the top snails.

Thalotia conica, common name the conical top shell, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Trochidae, the top snails.

Austrocochlea constricta, common names the southern periwinkle, common periwinkle, or ribbon monodonta, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Trochidae, the top snails.
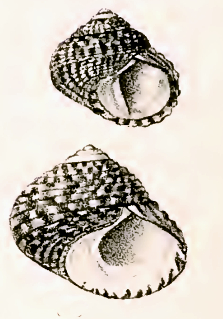
Diloma concameratum, common name the speckled periwinkle, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Trochidae, the top snails.

Clanculus albanyensis, common name the yellow top shell, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Trochidae, the top snails.

Clanculus dunkeri, common name Dunker's clanculus, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Trochidae, the top snails.

Clanculus limbatus, common name the keeled clanculus, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Trochidae, the top snails.

Clanculus philippii, common name Philippi's cone, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Trochidae, the top snails.

Clanculus plebejus, common name the plebeian clanculus, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Trochidae, the top snails.
Clanculus ringens, common name the ringent clanculus, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Trochidae, the top snails.

Phasianotrochus apicinus, common name the pointed kelp shell, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Trochidae, the top snails.

Fossarina legrandi, common name Legrand's top shell, is a species of very small sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusc or micromollusk in the family Trochidae, the top snails.

Notogibbula lehmanni, common name the many-coloured top shell, is a species of small sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Trochidae, the top shells.




















