
Juniperus virginiana, also known as eastern redcedar, red cedar, Virginian juniper, eastern juniper, red juniper, and other local names, is a species of juniper native to eastern North America from southeastern Canada to the Gulf of Mexico and east of the Great Plains. Further west it is replaced by the related Juniperus scopulorum and to the southwest by Juniperus ashei. It is not to be confused with Thuja occidentalis.

Quercus virginiana, also known as the southern live oak, is an evergreen oak tree endemic to the Southeastern United States. Though many other species are loosely called live oak, the southern live oak is particularly iconic of the Old South. Many very large and old specimens of live oak can be found today in the Deep South region of the United States.

The classification of the Indigenous peoples of the Americas is based upon cultural regions, geography, and linguistics. Anthropologists have named various cultural regions, with fluid boundaries, that are generally agreed upon with some variation. These cultural regions are broadly based upon the locations of the Indigenous peoples of the Americas from early European and African contact beginning in the late 15th century. When Indigenous peoples have been forcibly removed by nation-states, they retain their original geographic classification. Some groups span multiple cultural regions.

Helianthus is a genus comprising about 70 species of annual and perennial flowering plants in the daisy family Asteraceae commonly known as sunflowers. Except for three South American species, the species of Helianthus are native to North America and Central America. The best-known species is the common sunflower. This and other species, notably Jerusalem artichoke, are cultivated in temperate regions and some tropical regions, as food crops for humans, cattle, and poultry, and as ornamental plants. The species H. annuus typically grows during the summer and into early fall, with the peak growth season being mid-summer.

Ptilimnium is a group of plants in the family Apiaceae described as a genus in 1819. The common name is mock bishopweed or mock bishop's weed. It is endemic to the United States, primarily in the Southeast, the Lower Mississippi Valley, and the Lower Great Plains.
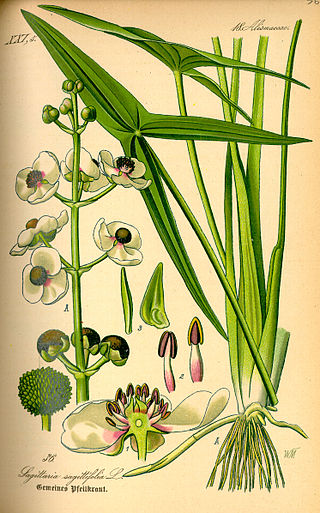
Sagittaria is a genus of about 30 species of aquatic plants whose members go by a variety of common names, including arrowhead, duck potato, katniss, Omodaka, swamp potato, tule potato, and wapato. Most are native to South, Central, and North America, but there are also some from Europe, Africa, and Asia.

Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands, Southeastern cultures, or Southeast Indians are an ethnographic classification for Native Americans who have traditionally inhabited the area now part of the Southeastern United States and the northeastern border of Mexico, that share common cultural traits. This classification is a part of the Eastern Woodlands. The concept of a southeastern cultural region was developed by anthropologists, beginning with Otis Mason and Franz Boas in 1887. The boundaries of the region are defined more by shared cultural traits than by geographic distinctions. Because the cultures gradually instead of abruptly shift into Plains, Prairie, or Northeastern Woodlands cultures, scholars do not always agree on the exact limits of the Southeastern Woodland culture region. Shawnee, Powhatan, Waco, Tawakoni, Tonkawa, Karankawa, Quapaw, and Mosopelea are usually seen as marginally southeastern and their traditional lands represent the borders of the cultural region.

Rudbeckia is a plant genus in the Asteraceae or composite family. Rudbeckia flowers feature a prominent, raised central disc in black, brown shades of green, and in-between tones, giving rise to their familiar common names of coneflowers and black-eyed-susans. All are native to North America, and many species are cultivated in gardens for their showy yellow or gold flower heads that bloom in mid to late summer.

Boltonia diffusa, the smallhead doll's daisy, is a North American species of plants in the family Asteraceae. It native to the United States, primarily the states along the Gulf of Mexico from Texas to Florida plus the lower Mississippi Valley from Louisiana to Illinois. There additional populations in the eastern United States as far north as Virginia.

Physostegia virginiana, the obedient plant, obedience or false dragonhead, is a species of flowering plant in the mint family, Lamiaceae. It is native to North America, where it is distributed from eastern Canada to northern Mexico. Physostegia are known commonly as obedient plants because a flower pushed to one side will often stay in that position. The name “false dragonhead” refers to the dragonheads of the related Dracocephalum, a genus to which the plant once belonged.

Ostrya virginiana, the American hophornbeam, is a species of Ostrya native to eastern North America, from Nova Scotia west to southern Manitoba and eastern Wyoming, southeast to northern Florida and southwest to eastern Texas. Populations from Mexico and Central America are also regarded as the same species, although some authors prefer to separate them as a distinct species, Ostrya guatemalensis. Other names include eastern hophornbeam, hardhack, ironwood, and leverwood.

Muhlenbergia is a genus of plants in the grass family.

Spermacoce or false buttonweed is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It comprises about 275 species found throughout the tropics and subtropics. Its highest diversity is found in the Americas, followed by Africa, Australia and Asia.

Pycnanthemum is a genus of herbaceous plants in the mint family (Lamiaceae). Species in this genus are often referred to as "mountain mints" and they often have a minty or thyme-like aroma when crushed. All species of Pycnanthemum are native to the United States and Canada. The center of diversity for the genus is North Carolina with 13 of the 20 species having been collected therein. Nineteen of the 20 species of Pycnanthemum occur in the Eastern US and Canada, and one disjunct species occurs in California and Oregon.

Pyrrhopappus is a genus of North American plants in the tribe Cichorieae within the family Asteraceae. Desert-chicory is a common name.

Bradburia pilosa, the soft goldenaster, is a North American species of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae, native to the south-central United States, primarily the southeastern Great Plains and lower Mississippi Valley, in the states of Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, Missouri, Arkansas, Louisiana, Tennessee, Mississippi, and Alabama. Additional populations are reported farther east but these appear to be introductions. Its habitats include disturbed roadsides and pine-oak-juniper woods.

Chaetopappa asteroides, called the tiny lazy daisy, or Arkansas leastdaisy, is a North American species of plants in the family Asteraceae. It is native to the southern Great Plains of the United States and also to northeastern Mexico.

Solidago radula, the western rough goldenrod, is a North American plant species in the family Asteraceae. It is found primarily in the southern Great Plains and the Mississippi Valley of the United States, with isolated populations farther east in Kentucky, Georgia, and the Carolinas.


















